Multi-Channel Multi-Speaker ASR Using Target Speaker's Solo Segment

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
• This paper presents a novel approach for multi-channel multi-speaker automatic speech recognition (ASR) that leverages the target speaker's solo segment. • The key idea is to use spatial features extracted from the target speaker's solo segment to enhance the recognition performance of the target speaker in a multi-speaker scenario. • The proposed method aims to address the challenges of speaker diarization and separation in multi-speaker ASR systems.
Plain English Explanation
• In many real-world scenarios, there are multiple people speaking at the same time, which can make it difficult for a speech recognition system to accurately transcribe what each individual is saying. • This paper introduces a new technique that can help improve the accuracy of speech recognition in these multi-speaker situations. • The main idea is to use the audio from the target speaker when they are talking alone (their "solo segment") to extract spatial information about how their voice is being picked up by the different microphones. • This spatial information is then used to help the speech recognition system better identify and transcribe the target speaker's voice, even when they are speaking at the same time as other people.
Technical Explanation
• The paper introduces the concept of "spatial features" - information about how a speaker's voice is captured by multiple microphones in a multi-channel audio setup. • These spatial features are extracted from the target speaker's solo segment using techniques like RIR-SF and ELF. • The extracted spatial features are then used to enhance the acoustic model of the target speaker in a multi-speaker transcription-free fine-tuning setup. • This allows the ASR system to better recognize the target speaker's voice even when they are speaking concurrently with other speakers, overcoming challenges in speaker diarization and separation.
Critical Analysis
• The paper acknowledges that the performance of the proposed method is dependent on the availability of a clean solo segment for the target speaker, which may not always be the case in real-world scenarios. • Further research could explore ways to relax this assumption, such as by using techniques like blind source separation to estimate the solo segment from the mixed audio. • The authors also note that the proposed method may not generalize well to scenarios with a large number of speakers or highly overlapping speech, suggesting the need for additional advancements in this area.
Conclusion
• This paper introduces a novel approach for multi-channel multi-speaker ASR that leverages the target speaker's solo segment to extract spatial features and enhance the recognition of the target speaker's voice. • The proposed method aims to address the challenges of speaker diarization and separation in multi-speaker ASR, potentially improving the accuracy and robustness of speech recognition systems in real-world, noisy environments. • While the method shows promising results, further research is needed to address its limitations and explore ways to make it more applicable to diverse real-world scenarios.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Multi-Channel Multi-Speaker ASR Using Target Speaker's Solo Segment
Yiwen Shao, Shi-Xiong Zhang, Yong Xu, Meng Yu, Dong Yu, Daniel Povey, Sanjeev Khudanpur
In the field of multi-channel, multi-speaker Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), the task of discerning and accurately transcribing a target speaker's speech within background noise remains a formidable challenge. Traditional approaches often rely on microphone array configurations and the information of the target speaker's location or voiceprint. This study introduces the Solo Spatial Feature (Solo-SF), an innovative method that utilizes a target speaker's isolated speech segment to enhance ASR performance, thereby circumventing the need for conventional inputs like microphone array layouts. We explore effective strategies for selecting optimal solo segments, a crucial aspect for Solo-SF's success. Through evaluations conducted on the AliMeeting dataset and AISHELL-1 simulations, Solo-SF demonstrates superior performance over existing techniques, significantly lowering Character Error Rates (CER) in various test conditions. Our findings highlight Solo-SF's potential as an effective solution for addressing the complexities of multi-channel, multi-speaker ASR tasks.
Read more6/19/2024
✨

0
RIR-SF: Room Impulse Response Based Spatial Feature for Target Speech Recognition in Multi-Channel Multi-Speaker Scenarios
Yiwen Shao, Shi-Xiong Zhang, Dong Yu
Automatic speech recognition (ASR) on multi-talker recordings is challenging. Current methods using 3D spatial data from multi-channel audio and visual cues focus mainly on direct waves from the target speaker, overlooking reflection wave impacts, which hinders performance in reverberant environments. Our research introduces RIR-SF, a novel spatial feature based on room impulse response (RIR) that leverages the speaker's position, room acoustics, and reflection dynamics. RIR-SF significantly outperforms traditional 3D spatial features, showing superior theoretical and empirical performance. We also propose an optimized all-neural multi-channel ASR framework for RIR-SF, achieving a relative 21.3% reduction in CER for target speaker ASR in multi-channel settings. RIR-SF enhances recognition accuracy and demonstrates robustness in high-reverberation scenarios, overcoming the limitations of previous methods.
Read more6/13/2024


0
Improving Speaker Assignment in Speaker-Attributed ASR for Real Meeting Applications
Can Cui (MULTISPEECH), Imran Ahamad Sheikh (MULTISPEECH), Mostafa Sadeghi (MULTISPEECH), Emmanuel Vincent (MULTISPEECH)
Past studies on end-to-end meeting transcription have focused on model architecture and have mostly been evaluated on simulated meeting data. We present a novel study aiming to optimize the use of a Speaker-Attributed ASR (SA-ASR) system in real-life scenarios, such as the AMI meeting corpus, for improved speaker assignment of speech segments. First, we propose a pipeline tailored to real-life applications involving Voice Activity Detection (VAD), Speaker Diarization (SD), and SA-ASR. Second, we advocate using VAD output segments to fine-tune the SA-ASR model, considering that it is also applied to VAD segments during test, and show that this results in a relative reduction of Speaker Error Rate (SER) up to 28%. Finally, we explore strategies to enhance the extraction of the speaker embedding templates used as inputs by the SA-ASR system. We show that extracting them from SD output rather than annotated speaker segments results in a relative SER reduction up to 20%.
Read more9/6/2024

0
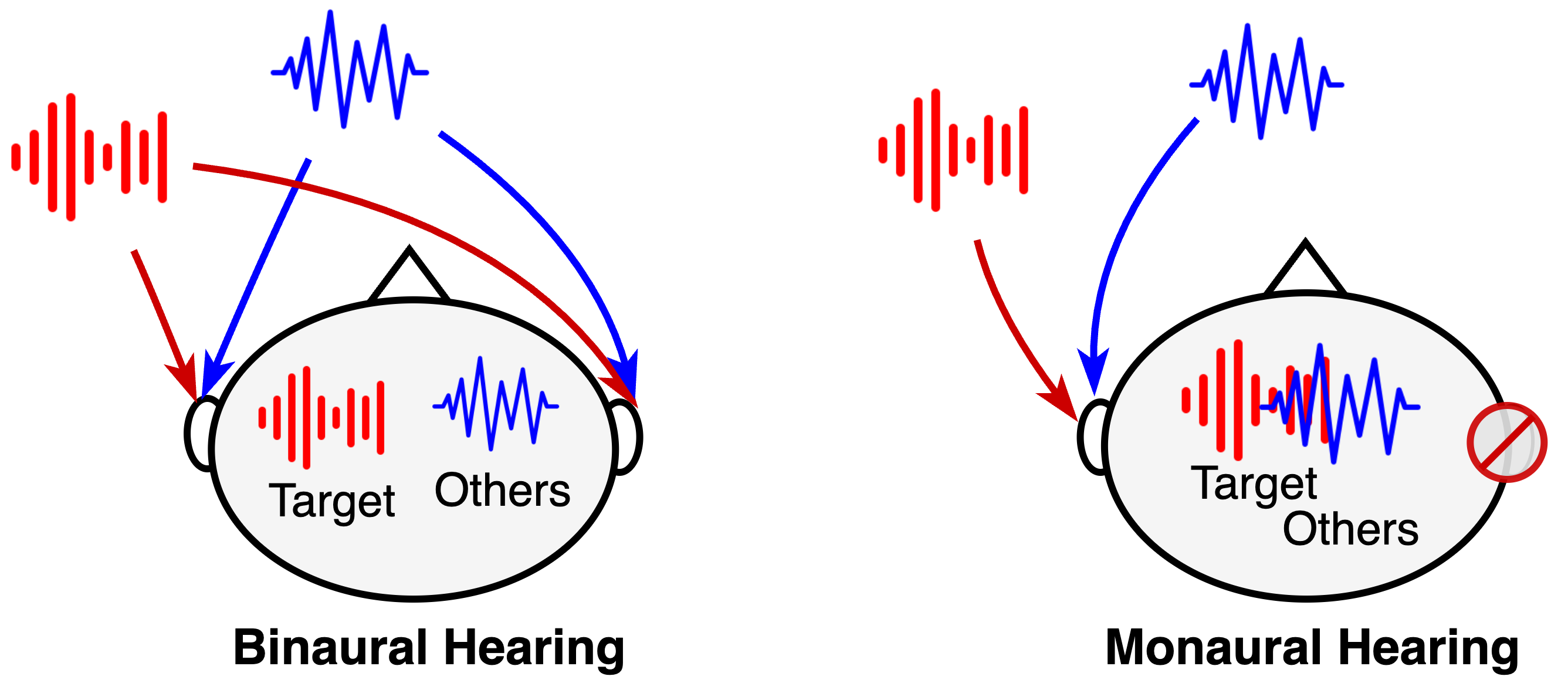
Binaural Selective Attention Model for Target Speaker Extraction
Hanyu Meng, Qiquan Zhang, Xiangyu Zhang, Vidhyasaharan Sethu, Eliathamby Ambikairajah
The remarkable ability of humans to selectively focus on a target speaker in cocktail party scenarios is facilitated by binaural audio processing. In this paper, we present a binaural time-domain Target Speaker Extraction model based on the Filter-and-Sum Network (FaSNet). Inspired by human selective hearing, our proposed model introduces target speaker embedding into separators using a multi-head attention-based selective attention block. We also compared two binaural interaction approaches -- the cosine similarity of time-domain signals and inter-channel correlation in learned spectral representations. Our experimental results show that our proposed model outperforms monaural configurations and state-of-the-art multi-channel target speaker extraction models, achieving best-in-class performance with 18.52 dB SI-SDR, 19.12 dB SDR, and 3.05 PESQ scores under anechoic two-speaker test configurations.
Read more6/19/2024