Adaptive Anchor Pairs Selection in a TDOA-based System Through Robot Localization Error Minimization
2404.05067

0
0
Abstract
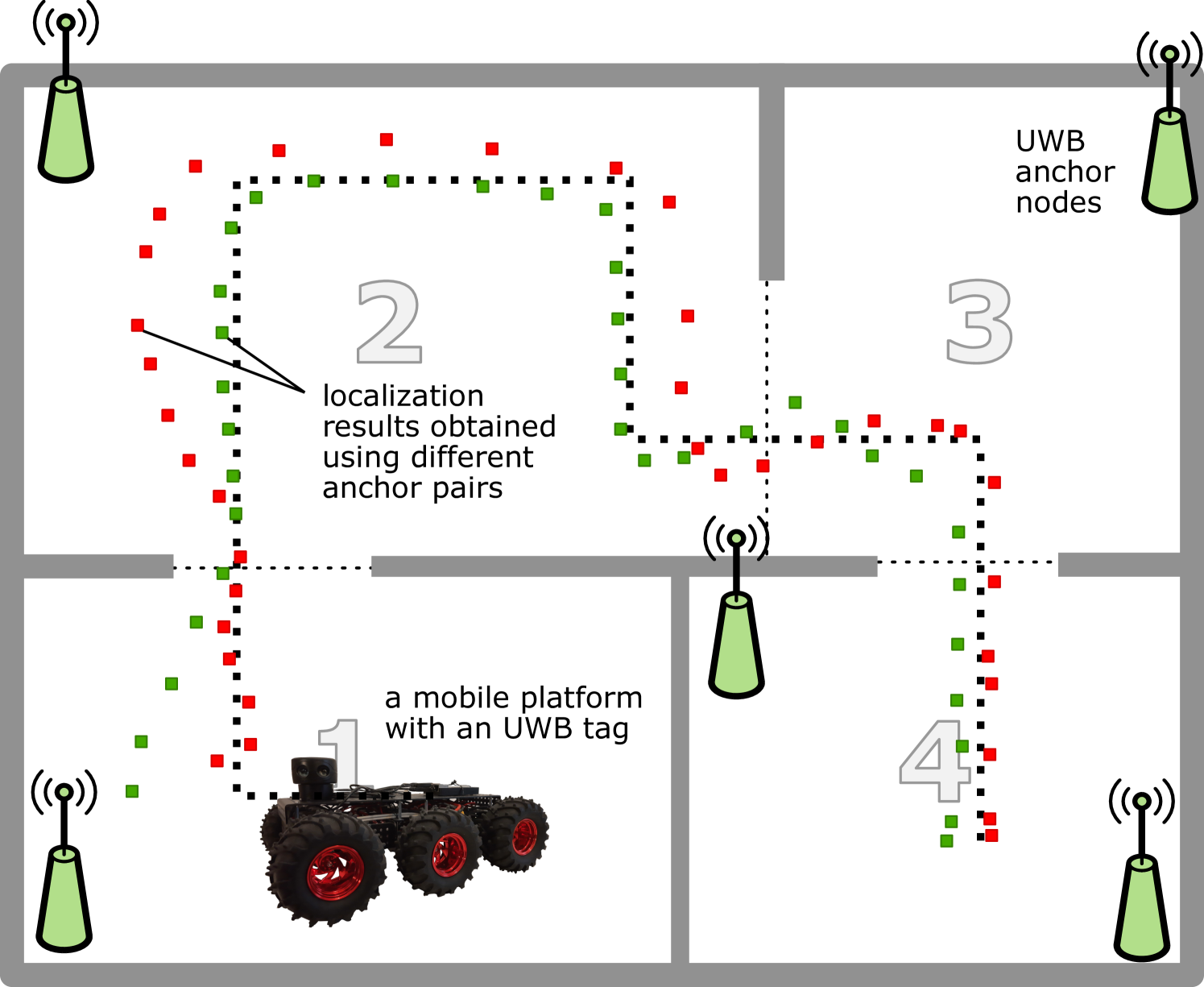
The following paper presents an adaptive anchor pairs selection method for ultra-wideband (UWB) Time Difference of Arrival (TDOA) based positioning systems. The method divides the area covered by the system into several zones and assigns them anchor pair sets. The pair sets are determined during calibration based on localization root mean square error (RMSE). The calibration assumes driving a mobile platform equipped with a LiDAR sensor and a UWB tag through the specified zones. The robot is localized separately based on a large set of different TDOA pairs and using a LiDAR, which acts as the reference. For each zone, the TDOA pairs set for which the registered RMSE is lowest is selected and used for localization in the routine system work. The proposed method has been tested with simulations and experiments. The results for both simulated static and experimental dynamic scenarios have proven that the adaptive selection of the anchor nodes leads to an increase in localization accuracy. In the experiment, the median trajectory error for a moving person localization was at a level of 25 cm.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This research paper explores an adaptive anchor pairs selection method for a Time Difference of Arrival (TDOA)-based positioning system, with the goal of minimizing robot localization error.
- The proposed approach dynamically selects the best anchor pairs to use for localization, based on the robot's current location and the estimated localization error.
- The research was partially funded by the National Centre for Research and Development in Poland.
Plain English Explanation
The research paper focuses on improving the accuracy of robot localization using a TDOA-based positioning system. TDOA is a technique that uses the time difference in signal arrival at multiple receivers (called anchors) to estimate the location of a transmitter (in this case, the robot).
The key idea behind the research is that the selection of anchor pairs, i.e., which pair of anchors to use for localization, can significantly impact the accuracy of the position estimate. The researchers developed an adaptive method to dynamically choose the best anchor pairs based on the robot's current location and the expected localization error.
By constantly adjusting the anchor pairs used for localization, the system can minimize the overall error in the robot's position estimate. This is particularly important in complex indoor environments where factors like obstacles and multipath effects can degrade the performance of TDOA-based positioning.
The research was funded in part by the National Centre for Research and Development in Poland, indicating its relevance and importance in the field of robotics and indoor positioning.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents an Adaptive Anchor Pairs Selection method for a TDOA-based localization system. The goal is to minimize the robot's localization error by dynamically selecting the best anchor pairs to use for position estimation.
The proposed approach involves the following key steps:
- Anchor Pair Selection: The system evaluates all possible anchor pairs and calculates the expected localization error for each pair, based on factors such as the geometry of the anchors and the robot's current position.
- Anchor Pair Optimization: The system selects the anchor pair that minimizes the expected localization error, considering both the current and predicted future positions of the robot.
- Localization Refinement: The system uses a Kalman Filter to refine the position estimate based on the selected anchor pair.
The researchers evaluated their approach using both simulations and real-world experiments in an indoor environment. The results demonstrate that the adaptive anchor pairs selection method can significantly improve the accuracy of robot localization compared to using a fixed set of anchor pairs.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a novel and promising approach to improving the accuracy of TDOA-based robot localization. The adaptive anchor pairs selection method is a thoughtful solution to address the challenge of anchor pair selection, which can have a significant impact on the overall localization performance.
One potential limitation of the research is the reliance on a priori knowledge of the environment, such as the positions of the anchors, to calculate the expected localization error. In real-world scenarios, this information may not always be readily available, and the system may need to rely on semi-supervised or learning-based techniques to estimate the required parameters.
Additionally, the paper does not explore the impact of dynamic changes in the environment, such as the presence of moving obstacles or people, on the localization performance. These factors could further complicate the anchor pair selection process and may require more sophisticated probabilistic positioning techniques.
Overall, the research presented in this paper is a valuable contribution to the field of TDOA-based robot localization, and the adaptive anchor pairs selection method shows promise for improving the accuracy and reliability of indoor positioning systems.
Conclusion
This research paper introduces an adaptive anchor pairs selection method for TDOA-based robot localization systems. By dynamically choosing the best anchor pairs to use for position estimation, the proposed approach can significantly reduce the robot's localization error, particularly in complex indoor environments.
The key innovation of this work is the integration of anchor pair selection optimization with a Kalman Filter-based localization refinement process. This allows the system to adapt to the robot's current and predicted future positions, leading to more accurate and stable position estimates.
The research findings have important implications for the development of robust and reliable indoor positioning systems for robotics and other applications. Further exploration of the method's performance under more dynamic environmental conditions and the incorporation of additional sensor modalities could lead to even more robust and accurate localization solutions.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Error Mitigation for TDoA UWB Indoor Localization using Unsupervised Machine Learning
Phuong Bich Duong, Ben Van Herbruggen, Arne Broering, Adnan Shahid, Eli De Poorter

0
0
Indoor positioning systems based on Ultra-wideband (UWB) technology are gaining recognition for their ability to provide cm-level localization accuracy. However, these systems often encounter challenges caused by dense multi-path fading, leading to positioning errors. To address this issue, in this letter, we propose a novel methodology for unsupervised anchor node selection using deep embedded clustering (DEC). Our approach uses an Auto Encoder (AE) before clustering, thereby better separating UWB features into separable clusters of UWB input signals. We furthermore investigate how to rank these clusters based on their cluster quality, allowing us to remove untrustworthy signals. Experimental results show the efficiency of our proposed method, demonstrating a significant 23.1% reduction in mean absolute error (MAE) compared to without anchor exclusion. Especially in the dense multi-path area, our algorithm achieves even more significant enhancements, reducing the MAE by 26.6% and the 95th percentile error by 49.3% compared to without anchor exclusion.
4/11/2024
❗
Utilizing acceleration measurements to improve TDOA based localization
Marcin Kolakowski

0
0
In this paper localization using UWB positioning system and an inertial unit containing a single accelerometer is considered. The main part of the paper describes a novel algorithm for person localization. The algorithm is based on modified Extended Kalman Filter and utilizes TDOA (Time Difference of Arrival) results obtained from UWB system and results of acceleration measurement performed by the localized tag device. The proposed algorithm has been experimentally investigated through simulation and experiments. The results are included in the paper.
4/1/2024
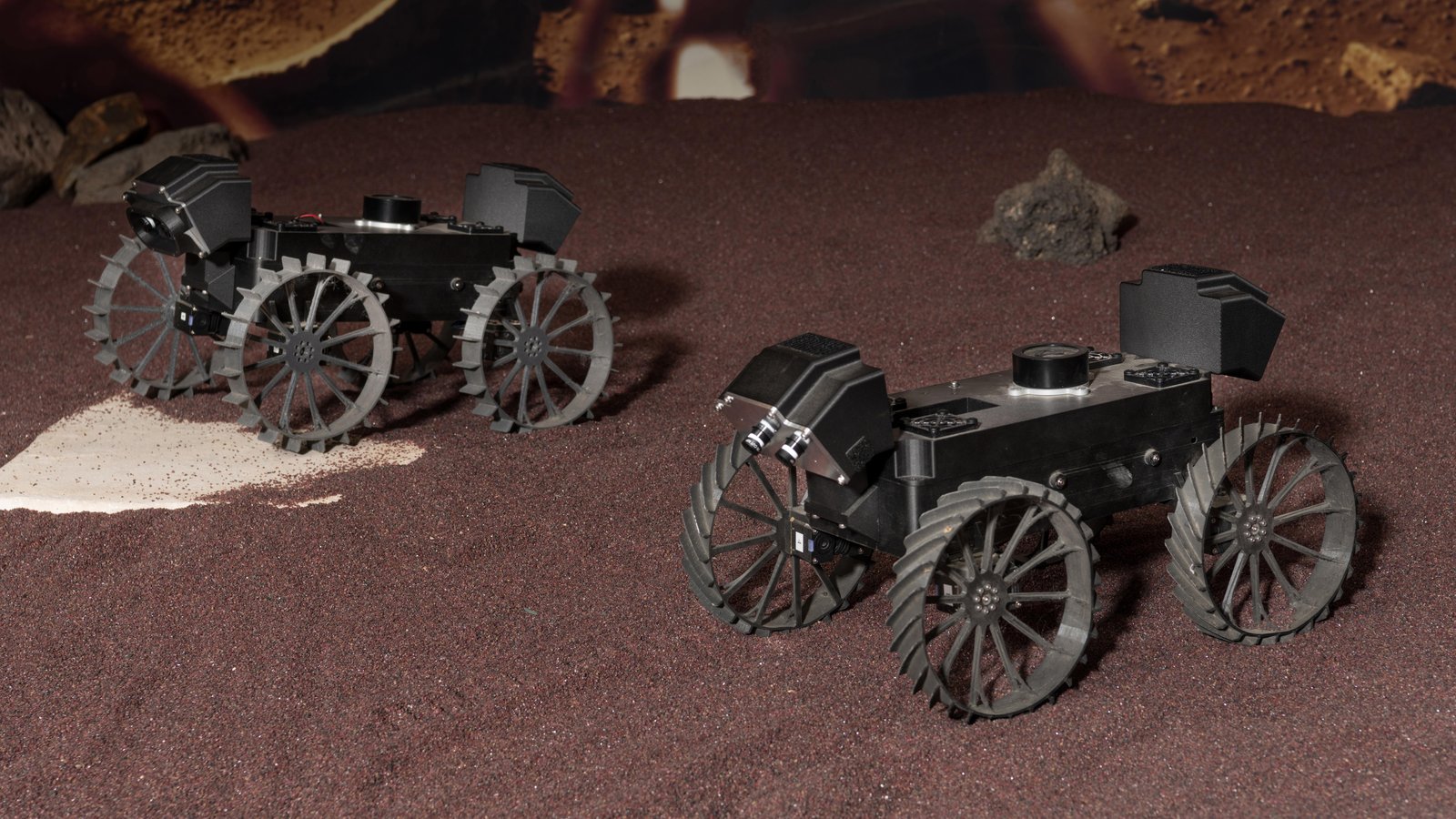

Multi-Robot Collaborative Localization and Planning with Inter-Ranging
Derek Knowles, Adam Dai, Grace Gao

0
0
Robots often use feature-based image tracking to identify their position in their surrounding environment; however, feature-based image tracking is prone to errors in low-textured and poorly lit environments. Specifically, we investigate a scenario where robots are tasked with exploring the surface of the Moon and are required to have an accurate estimate of their position to be able to correctly geotag scientific measurements. To reduce localization error, we complement traditional feature-based image tracking with ultra-wideband (UWB) distance measurements between the robots. The robots use an advanced mesh-ranging protocol that allows them to continuously share distance measurements amongst each other rather than relying on the common anchor and tag UWB architecture. We develop a decentralized multi-robot coordination algorithm that actively plans paths based on measurement line-of-sight vectors amongst all robots to minimize collective localization error. We then demonstrate the emergent behavior of the proposed multi-robot coordination algorithm both in simulation and hardware to lower a geometry-based uncertainty metric and reduce localization error.
6/26/2024
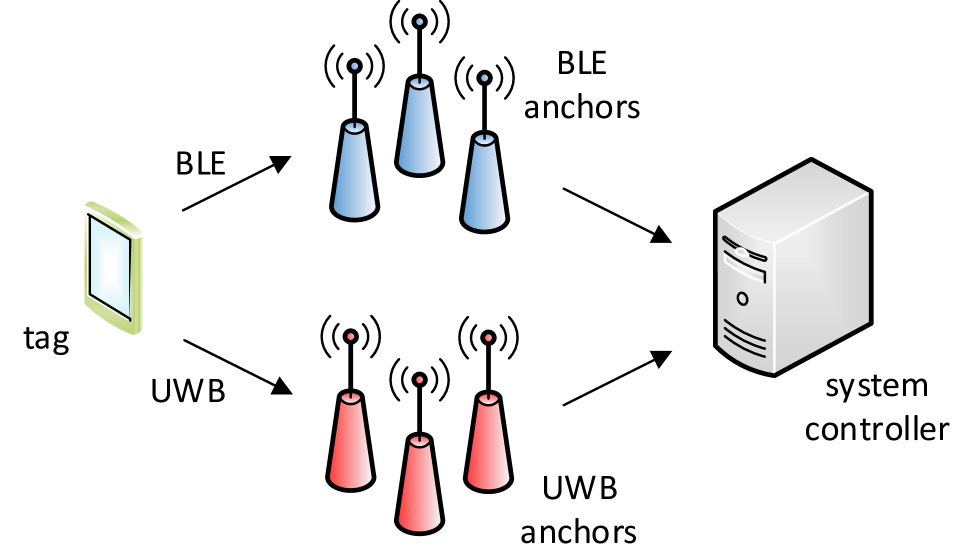
Kalman filter based localization in hybrid BLE-UWB positioning system
Marcin Kolakowski

0
0
In this paper a concept of hybrid Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) Ultra-wideband (UWB) positioning system is presented. The system is intended to be energy efficient. Low energy BLE unit is used as a primary source of measurement data and for most of the time localization is calculated based on received signal strength (RSS). UWB technology is used less often. Time difference of arrival (TDOA) values measured with UWB radios are periodically used to improve RSS based localization. The paper contains a description of proposed hybrid positioning algorithm. Results of simulations and experiments confirming algorithm's efficiency are also included.
4/4/2024