A Linguistic Comparison between Human and ChatGPT-Generated Conversations
2401.16587

0
0
Abstract
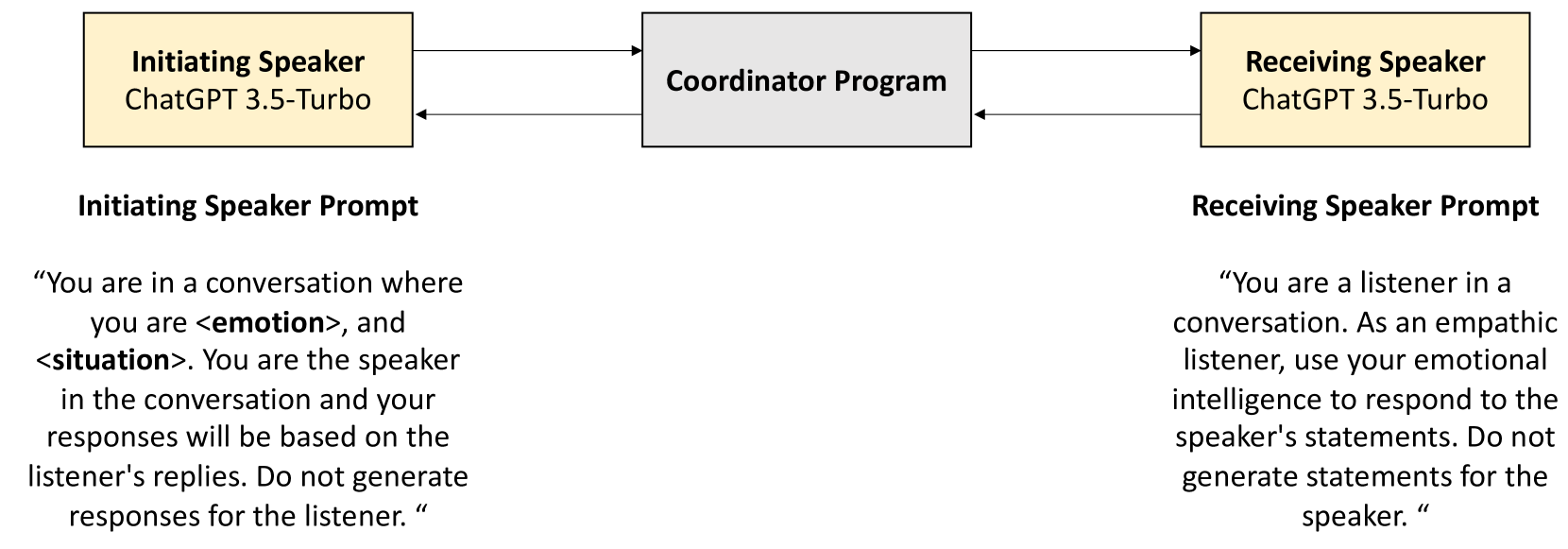
This study explores linguistic differences between human and LLM-generated dialogues, using 19.5K dialogues generated by ChatGPT-3.5 as a companion to the EmpathicDialogues dataset. The research employs Linguistic Inquiry and Word Count (LIWC) analysis, comparing ChatGPT-generated conversations with human conversations across 118 linguistic categories. Results show greater variability and authenticity in human dialogues, but ChatGPT excels in categories such as social processes, analytical style, cognition, attentional focus, and positive emotional tone, reinforcing recent findings of LLMs being more human than human. However, no significant difference was found in positive or negative affect between ChatGPT and human dialogues. Classifier analysis of dialogue embeddings indicates implicit coding of the valence of affect despite no explicit mention of affect in the conversations. The research also contributes a novel, companion ChatGPT-generated dataset of conversations between two independent chatbots, which were designed to replicate a corpus of human conversations available for open access and used widely in AI research on language modeling. Our findings enhance understanding of ChatGPT's linguistic capabilities and inform ongoing efforts to distinguish between human and LLM-generated text, which is critical in detecting AI-generated fakes, misinformation, and disinformation.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- This paper presents a linguistic comparison between human and ChatGPT-generated conversations.
- The researchers generated conversational data using both human participants and the ChatGPT language model.
- They then analyzed the linguistic characteristics of the conversations to identify similarities and differences between human and AI-generated dialogues.
- The findings provide insights into the capabilities and limitations of large language models like ChatGPT in terms of natural language generation and interactive dialogue.
Plain English Explanation
The researchers in this study wanted to better understand how conversations generated by humans differ from those created by a powerful AI language model called ChatGPT. They collected conversational data from both human participants and the ChatGPT system, and then analyzed the linguistic characteristics of the dialogues.
By comparing the human and AI-generated conversations, the researchers aimed to uncover the strengths and weaknesses of ChatGPT when it comes to natural language processing and interactive dialogue. This could help researchers and developers better understand the current capabilities and limitations of large language models, and inform the development of more advanced AI systems that can engage in more natural and human-like conversations.
Technical Explanation
The researchers first generated conversational data using two methods: [1] recruiting human participants to engage in free-form dialogues, and [2] using the ChatGPT language model to generate conversations based on prompts. They then conducted a linguistic analysis of the resulting dialogues, examining features such as link lexical diversity, link syntactic complexity, link pragmatic markers, and link response coherence.
The analysis revealed both link similarities and differences between human and ChatGPT-generated conversations. For example, the ChatGPT dialogues exhibited higher lexical diversity, but lower syntactic complexity compared to the human conversations. The researchers also found differences in the use of pragmatic markers and the overall coherence of the responses.
Critical Analysis
The researchers acknowledge several limitations of their study, such as the relatively small sample size of human-generated conversations and the fact that they only used a single language model (ChatGPT) for comparison. Additionally, the prompts used to generate the ChatGPT dialogues may have influenced the linguistic characteristics of the responses.
While the findings provide valuable insights into the current capabilities of large language models, further research is needed to better understand the nuances of human-AI conversational dynamics. For example, the study did not explore the emotional or social aspects of the dialogues, which could be an important factor in evaluating the human-likeness of AI-generated conversations.
Conclusion
This study offers a linguistic comparison of human and ChatGPT-generated conversations, shedding light on the strengths and weaknesses of current large language models in terms of natural language processing and interactive dialogue. The findings suggest that while ChatGPT can generate responses with high lexical diversity, it may struggle to match the syntactic complexity and pragmatic coherence of human conversations.
The insights from this research can inform the development of more advanced AI systems that can engage in more natural and human-like dialogues, potentially enhancing their usefulness in various applications, such as link customer service, link software development, and link educational settings.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
💬
ChatGPT as an inventor: Eliciting the strengths and weaknesses of current large language models against humans in engineering design
Daniel Nyg{aa}rd Ege, Henrik H. {O}vreb{o}, Vegar Stubberud, Martin Francis Berg, Christer Elverum, Martin Steinert, H{aa}vard Vestad

0
0
This study compares the design practices and performance of ChatGPT 4.0, a large language model (LLM), against graduate engineering students in a 48-hour prototyping hackathon, based on a dataset comprising more than 100 prototypes. The LLM participated by instructing two participants who executed its instructions and provided objective feedback, generated ideas autonomously and made all design decisions without human intervention. The LLM exhibited similar prototyping practices to human participants and finished second among six teams, successfully designing and providing building instructions for functional prototypes. The LLM's concept generation capabilities were particularly strong. However, the LLM prematurely abandoned promising concepts when facing minor difficulties, added unnecessary complexity to designs, and experienced design fixation. Communication between the LLM and participants was challenging due to vague or unclear descriptions, and the LLM had difficulty maintaining continuity and relevance in answers. Based on these findings, six recommendations for implementing an LLM like ChatGPT in the design process are proposed, including leveraging it for ideation, ensuring human oversight for key decisions, implementing iterative feedback loops, prompting it to consider alternatives, and assigning specific and manageable tasks at a subsystem level.
4/30/2024
👨🏫
The high dimensional psychological profile and cultural bias of ChatGPT
Hang Yuan (Sun Yat-Sen University), Zhongyue Che (Sun Yat-Sen University), Shao Li (Sun Yat-Sen University), Yue Zhang (Renmin University of China), Xiaomeng Hu (Renmin University of China), Siyang Luo (Sun Yat-Sen University)

0
0
Given the rapid advancement of large-scale language models, artificial intelligence (AI) models, like ChatGPT, are playing an increasingly prominent role in human society. However, to ensure that artificial intelligence models benefit human society, we must first fully understand the similarities and differences between the human-like characteristics exhibited by artificial intelligence models and real humans, as well as the cultural stereotypes and biases that artificial intelligence models may exhibit in the process of interacting with humans. This study first measured ChatGPT in 84 dimensions of psychological characteristics, revealing differences between ChatGPT and human norms in most dimensions as well as in high-dimensional psychological representations. Additionally, through the measurement of ChatGPT in 13 dimensions of cultural values, it was revealed that ChatGPT's cultural value patterns are dissimilar to those of various countries/regions worldwide. Finally, an analysis of ChatGPT's performance in eight decision-making tasks involving interactions with humans from different countries/regions revealed that ChatGPT exhibits clear cultural stereotypes in most decision-making tasks and shows significant cultural bias in third-party punishment and ultimatum games. The findings indicate that, compared to humans, ChatGPT exhibits a distinct psychological profile and cultural value orientation, and it also shows cultural biases and stereotypes in interpersonal decision-making. Future research endeavors should emphasize enhanced technical oversight and augmented transparency in the database and algorithmic training procedures to foster more efficient cross-cultural communication and mitigate social disparities.
5/7/2024
👨🏫
Text and Audio Simplification: Human vs. ChatGPT
Gondy Leroy, David Kauchak, Philip Harber, Ankit Pal, Akash Shukla

0
0
Text and audio simplification to increase information comprehension are important in healthcare. With the introduction of ChatGPT, an evaluation of its simplification performance is needed. We provide a systematic comparison of human and ChatGPT simplified texts using fourteen metrics indicative of text difficulty. We briefly introduce our online editor where these simplification tools, including ChatGPT, are available. We scored twelve corpora using our metrics: six text, one audio, and five ChatGPT simplified corpora. We then compare these corpora with texts simplified and verified in a prior user study. Finally, a medical domain expert evaluated these texts and five, new ChatGPT simplified versions. We found that simple corpora show higher similarity with the human simplified texts. ChatGPT simplification moves metrics in the right direction. The medical domain expert evaluation showed a preference for the ChatGPT style, but the text itself was rated lower for content retention.
5/6/2024
✨
Beyond Code Generation: An Observational Study of ChatGPT Usage in Software Engineering Practice
Ranim Khojah, Mazen Mohamad, Philipp Leitner, Francisco Gomes de Oliveira Neto

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) are frequently discussed in academia and the general public as support tools for virtually any use case that relies on the production of text, including software engineering. Currently there is much debate, but little empirical evidence, regarding the practical usefulness of LLM-based tools such as ChatGPT for engineers in industry. We conduct an observational study of 24 professional software engineers who have been using ChatGPT over a period of one week in their jobs, and qualitatively analyse their dialogues with the chatbot as well as their overall experience (as captured by an exit survey). We find that, rather than expecting ChatGPT to generate ready-to-use software artifacts (e.g., code), practitioners more often use ChatGPT to receive guidance on how to solve their tasks or learn about a topic in more abstract terms. We also propose a theoretical framework for how (i) purpose of the interaction, (ii) internal factors (e.g., the user's personality), and (iii) external factors (e.g., company policy) together shape the experience (in terms of perceived usefulness and trust). We envision that our framework can be used by future research to further the academic discussion on LLM usage by software engineering practitioners, and to serve as a reference point for the design of future empirical LLM research in this domain.
4/24/2024