Responsible Adoption of Generative AI in Higher Education: Developing a Points to Consider Approach Based on Faculty Perspectives

0
🤖
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper proposes a framework for the responsible adoption of generative AI in higher education, taking into account the unique goals, values, and structural features of universities.
- The research was based on a collaborative, interdisciplinary process at the University of Pittsburgh that gathered perspectives on the use of generative AI in higher education.
- The paper presents insights on the benefits, risks, and barriers to adoption of generative AI, culminating in six "points to consider" for governing its use in higher education.
Plain English Explanation
The paper argues that the traditional structure and values of universities, such as collaborative faculty governance and academic freedom, conflict with the more centralized, top-down approaches to governing AI that are common in the private sector. To address this, the researchers at the University of Pittsburgh organized a collaborative effort to gather diverse perspectives on the use of generative AI in higher education.
Through this process, the researchers identified both the potential benefits and risks of using generative AI in universities, as well as the barriers to its adoption. Based on these insights, the paper proposes a "points to consider" approach to help higher education institutions thoughtfully integrate generative AI in a way that aligns with their unique values and goals.
Technical Explanation
The researchers at the University of Pittsburgh conducted a semester-long collaborative effort to gather and organize perspectives on the use of generative AI in higher education. This included recurring group discussions, three standalone focus groups, and an informal survey.
From this process, the researchers identified several key insights:
- The potential benefits of using generative AI in higher education, such as enhancing research and improving pedagogy
- The potential risks, such as academic integrity concerns and issues of bias and fairness
- Barriers to adoption, including concerns about faculty autonomy and the need for robust training and support
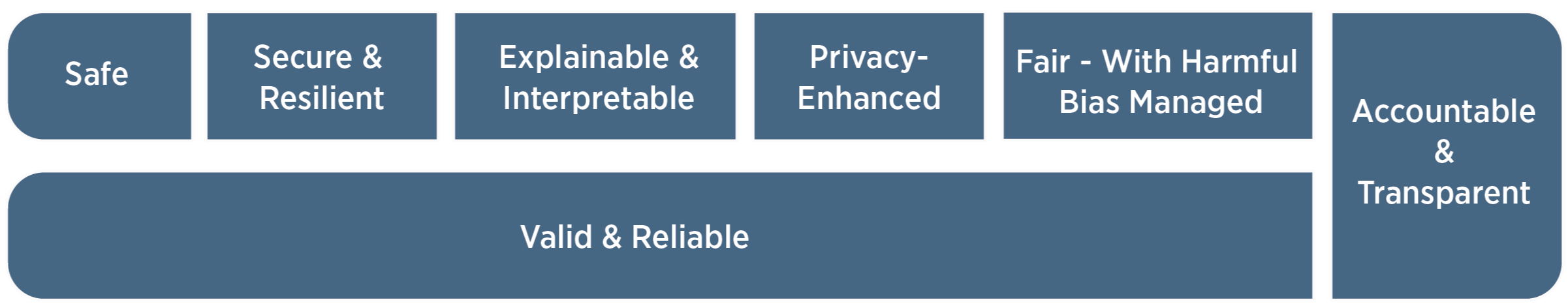
Based on these insights, the paper proposes a "points to consider" framework for the responsible integration of generative AI in higher education. This framework outlines six normative considerations that institutions should weigh, such as aligning AI use with educational goals, ensuring transparency and accountability, and protecting academic freedom.
Critical Analysis
The paper acknowledges several limitations of the research, including the relatively small scale of the study and the need for further investigation into the specific implications of generative AI across different disciplines and institutional contexts.
One area that could be explored further is the potential impact of generative AI on student learning and assessment. The paper briefly mentions concerns about academic integrity, but does not delve deeply into how generative AI could transform the ways students engage with course material and demonstrate their knowledge.
Additionally, while the paper highlights the importance of aligning the use of generative AI with the values and goals of higher education, it could be strengthened by a more thorough examination of the potential tensions and tradeoffs involved in this process. For example, how might institutions balance the desire for academic freedom with the need for effective governance and oversight of AI systems?
Overall, the paper provides a valuable starting point for higher education institutions to consider the responsible integration of generative AI. However, continued research and discussion will be necessary to fully address the complex challenges and opportunities presented by this emerging technology.
Conclusion
This paper proposes a thoughtful approach to the responsible adoption of generative AI in higher education, drawing on insights from a collaborative effort at the University of Pittsburgh. By accounting for the unique goals, values, and structural features of universities, the "points to consider" framework outlined in the paper can help guide institutions as they navigate the integration of this powerful technology in a way that aligns with their academic mission and principles. As generative AI continues to evolve, this research serves as an important step towards ensuring that its implementation in higher education is both innovative and ethically grounded.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🤖

0
Responsible Adoption of Generative AI in Higher Education: Developing a Points to Consider Approach Based on Faculty Perspectives
Ravit Dotan, Lisa S. Parker, John G. Radzilowicz
This paper proposes an approach to the responsible adoption of generative AI in higher education, employing a ''points to consider'' approach that is sensitive to the goals, values, and structural features of higher education. Higher education's ethos of collaborative faculty governance, pedagogical and research goals, and embrace of academic freedom conflict, the paper argues, with centralized top down approaches to governing AI that are common in the private sector. The paper is based on a semester long effort at the University of Pittsburgh which gathered and organized perspectives on generative AI in higher education through a collaborative, iterative, interdisciplinary process that included recurring group discussions, three standalone focus groups, and an informal survey. The paper presents insights drawn from this effort that give rise to the ''points to consider'' approach the paper develops. These insights include the benefits and risks of potential uses of generative AI In higher education, as well as barriers to its adoption, and culminate in the six normative points to consider when adopting and governing generative AI in institutions of higher education.
Read more6/5/2024


0
Generative AI in Higher Education: A Global Perspective of Institutional Adoption Policies and Guidelines
Yueqiao Jin, Lixiang Yan, Vanessa Echeverria, Dragan Gav{s}evi'c, Roberto Martinez-Maldonado
Integrating generative AI (GAI) into higher education is crucial for preparing a future generation of GAI-literate students. Yet a thorough understanding of the global institutional adoption policy remains absent, with most of the prior studies focused on the Global North and the promises and challenges of GAI, lacking a theoretical lens. This study utilizes the Diffusion of Innovations Theory to examine GAI adoption strategies in higher education across 40 universities from six global regions. It explores the characteristics of GAI innovation, including compatibility, trialability, and observability, and analyses the communication channels and roles and responsibilities outlined in university policies and guidelines. The findings reveal a proactive approach by universities towards GAI integration, emphasizing academic integrity, teaching and learning enhancement, and equity. Despite a cautious yet optimistic stance, a comprehensive policy framework is needed to evaluate the impacts of GAI integration and establish effective communication strategies that foster broader stakeholder engagement. The study highlights the importance of clear roles and responsibilities among faculty, students, and administrators for successful GAI integration, supporting a collaborative model for navigating the complexities of GAI in education. This study contributes insights for policymakers in crafting detailed strategies for its integration.
Read more5/21/2024

0
AI Governance in Higher Education: Case Studies of Guidance at Big Ten Universities
Chuhao Wu, He Zhang, John M. Carroll
Generative AI has drawn significant attention from stakeholders in higher education. As it introduces new opportunities for personalized learning and tutoring support, it simultaneously poses challenges to academic integrity and leads to ethical issues. Consequently, governing responsible AI usage within higher education institutions (HEIs) becomes increasingly important. Leading universities have already published guidelines on Generative AI, with most attempting to embrace this technology responsibly. This study provides a new perspective by focusing on strategies for responsible AI governance as demonstrated in these guidelines. Through a case study of 14 prestigious universities in the United States, we identified the multi-unit governance of AI, the role-specific governance of AI, and the academic characteristics of AI governance from their AI guidelines. The strengths and potential limitations of these strategies and characteristics are discussed. The findings offer practical implications for guiding responsible AI usage in HEIs and beyond.
Read more9/4/2024


0
A University Framework for the Responsible use of Generative AI in Research
Shannon Smith, Melissa Tate, Keri Freeman, Anne Walsh, Brian Ballsun-Stanton, Mark Hooper, Murray Lane
Generative Artificial Intelligence (generative AI) poses both opportunities and risks for the integrity of research. Universities must guide researchers in using generative AI responsibly, and in navigating a complex regulatory landscape subject to rapid change. By drawing on the experiences of two Australian universities, we propose a framework to help institutions promote and facilitate the responsible use of generative AI. We provide guidance to help distil the diverse regulatory environment into a principles-based position statement. Further, we explain how a position statement can then serve as a foundation for initiatives in training, communications, infrastructure, and process change. Despite the growing body of literature about AI's impact on academic integrity for undergraduate students, there has been comparatively little attention on the impacts of generative AI for research integrity, and the vital role of institutions in helping to address those challenges. This paper underscores the urgency for research institutions to take action in this area and suggests a practical and adaptable framework for so doing.
Read more5/1/2024