MaFreeI2P: A Matching-Free Image-to-Point Cloud Registration Paradigm with Active Camera Pose Retrieval

0

Sign in to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
MaFreeI2P: A Matching-Free Image-to-Point Cloud Registration Paradigm with Active Camera Pose Retrieval
Gongxin Yao, Xinyang Li, Yixin Xuan, Yu Pan
Image-to-point cloud registration seeks to estimate their relative camera pose, which remains an open question due to the data modality gaps. The recent matching-based methods tend to tackle this by building 2D-3D correspondences. In this paper, we reveal the information loss inherent in these methods and propose a matching-free paradigm, named MaFreeI2P. Our key insight is to actively retrieve the camera pose in SE(3) space by contrasting the geometric features between the point cloud and the query image. To achieve this, we first sample a set of candidate camera poses and construct their cost volume using the cross-modal features. Superior to matching, cost volume can preserve more information and its feature similarity implicitly reflects the confidence level of the sampled poses. Afterwards, we employ a convolutional network to adaptively formulate a similarity assessment function, where the input cost volume is further improved by filtering and pose-based weighting. Finally, we update the camera pose based on the similarity scores, and adopt a heuristic strategy to iteratively shrink the pose sampling space for convergence. Our MaFreeI2P achieves a very competitive registration accuracy and recall on the KITTI-Odometry and Apollo-DaoxiangLake datasets.
Read more8/6/2024

0
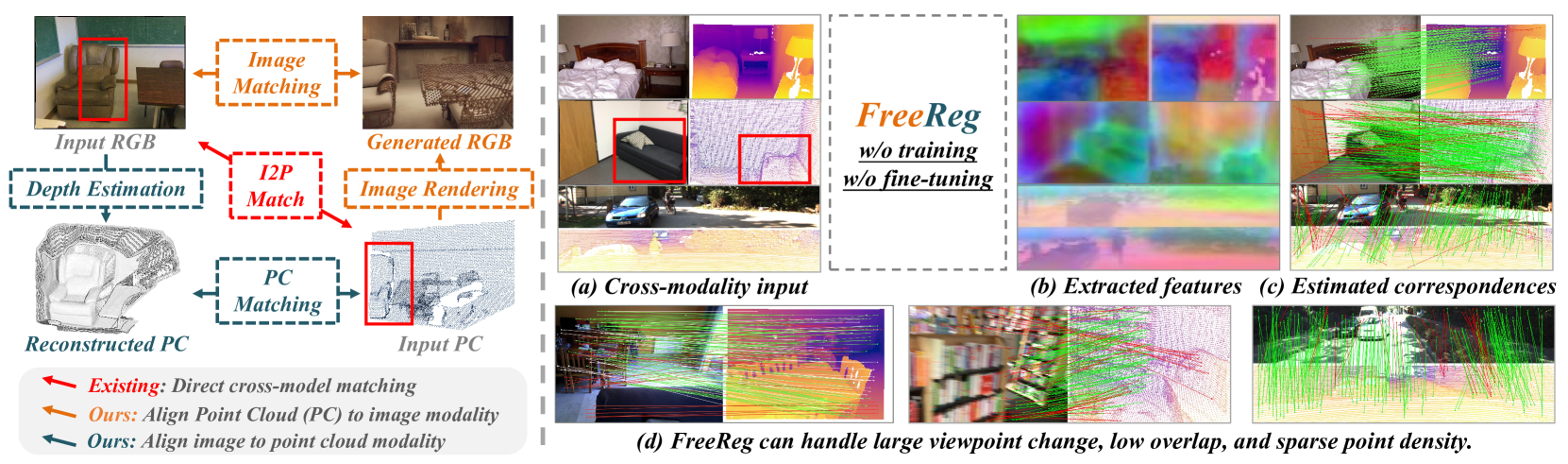
FreeReg: Image-to-Point Cloud Registration Leveraging Pretrained Diffusion Models and Monocular Depth Estimators
Haiping Wang, Yuan Liu, Bing Wang, Yujing Sun, Zhen Dong, Wenping Wang, Bisheng Yang
Matching cross-modality features between images and point clouds is a fundamental problem for image-to-point cloud registration. However, due to the modality difference between images and points, it is difficult to learn robust and discriminative cross-modality features by existing metric learning methods for feature matching. Instead of applying metric learning on cross-modality data, we propose to unify the modality between images and point clouds by pretrained large-scale models first, and then establish robust correspondence within the same modality. We show that the intermediate features, called diffusion features, extracted by depth-to-image diffusion models are semantically consistent between images and point clouds, which enables the building of coarse but robust cross-modality correspondences. We further extract geometric features on depth maps produced by the monocular depth estimator. By matching such geometric features, we significantly improve the accuracy of the coarse correspondences produced by diffusion features. Extensive experiments demonstrate that without any task-specific training, direct utilization of both features produces accurate image-to-point cloud registration. On three public indoor and outdoor benchmarks, the proposed method averagely achieves a 20.6 percent improvement in Inlier Ratio, a three-fold higher Inlier Number, and a 48.6 percent improvement in Registration Recall than existing state-of-the-arts.
Read more4/16/2024
🧪

0
CoFiI2P: Coarse-to-Fine Correspondences for Image-to-Point Cloud Registration
Shuhao Kang, Youqi Liao, Jianping Li, Fuxun Liang, Yuhao Li, Xianghong Zou, Fangning Li, Xieyuanli Chen, Zhen Dong, Bisheng Yang
Image-to-point cloud (I2P) registration is a fundamental task for robots and autonomous vehicles to achieve cross-modality data fusion and localization. Current I2P registration methods primarily focus on estimating correspondences at the point or pixel level, often neglecting global alignment. As a result, I2P matching can easily converge to a local optimum if it lacks high-level guidance from global constraints. To improve the success rate and general robustness, this paper introduces CoFiI2P, a novel I2P registration network that extracts correspondences in a coarse-to-fine manner. First, the image and point cloud data are processed through a two-stream encoder-decoder network for hierarchical feature extraction. Second, a coarse-to-fine matching module is designed to leverage these features and establish robust feature correspondences. Specifically, In the coarse matching phase, a novel I2P transformer module is employed to capture both homogeneous and heterogeneous global information from the image and point cloud data. This enables the estimation of coarse super-point/super-pixel matching pairs with discriminative descriptors. In the fine matching module, point/pixel pairs are established with the guidance of super-point/super-pixel correspondences. Finally, based on matching pairs, the transform matrix is estimated with the EPnP-RANSAC algorithm. Experiments conducted on the KITTI Odometry dataset demonstrate that CoFiI2P achieves impressive results, with a relative rotation error (RRE) of 1.14 degrees and a relative translation error (RTE) of 0.29 meters, while maintaining real-time speed.Additional experiments on the Nuscenes datasets confirm our method's generalizability. The project page is available at url{https://whu-usi3dv.github.io/CoFiI2P}.
Read more9/14/2024


0
Deep-PE: A Learning-Based Pose Evaluator for Point Cloud Registration
Junjie Gao, Chongjian Wang, Zhongjun Ding, Shuangmin Chen, Shiqing Xin, Changhe Tu, Wenping Wang
In the realm of point cloud registration, the most prevalent pose evaluation approaches are statistics-based, identifying the optimal transformation by maximizing the number of consistent correspondences. However, registration recall decreases significantly when point clouds exhibit a low overlap rate, despite efforts in designing feature descriptors and establishing correspondences. In this paper, we introduce Deep-PE, a lightweight, learning-based pose evaluator designed to enhance the accuracy of pose selection, especially in challenging point cloud scenarios with low overlap. Our network incorporates a Pose-Aware Attention (PAA) module to simulate and learn the alignment status of point clouds under various candidate poses, alongside a Pose Confidence Prediction (PCP) module that predicts the likelihood of successful registration. These two modules facilitate the learning of both local and global alignment priors. Extensive tests across multiple benchmarks confirm the effectiveness of Deep-PE. Notably, on 3DLoMatch with a low overlap rate, Deep-PE significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods by at least 8% and 11% in registration recall under handcrafted FPFH and learning-based FCGF descriptors, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to utilize deep learning to select the optimal pose without the explicit need for input correspondences.
Read more5/28/2024