Markerless Multi-view 3D Human Pose Estimation: a survey

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper provides a comprehensive survey of markerless multi-view 3D human pose estimation, a field that aims to reconstruct the 3D body pose of people from multiple camera views without the use of markers or sensors attached to the body.
- The survey covers the key technical approaches, datasets, and evaluation metrics in this domain, as well as discussing the challenges and future directions.
- The paper is intended to serve as a reference for researchers and practitioners working on 3D human pose estimation from multi-view camera inputs.
Plain English Explanation
Markerless multi-view 3D human pose estimation is a technology that allows computers to understand the 3D body positions of people using multiple cameras, without requiring the people to wear any special sensors or markers. This is a challenging computer vision problem that has important applications in areas like animation, robotics, and sports analysis.
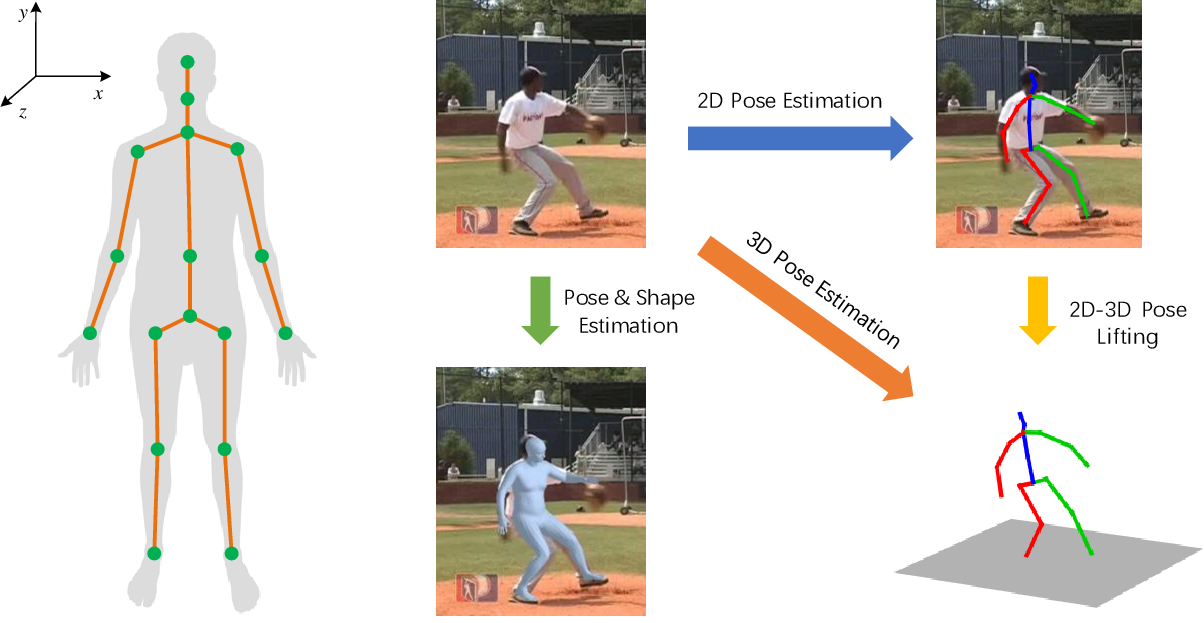
3D Human Pose Estimation from Multiple Cameras
The core idea is to use the visual information captured by multiple cameras surrounding a person to reconstruct their 3D body pose. By combining the different camera views, the system can overcome occlusions and infer the full 3D structure of the person's body, without needing the person to wear any special equipment.
Challenges in 3D Pose Estimation
Some key challenges include dealing with variations in clothing, body shape, lighting conditions, and camera viewpoints. The system also needs to be able to handle multiple people in the same scene and track their poses over time. Efficient algorithms are required to process the large amounts of visual data in real-time.
Advances in 3D Human Modeling and Pose Estimation
Recent progress in deep learning and computer vision has led to significant advancements in markerless 3D pose estimation. Techniques like SelfPose3D leverage self-supervised training and multi-view fusion to achieve accurate 3D pose reconstruction without the need for expensive motion capture data.
Technical Explanation
The paper begins by surveying previous literature reviews in the field of 3D human pose estimation, noting that this is the first comprehensive survey focused specifically on markerless multi-view approaches.
The core technical components covered include:
Data Acquisition
- Multi-view camera setups used to capture 3D human motion data
- Challenges in camera calibration, synchronization, and occlusion handling
3D Pose Estimation Approaches
- Model-based methods that fit parametric 3D body models to the camera observations
- Data-driven techniques that directly regress 3D pose from image inputs using deep neural networks
- Hybrid approaches combining model-based and data-driven elements
Evaluation and Benchmarking
- Standard datasets and evaluation metrics used to assess 3D pose estimation performance
- Discussions of the tradeoffs between accuracy, efficiency, and robustness
Emerging Trends
- Leveraging self-supervised learning to reduce reliance on expensive motion capture data
- Integrating 3D pose estimation with other computer vision tasks like 3D reconstruction and action recognition
Critical Analysis
The survey provides a thorough overview of the state-of-the-art in markerless multi-view 3D human pose estimation, highlighting the key technical advances and remaining challenges in the field.
One limitation noted is the heavy reliance on controlled laboratory settings in many of the existing datasets and benchmark evaluations. Expanding to more unconstrained, real-world environments would be an important next step to assess the practical applicability of these techniques.
Additionally, the paper suggests that further research is needed to improve the scalability and robustness of multi-view 3D pose estimation, particularly when dealing with large numbers of people, occlusions, and variations in clothing and lighting conditions.
Conclusion
This comprehensive survey provides a valuable reference for researchers and practitioners working on the problem of markerless multi-view 3D human pose estimation. By summarizing the key technical approaches, datasets, and evaluation metrics in the field, the paper serves as a useful starting point for understanding the current state-of-the-art and identifying promising directions for future work.
The continued advancement of this technology has important implications for a wide range of applications, from animation and virtual reality to sports analysis and human-robot interaction. As the authors note, addressing the remaining challenges in scaling, robustness, and real-world deployment will be crucial to unlocking the full potential of markerless multi-view 3D pose estimation.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Markerless Multi-view 3D Human Pose Estimation: a survey
Ana Filipa Rodrigues Nogueira, H'elder P. Oliveira, Lu'is F. Teixeira
3D human pose estimation aims to reconstruct the human skeleton of all the individuals in a scene by detecting several body joints. The creation of accurate and efficient methods is required for several real-world applications including animation, human-robot interaction, surveillance systems or sports, among many others. However, several obstacles such as occlusions, random camera perspectives, or the scarcity of 3D labelled data, have been hampering the models' performance and limiting their deployment in real-world scenarios. The higher availability of cameras has led researchers to explore multi-view solutions due to the advantage of being able to exploit different perspectives to reconstruct the pose. Thus, the goal of this survey is to present an overview of the methodologies used to estimate the 3D pose in multi-view settings, understand what were the strategies found to address the various challenges and also, identify their limitations. Based on the reviewed articles, it was possible to find that no method is yet capable of solving all the challenges associated with the reconstruction of the 3D pose. Due to the existing trade-off between complexity and performance, the best method depends on the application scenario. Therefore, further research is still required to develop an approach capable of quickly inferring a highly accurate 3D pose with bearable computation cost. To this goal, techniques such as active learning, methods that learn with a low level of supervision, the incorporation of temporal consistency, view selection, estimation of depth information and multi-modal approaches might be interesting strategies to keep in mind when developing a new methodology to solve this task.
Read more7/8/2024
📊

0
Multi-person 3D pose estimation from unlabelled data
Daniel Rodriguez-Criado, Pilar Bachiller, George Vogiatzis, Luis J. Manso
Its numerous applications make multi-human 3D pose estimation a remarkably impactful area of research. Nevertheless, assuming a multiple-view system composed of several regular RGB cameras, 3D multi-pose estimation presents several challenges. First of all, each person must be uniquely identified in the different views to separate the 2D information provided by the cameras. Secondly, the 3D pose estimation process from the multi-view 2D information of each person must be robust against noise and potential occlusions in the scenario. In this work, we address these two challenges with the help of deep learning. Specifically, we present a model based on Graph Neural Networks capable of predicting the cross-view correspondence of the people in the scenario along with a Multilayer Perceptron that takes the 2D points to yield the 3D poses of each person. These two models are trained in a self-supervised manner, thus avoiding the need for large datasets with 3D annotations.
Read more4/10/2024


0
Multi-view Pose Fusion for Occlusion-Aware 3D Human Pose Estimation
Laura Bragagnolo, Matteo Terreran, Davide Allegro, Stefano Ghidoni
Robust 3D human pose estimation is crucial to ensure safe and effective human-robot collaboration. Accurate human perception,however, is particularly challenging in these scenarios due to strong occlusions and limited camera viewpoints. Current 3D human pose estimation approaches are rather vulnerable in such conditions. In this work we present a novel approach for robust 3D human pose estimation in the context of human-robot collaboration. Instead of relying on noisy 2D features triangulation, we perform multi-view fusion on 3D skeletons provided by absolute monocular methods. Accurate 3D pose estimation is then obtained via reprojection error optimization, introducing limbs length symmetry constraints. We evaluate our approach on the public dataset Human3.6M and on a novel version Human3.6M-Occluded, derived adding synthetic occlusions on the camera views with the purpose of testing pose estimation algorithms under severe occlusions. We further validate our method on real human-robot collaboration workcells, in which we strongly surpass current 3D human pose estimation methods. Our approach outperforms state-of-the-art multi-view human pose estimation techniques and demonstrates superior capabilities in handling challenging scenarios with strong occlusions, representing a reliable and effective solution for real human-robot collaboration setups.
Read more8/29/2024

0
A Survey on 3D Egocentric Human Pose Estimation
Md Mushfiqur Azam, Kevin Desai
Egocentric human pose estimation aims to estimate human body poses and develop body representations from a first-person camera perspective. It has gained vast popularity in recent years because of its wide range of applications in sectors like XR-technologies, human-computer interaction, and fitness tracking. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no systematic literature review based on the proposed solutions regarding egocentric 3D human pose estimation. To that end, the aim of this survey paper is to provide an extensive overview of the current state of egocentric pose estimation research. In this paper, we categorize and discuss the popular datasets and the different pose estimation models, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of different methods by comparative analysis. This survey can be a valuable resource for both researchers and practitioners in the field, offering insights into key concepts and cutting-edge solutions in egocentric pose estimation, its wide-ranging applications, as well as the open problems with future scope.
Read more4/19/2024