OneTo3D: One Image to Re-editable Dynamic 3D Model and Video Generation

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
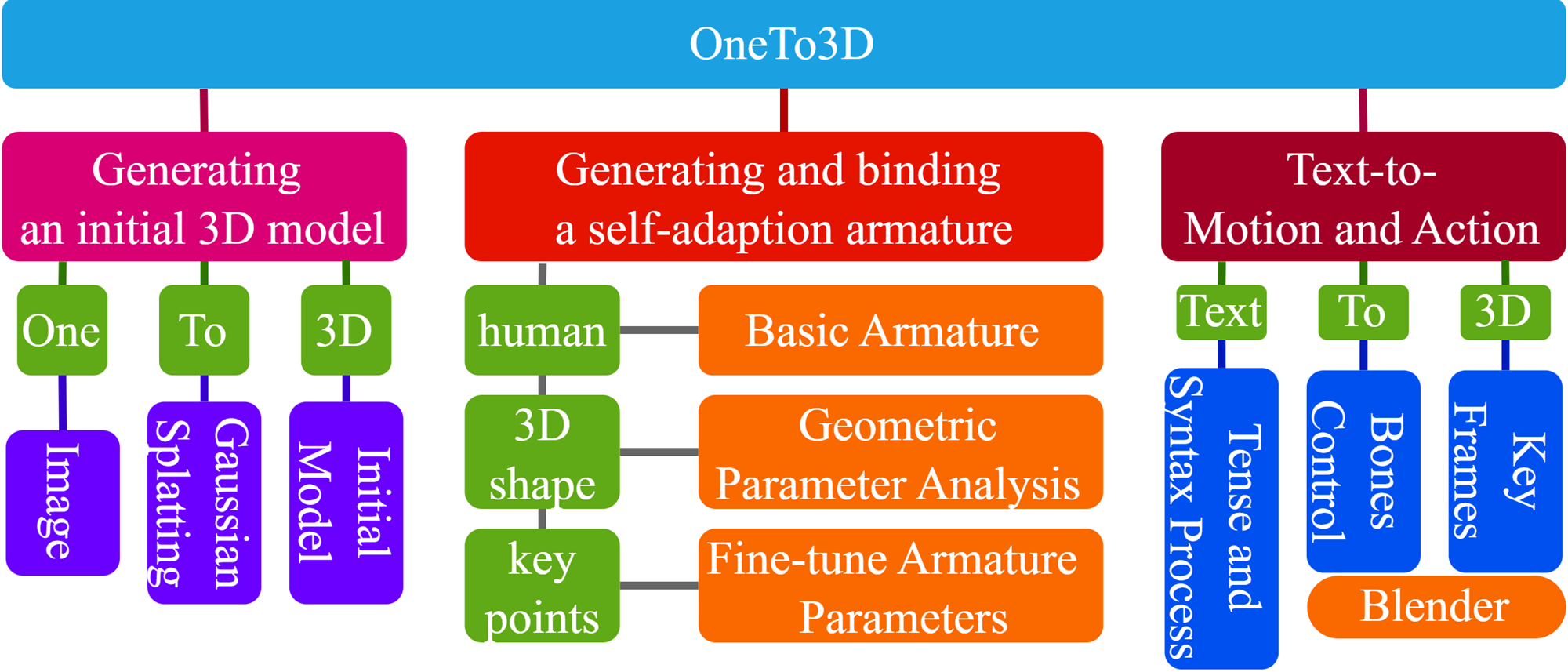
- This paper presents a novel system called "OneTo3D" that can generate a re-editable and dynamic 3D model and video from a single input image.
- The system uses a self-adapting armature approach to create a 3D model that can be manipulated and animated, addressing the challenge of creating high-quality 3D content from limited input data.
- The generated 3D model can be further edited and used to produce dynamic videos, automating the content creation process.
Plain English Explanation
The paper introduces a system called "OneTo3D" that can take a single image as input and generate a 3D model and video from it. This is a significant advancement, as typically creating 3D models and animations requires extensive manual work and expertise.
The key innovation in OneTo3D is its "self-adapting armature" approach. This means the system can automatically generate a 3D model that can be edited and animated, without the user having to painstakingly model every detail. The 3D model is created in a way that allows for further manipulation and animation, making the content creation process more efficient and accessible.
Once the 3D model is generated, the system can also use it to automatically produce dynamic videos. This means the user doesn't have to separately create the video - the system can generate it directly from the 3D model.
Overall, OneTo3D aims to streamline the process of creating high-quality 3D content and animations from limited input data, making content creation more accessible and automated.
Technical Explanation
The core of the OneTo3D system is its self-adapting armature approach to generating 3D models from a single image. Interactive3D: Create What You Want by Interactive and DreamScene360: Unconstrained Text-to-3D Scene Generation have demonstrated the potential of using armatures to create manipulable 3D content, but OneTo3D advances this by automating the process.
The system first extracts a semantic segmentation of the input image, which allows it to identify the different objects and parts. It then applies a deformable Dig3D: Marrying Gaussian Splatting & Deformable Transformer for Single-view 3D Reconstruction network to generate an initial 3D mesh.
Next, the system adds a self-adapting armature to the 3D mesh, which acts as a skeletal structure that can be used to edit and animate the model. This armature is generated automatically based on the semantic segmentation, without requiring manual rigging or posing.
Finally, the system uses the 3D model and armature to generate a dynamic video, demonstrating the model's re-editability and animation capabilities. This video generation process is inspired by Guess Unseen: Dynamic 3D Scene Reconstruction from a Single Image.
Critical Analysis
The authors demonstrate the effectiveness of the OneTo3D system through extensive experiments, showing its ability to generate high-quality 3D models and videos from single input images. However, the paper does not fully address the limitations of the approach.
One potential concern is the reliance on semantic segmentation, which could introduce errors if the segmentation is not accurate. Additionally, the self-adapting armature approach, while innovative, may struggle with complex or articulated 3D shapes that do not fit well with the automatically generated armature structure.
Further research could explore ways to make the system more robust to segmentation errors, as well as investigate methods for generating more flexible and adaptive armature structures to handle a wider range of 3D shapes and scenes.
Conclusion
The OneTo3D system represents a significant advancement in the field of content creation, demonstrating the ability to generate re-editable and dynamic 3D models and videos from a single input image. By automating the 3D modeling and animation process, the system has the potential to make high-quality 3D content more accessible and streamline the content creation workflow.
While the current approach has some limitations, the core ideas behind OneTo3D, such as the self-adapting armature and automated video generation, could inspire further research and development in this area. As the capabilities of AI-powered content creation tools continue to evolve, systems like OneTo3D may play an increasingly important role in democratizing 3D modeling and animation.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
OneTo3D: One Image to Re-editable Dynamic 3D Model and Video Generation
Jinwei Lin
One image to editable dynamic 3D model and video generation is novel direction and change in the research area of single image to 3D representation or 3D reconstruction of image. Gaussian Splatting has demonstrated its advantages in implicit 3D reconstruction, compared with the original Neural Radiance Fields. As the rapid development of technologies and principles, people tried to used the Stable Diffusion models to generate targeted models with text instructions. However, using the normal implicit machine learning methods is hard to gain the precise motions and actions control, further more, it is difficult to generate a long content and semantic continuous 3D video. To address this issue, we propose the OneTo3D, a method and theory to used one single image to generate the editable 3D model and generate the targeted semantic continuous time-unlimited 3D video. We used a normal basic Gaussian Splatting model to generate the 3D model from a single image, which requires less volume of video memory and computer calculation ability. Subsequently, we designed an automatic generation and self-adaptive binding mechanism for the object armature. Combined with the re-editable motions and actions analyzing and controlling algorithm we proposed, we can achieve a better performance than the SOTA projects in the area of building the 3D model precise motions and actions control, and generating a stable semantic continuous time-unlimited 3D video with the input text instructions. Here we will analyze the detailed implementation methods and theories analyses. Relative comparisons and conclusions will be presented. The project code is open source.
Read more5/13/2024


0
3D Gaussian Editing with A Single Image
Guan Luo, Tian-Xing Xu, Ying-Tian Liu, Xiao-Xiong Fan, Fang-Lue Zhang, Song-Hai Zhang
The modeling and manipulation of 3D scenes captured from the real world are pivotal in various applications, attracting growing research interest. While previous works on editing have achieved interesting results through manipulating 3D meshes, they often require accurately reconstructed meshes to perform editing, which limits their application in 3D content generation. To address this gap, we introduce a novel single-image-driven 3D scene editing approach based on 3D Gaussian Splatting, enabling intuitive manipulation via directly editing the content on a 2D image plane. Our method learns to optimize the 3D Gaussians to align with an edited version of the image rendered from a user-specified viewpoint of the original scene. To capture long-range object deformation, we introduce positional loss into the optimization process of 3D Gaussian Splatting and enable gradient propagation through reparameterization. To handle occluded 3D Gaussians when rendering from the specified viewpoint, we build an anchor-based structure and employ a coarse-to-fine optimization strategy capable of handling long-range deformation while maintaining structural stability. Furthermore, we design a novel masking strategy to adaptively identify non-rigid deformation regions for fine-scale modeling. Extensive experiments show the effectiveness of our method in handling geometric details, long-range, and non-rigid deformation, demonstrating superior editing flexibility and quality compared to previous approaches.
Read more8/15/2024


0
Hi3D: Pursuing High-Resolution Image-to-3D Generation with Video Diffusion Models
Haibo Yang, Yang Chen, Yingwei Pan, Ting Yao, Zhineng Chen, Chong-Wah Ngo, Tao Mei
Despite having tremendous progress in image-to-3D generation, existing methods still struggle to produce multi-view consistent images with high-resolution textures in detail, especially in the paradigm of 2D diffusion that lacks 3D awareness. In this work, we present High-resolution Image-to-3D model (Hi3D), a new video diffusion based paradigm that redefines a single image to multi-view images as 3D-aware sequential image generation (i.e., orbital video generation). This methodology delves into the underlying temporal consistency knowledge in video diffusion model that generalizes well to geometry consistency across multiple views in 3D generation. Technically, Hi3D first empowers the pre-trained video diffusion model with 3D-aware prior (camera pose condition), yielding multi-view images with low-resolution texture details. A 3D-aware video-to-video refiner is learnt to further scale up the multi-view images with high-resolution texture details. Such high-resolution multi-view images are further augmented with novel views through 3D Gaussian Splatting, which are finally leveraged to obtain high-fidelity meshes via 3D reconstruction. Extensive experiments on both novel view synthesis and single view reconstruction demonstrate that our Hi3D manages to produce superior multi-view consistency images with highly-detailed textures. Source code and data are available at url{https://github.com/yanghb22-fdu/Hi3D-Official}.
Read more9/12/2024


0
Unique3D: High-Quality and Efficient 3D Mesh Generation from a Single Image
Kailu Wu, Fangfu Liu, Zhihan Cai, Runjie Yan, Hanyang Wang, Yating Hu, Yueqi Duan, Kaisheng Ma
In this work, we introduce Unique3D, a novel image-to-3D framework for efficiently generating high-quality 3D meshes from single-view images, featuring state-of-the-art generation fidelity and strong generalizability. Previous methods based on Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) can produce diversified 3D results by distilling 3D knowledge from large 2D diffusion models, but they usually suffer from long per-case optimization time with inconsistent issues. Recent works address the problem and generate better 3D results either by finetuning a multi-view diffusion model or training a fast feed-forward model. However, they still lack intricate textures and complex geometries due to inconsistency and limited generated resolution. To simultaneously achieve high fidelity, consistency, and efficiency in single image-to-3D, we propose a novel framework Unique3D that includes a multi-view diffusion model with a corresponding normal diffusion model to generate multi-view images with their normal maps, a multi-level upscale process to progressively improve the resolution of generated orthographic multi-views, as well as an instant and consistent mesh reconstruction algorithm called ISOMER, which fully integrates the color and geometric priors into mesh results. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our Unique3D significantly outperforms other image-to-3D baselines in terms of geometric and textural details.
Read more6/14/2024