Multi-view Pose Fusion for Occlusion-Aware 3D Human Pose Estimation

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a multi-view 3D human pose estimation method that addresses the challenge of occlusions.
- It fuses information from multiple camera views to obtain a more robust and accurate 3D pose estimation, even in the presence of occlusions.
- The proposed approach outperforms state-of-the-art single-view and multi-view 3D pose estimation methods on several benchmark datasets.
Plain English Explanation
Estimating the 3D pose of a person from camera images is an important task for applications like human-robot interaction and motion capture. However, when parts of the person's body are occluded (hidden from view), it becomes challenging to accurately estimate their 3D pose from a single camera.
This research paper presents a new method that uses information from multiple camera views to overcome the problem of occlusions and estimate the 3D pose more accurately. The key idea is to fuse the pose estimates from different camera views, taking advantage of the complementary information they provide. This allows the system to reconstruct the full 3D pose, even when parts of the body are occluded in some of the camera views.
The researchers show that their multi-view fusion approach outperforms state-of-the-art single-view and multi-view 3D pose estimation methods on several standard benchmarks. This suggests that their technique could be useful for real-world applications that require robust and accurate 3D human pose estimation, such as human-robot collaboration.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a multi-view 3D human pose estimation method that addresses the challenge of occlusions. The key components of the approach are:
-
Pose Estimation: The method first uses a 2D pose estimation network to obtain 2D joint locations from each camera view independently.
-
Occlusion Handling: An occlusion-aware module is introduced to handle cases where body parts are occluded in some views. This module learns to predict the visibility of each joint, which is then used to weight the contributions of different views during the fusion process.
-
Multi-view Fusion: The 2D pose estimates from multiple camera views are then fused into a single 3D pose estimate. The fusion process considers the predicted joint visibilities to focus on the most reliable information and reconstruct the full 3D pose.
-
Training: The model is trained end-to-end using a combination of 2D and 3D pose supervision, as well as an occlusion prediction loss to improve the occlusion handling capabilities.
The researchers evaluate their approach on several benchmark datasets for 3D human pose estimation, including Human3.6M, MPI-INF-3DHP, and 3DPW. They show that their multi-view fusion method outperforms state-of-the-art single-view and multi-view 3D pose estimation techniques, demonstrating the benefits of their occlusion-aware fusion approach.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach for addressing the challenge of occlusions in 3D human pose estimation. The key strengths of the method are:
-
Occlusion Handling: The occlusion-aware module allows the system to identify and downweight the contributions of occluded joints, improving the overall 3D pose estimation accuracy.
-
Multi-view Fusion: Fusing information from multiple camera views helps to reconstruct the full 3D pose, even when parts of the body are occluded in some views.
-
Strong Empirical Results: The method outperforms state-of-the-art single-view and multi-view 3D pose estimation techniques on several benchmark datasets, demonstrating its practical utility.
However, the paper also has some potential limitations:
-
Requirement for Multiple Cameras: The method requires multiple camera views to be available, which may not always be the case in real-world applications.
-
Camera Calibration: Accurate camera calibration is crucial for the multi-view fusion to work effectively, which can be a complex and error-prone process.
-
Computational Complexity: Fusing information from multiple camera views may increase the computational complexity of the system, which could be a concern for real-time applications.
Future research could explore ways to address these limitations, such as investigating methods that can work with fewer cameras or exploring more efficient fusion techniques. Additionally, further experiments on more diverse and realistic datasets would help to better understand the method's performance in real-world settings.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel multi-view 3D human pose estimation method that effectively handles occlusions by fusing information from multiple camera views. The proposed approach outperforms state-of-the-art single-view and multi-view 3D pose estimation techniques, demonstrating the benefits of the occlusion-aware fusion process.
The research has important implications for applications that require robust and accurate 3D human pose estimation, such as human-robot collaboration, motion capture, and virtual/augmented reality. By addressing the challenge of occlusions, the method could enable more reliable and effective human-machine interactions in a wide range of real-world settings.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Multi-view Pose Fusion for Occlusion-Aware 3D Human Pose Estimation
Laura Bragagnolo, Matteo Terreran, Davide Allegro, Stefano Ghidoni
Robust 3D human pose estimation is crucial to ensure safe and effective human-robot collaboration. Accurate human perception,however, is particularly challenging in these scenarios due to strong occlusions and limited camera viewpoints. Current 3D human pose estimation approaches are rather vulnerable in such conditions. In this work we present a novel approach for robust 3D human pose estimation in the context of human-robot collaboration. Instead of relying on noisy 2D features triangulation, we perform multi-view fusion on 3D skeletons provided by absolute monocular methods. Accurate 3D pose estimation is then obtained via reprojection error optimization, introducing limbs length symmetry constraints. We evaluate our approach on the public dataset Human3.6M and on a novel version Human3.6M-Occluded, derived adding synthetic occlusions on the camera views with the purpose of testing pose estimation algorithms under severe occlusions. We further validate our method on real human-robot collaboration workcells, in which we strongly surpass current 3D human pose estimation methods. Our approach outperforms state-of-the-art multi-view human pose estimation techniques and demonstrates superior capabilities in handling challenging scenarios with strong occlusions, representing a reliable and effective solution for real human-robot collaboration setups.
Read more8/29/2024


0
Markerless Multi-view 3D Human Pose Estimation: a survey
Ana Filipa Rodrigues Nogueira, H'elder P. Oliveira, Lu'is F. Teixeira
3D human pose estimation aims to reconstruct the human skeleton of all the individuals in a scene by detecting several body joints. The creation of accurate and efficient methods is required for several real-world applications including animation, human-robot interaction, surveillance systems or sports, among many others. However, several obstacles such as occlusions, random camera perspectives, or the scarcity of 3D labelled data, have been hampering the models' performance and limiting their deployment in real-world scenarios. The higher availability of cameras has led researchers to explore multi-view solutions due to the advantage of being able to exploit different perspectives to reconstruct the pose. Thus, the goal of this survey is to present an overview of the methodologies used to estimate the 3D pose in multi-view settings, understand what were the strategies found to address the various challenges and also, identify their limitations. Based on the reviewed articles, it was possible to find that no method is yet capable of solving all the challenges associated with the reconstruction of the 3D pose. Due to the existing trade-off between complexity and performance, the best method depends on the application scenario. Therefore, further research is still required to develop an approach capable of quickly inferring a highly accurate 3D pose with bearable computation cost. To this goal, techniques such as active learning, methods that learn with a low level of supervision, the incorporation of temporal consistency, view selection, estimation of depth information and multi-modal approaches might be interesting strategies to keep in mind when developing a new methodology to solve this task.
Read more7/8/2024
📊

0
Multi-person 3D pose estimation from unlabelled data
Daniel Rodriguez-Criado, Pilar Bachiller, George Vogiatzis, Luis J. Manso
Its numerous applications make multi-human 3D pose estimation a remarkably impactful area of research. Nevertheless, assuming a multiple-view system composed of several regular RGB cameras, 3D multi-pose estimation presents several challenges. First of all, each person must be uniquely identified in the different views to separate the 2D information provided by the cameras. Secondly, the 3D pose estimation process from the multi-view 2D information of each person must be robust against noise and potential occlusions in the scenario. In this work, we address these two challenges with the help of deep learning. Specifically, we present a model based on Graph Neural Networks capable of predicting the cross-view correspondence of the people in the scenario along with a Multilayer Perceptron that takes the 2D points to yield the 3D poses of each person. These two models are trained in a self-supervised manner, thus avoiding the need for large datasets with 3D annotations.
Read more4/10/2024
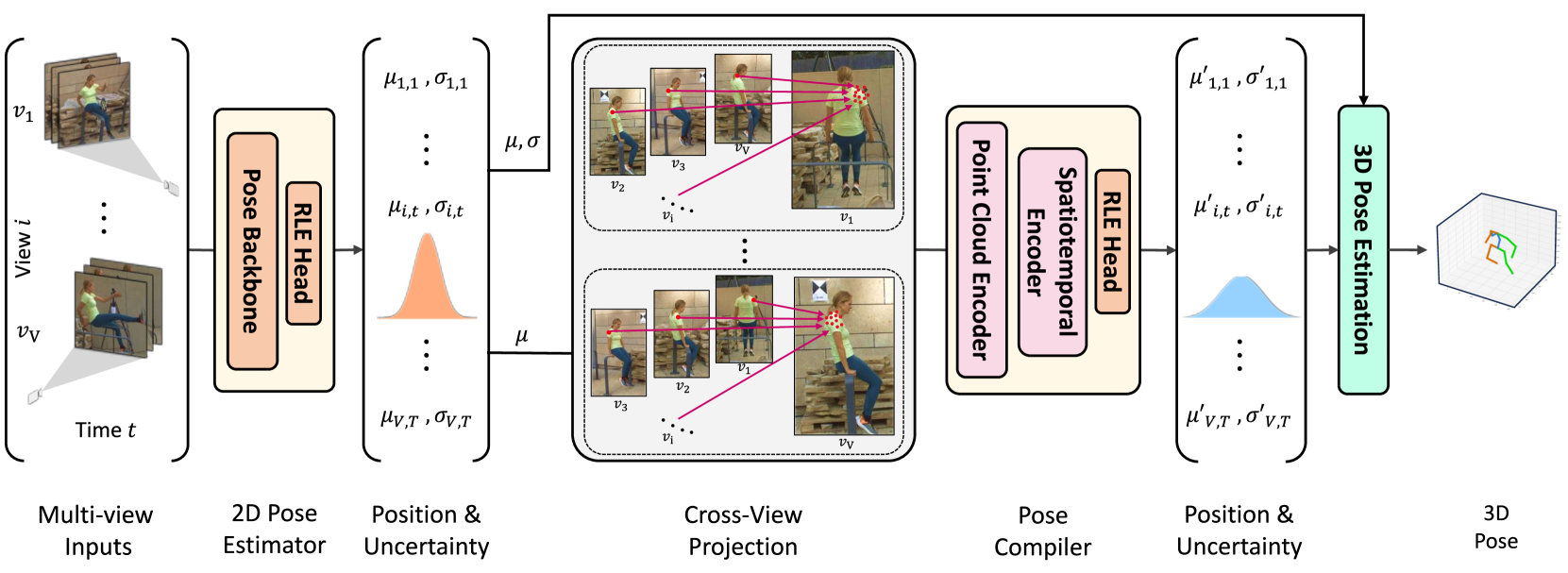

0
UPose3D: Uncertainty-Aware 3D Human Pose Estimation with Cross-View and Temporal Cues
Vandad Davoodnia, Saeed Ghorbani, Marc-Andr'e Carbonneau, Alexandre Messier, Ali Etemad
We introduce UPose3D, a novel approach for multi-view 3D human pose estimation, addressing challenges in accuracy and scalability. Our method advances existing pose estimation frameworks by improving robustness and flexibility without requiring direct 3D annotations. At the core of our method, a pose compiler module refines predictions from a 2D keypoints estimator that operates on a single image by leveraging temporal and cross-view information. Our novel cross-view fusion strategy is scalable to any number of cameras, while our synthetic data generation strategy ensures generalization across diverse actors, scenes, and viewpoints. Finally, UPose3D leverages the prediction uncertainty of both the 2D keypoint estimator and the pose compiler module. This provides robustness to outliers and noisy data, resulting in state-of-the-art performance in out-of-distribution settings. In addition, for in-distribution settings, UPose3D yields performance rivalling methods that rely on 3D annotated data while being the state-of-the-art among methods relying only on 2D supervision.
Read more7/11/2024