Reinforcement Learning from Delayed Observations via World Models
2403.12309

0
0
Abstract
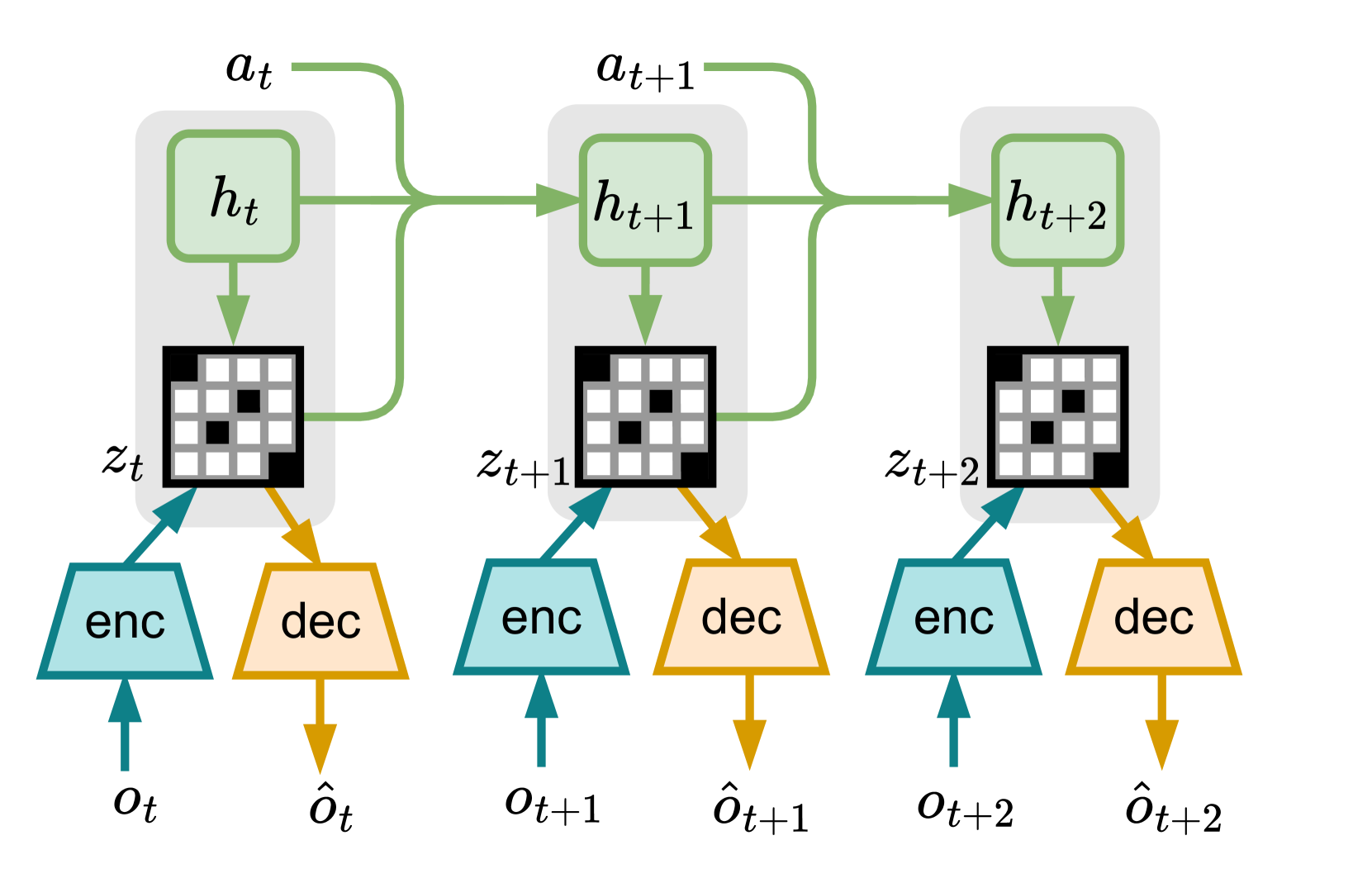
In standard reinforcement learning settings, agents typically assume immediate feedback about the effects of their actions after taking them. However, in practice, this assumption may not hold true due to physical constraints and can significantly impact the performance of learning algorithms. In this paper, we address observation delays in partially observable environments. We propose leveraging world models, which have shown success in integrating past observations and learning dynamics, to handle observation delays. By reducing delayed POMDPs to delayed MDPs with world models, our methods can effectively handle partial observability, where existing approaches achieve sub-optimal performance or degrade quickly as observability decreases. Experiments suggest that one of our methods can outperform a naive model-based approach by up to 250%. Moreover, we evaluate our methods on visual delayed environments, for the first time showcasing delay-aware reinforcement learning continuous control with visual observations.
Create account to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🏅
Provable Representation with Efficient Planning for Partial Observable Reinforcement Learning
Hongming Zhang, Tongzheng Ren, Chenjun Xiao, Dale Schuurmans, Bo Dai

0
0
In most real-world reinforcement learning applications, state information is only partially observable, which breaks the Markov decision process assumption and leads to inferior performance for algorithms that conflate observations with state. Partially Observable Markov Decision Processes (POMDPs), on the other hand, provide a general framework that allows for partial observability to be accounted for in learning, exploration and planning, but presents significant computational and statistical challenges. To address these difficulties, we develop a representation-based perspective that leads to a coherent framework and tractable algorithmic approach for practical reinforcement learning from partial observations. We provide a theoretical analysis for justifying the statistical efficiency of the proposed algorithm, and also empirically demonstrate the proposed algorithm can surpass state-of-the-art performance with partial observations across various benchmarks, advancing reliable reinforcement learning towards more practical applications.
6/12/2024
❗
Informed POMDP: Leveraging Additional Information in Model-Based RL
Gaspard Lambrechts, Adrien Bolland, Damien Ernst

0
0
In this work, we generalize the problem of learning through interaction in a POMDP by accounting for eventual additional information available at training time. First, we introduce the informed POMDP, a new learning paradigm offering a clear distinction between the information at training and the observation at execution. Next, we propose an objective that leverages this information for learning a sufficient statistic of the history for the optimal control. We then adapt this informed objective to learn a world model able to sample latent trajectories. Finally, we empirically show a learning speed improvement in several environments using this informed world model in the Dreamer algorithm. These results and the simplicity of the proposed adaptation advocate for a systematic consideration of eventual additional information when learning in a POMDP using model-based RL.
6/13/2024
🌀
Efficient Imitation Learning with Conservative World Models
Victor Kolev, Rafael Rafailov, Kyle Hatch, Jiajun Wu, Chelsea Finn

0
0
We tackle the problem of policy learning from expert demonstrations without a reward function. A central challenge in this space is that these policies fail upon deployment due to issues of distributional shift, environment stochasticity, or compounding errors. Adversarial imitation learning alleviates this issue but requires additional on-policy training samples for stability, which presents a challenge in realistic domains due to inefficient learning and high sample complexity. One approach to this issue is to learn a world model of the environment, and use synthetic data for policy training. While successful in prior works, we argue that this is sub-optimal due to additional distribution shifts between the learned model and the real environment. Instead, we re-frame imitation learning as a fine-tuning problem, rather than a pure reinforcement learning one. Drawing theoretical connections to offline RL and fine-tuning algorithms, we argue that standard online world model algorithms are not well suited to the imitation learning problem. We derive a principled conservative optimization bound and demonstrate empirically that it leads to improved performance on two very challenging manipulation environments from high-dimensional raw pixel observations. We set a new state-of-the-art performance on the Franka Kitchen environment from images, requiring only 10 demos on no reward labels, as well as solving a complex dexterity manipulation task.
5/24/2024
🛠️
Variational Delayed Policy Optimization
Qingyuan Wu, Simon Sinong Zhan, Yixuan Wang, Yuhui Wang, Chung-Wei Lin, Chen Lv, Qi Zhu, Chao Huang

0
0
In environments with delayed observation, state augmentation by including actions within the delay window is adopted to retrieve Markovian property to enable reinforcement learning (RL). However, state-of-the-art (SOTA) RL techniques with Temporal-Difference (TD) learning frameworks often suffer from learning inefficiency, due to the significant expansion of the augmented state space with the delay. To improve learning efficiency without sacrificing performance, this work introduces a novel framework called Variational Delayed Policy Optimization (VDPO), which reformulates delayed RL as a variational inference problem. This problem is further modelled as a two-step iterative optimization problem, where the first step is TD learning in the delay-free environment with a small state space, and the second step is behaviour cloning which can be addressed much more efficiently than TD learning. We not only provide a theoretical analysis of VDPO in terms of sample complexity and performance, but also empirically demonstrate that VDPO can achieve consistent performance with SOTA methods, with a significant enhancement of sample efficiency (approximately 50% less amount of samples) in the MuJoCo benchmark.
5/24/2024