Investigating the Privacy Risk of Using Robot Vacuum Cleaners in Smart Environments

0
🐍
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Robot vacuum cleaners are widely used in smart homes
- Many have companion smartphone apps for customization and control
- This integration raises privacy concerns as user data may be exposed
- The paper investigates risks of private information leakage via network metadata
Plain English Explanation
The paper explores the potential privacy risks associated with robot vacuum cleaners and their accompanying smartphone apps. These apps allow users to customize cleaning settings or access information about their robot vacuums, enhancing convenience. However, this integration also means users' personal data could be exposed.
To address these concerns, the devices use end-to-end encryption when communicating. But even with encryption, some metadata about the network traffic remains unprotected and vulnerable to eavesdropping. The researchers investigated whether this metadata alone could reveal private information about users and their activities.
They set up a real-world smart environment with a popular robot vacuum cleaner and monitored the network traffic during cleaning sessions. Using Association Rule Learning, the researchers were able to identify certain events based solely on the unencrypted network metadata. This suggests that even with encryption, the metadata could potentially expose private user information, raising significant privacy concerns.
Technical Explanation
The researchers deployed a popular robot vacuum cleaner in a real smart environment and conducted passive network eavesdropping during several cleaning sessions. They then used Association Rule Learning, a data mining technique, to analyze the captured network traffic metadata.
The results of their extensive analysis demonstrate that it is feasible to identify certain events solely based on the unencrypted network header information. This means that even though the device-to-app communication is secured with end-to-end encryption, the network metadata remains vulnerable to eavesdropping and could potentially expose private user information.
Critical Analysis
The paper highlights an important privacy concern related to the use of robot vacuum cleaners and their companion apps. While the encryption of the communication channel is a valuable security measure, the researchers show that the unprotected network metadata can still be exploited to infer private user activities.
One limitation of the study is that it was conducted in a specific smart environment with a single robot vacuum model. Further research is needed to assess the generalizability of these findings across a broader range of devices and environments.
Additionally, the paper does not provide detailed information on the potential impact or severity of the privacy risks identified. A more thorough discussion of the specific types of private information that could be exposed and the potential consequences for users would be valuable.
Overall, this research highlights the importance of considering network metadata security in addition to end-to-end encryption when designing smart home devices and their accompanying applications. Addressing these privacy concerns is crucial to ensure the trustworthiness and widespread adoption of such technologies.
Conclusion
The paper investigates the potential privacy risks associated with the use of robot vacuum cleaners and their companion smartphone apps. Despite the implementation of end-to-end encryption, the researchers demonstrate that the unprotected network metadata can still be exploited to infer private user information and activities.
This finding raises significant privacy concerns and underscores the need for a more holistic approach to securing smart home devices and their associated applications. As these technologies become increasingly prevalent, addressing both communication channel encryption and network metadata protection will be essential to safeguarding user privacy and maintaining public trust in smart home systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🐍

0
Investigating the Privacy Risk of Using Robot Vacuum Cleaners in Smart Environments
Benjamin Ulsmaag, Jia-Chun Lin, Ming-Chang Lee
Robot vacuum cleaners have become increasingly popular and are widely used in various smart environments. To improve user convenience, manufacturers also introduced smartphone applications that enable users to customize cleaning settings or access information about their robot vacuum cleaners. While this integration enhances the interaction between users and their robot vacuum cleaners, it results in potential privacy concerns because users' personal information may be exposed. To address these concerns, end-to-end encryption is implemented between the application, cloud service, and robot vacuum cleaners to secure the exchanged information. Nevertheless, network header metadata remains unencrypted and it is still vulnerable to network eavesdropping. In this paper, we investigate the potential risk of private information exposure through such metadata. A popular robot vacuum cleaner was deployed in a real smart environment where passive network eavesdropping was conducted during several selected cleaning events. Our extensive analysis, based on Association Rule Learning, demonstrates that it is feasible to identify certain events using only the captured Internet traffic metadata, thereby potentially exposing private user information and raising privacy concerns.
Read more7/29/2024
🖼️

0
New!Securing the Future: Exploring Privacy Risks and Security Questions in Robotic Systems
Diba Afroze, Yazhou Tu, Xiali Hei
The integration of artificial intelligence, especially large language models in robotics, has led to rapid advancements in the field. We are now observing an unprecedented surge in the use of robots in our daily lives. The development and continual improvements of robots are moving at an astonishing pace. Although these remarkable improvements facilitate and enhance our lives, several security and privacy concerns have not been resolved yet. Therefore, it has become crucial to address the privacy and security threats of robotic systems while improving our experiences. In this paper, we aim to present existing applications and threats of robotics, anticipated future evolution, and the security and privacy issues they may imply. We present a series of open questions for researchers and practitioners to explore further.
Read more9/17/2024
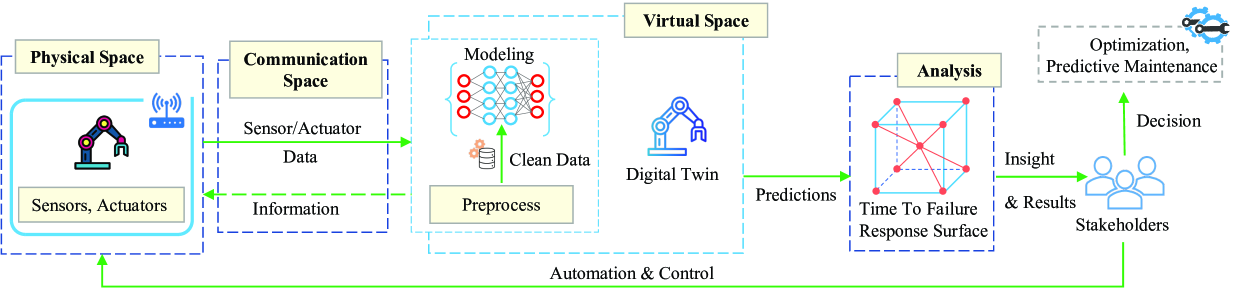

0
A Survey on Privacy Attacks Against Digital Twin Systems in AI-Robotics
Ivan A. Fernandez, Subash Neupane, Trisha Chakraborty, Shaswata Mitra, Sudip Mittal, Nisha Pillai, Jingdao Chen, Shahram Rahimi
Industry 4.0 has witnessed the rise of complex robots fueled by the integration of Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning (AI/ML) and Digital Twin (DT) technologies. While these technologies offer numerous benefits, they also introduce potential privacy and security risks. This paper surveys privacy attacks targeting robots enabled by AI and DT models. Exfiltration and data leakage of ML models are discussed in addition to the potential extraction of models derived from first-principles (e.g., physics-based). We also discuss design considerations with DT-integrated robotics touching on the impact of ML model training, responsible AI and DT safeguards, data governance and ethical considerations on the effectiveness of these attacks. We advocate for a trusted autonomy approach, emphasizing the need to combine robotics, AI, and DT technologies with robust ethical frameworks and trustworthiness principles for secure and reliable AI robotic systems.
Read more6/28/2024
🏅

0
Towards Privacy-Aware and Personalised Assistive Robots: A User-Centred Approach
Fernando E. Casado
The global increase in the elderly population necessitates innovative long-term care solutions to improve the quality of life for vulnerable individuals while reducing caregiver burdens. Assistive robots, leveraging advancements in Machine Learning, offer promising personalised support. However, their integration into daily life raises significant privacy concerns. Widely used frameworks like the Robot Operating System (ROS) historically lack inherent privacy mechanisms, complicating data-driven approaches in robotics. This research pioneers user-centric, privacy-aware technologies such as Federated Learning (FL) to advance assistive robotics. FL enables collaborative learning without sharing sensitive data, addressing privacy and scalability issues. This work includes developing solutions for smart wheelchair assistance, enhancing user independence and well-being. By tackling challenges related to non-stationary data and heterogeneous environments, the research aims to improve personalisation and user experience. Ultimately, it seeks to lead the responsible integration of assistive robots into society, enhancing the quality of life for elderly and care-dependent individuals.
Read more5/24/2024