A Survey of Embodied Learning for Object-Centric Robotic Manipulation

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper provides a comprehensive survey of embodied learning approaches for object-centric robotic manipulation.
- It covers key research areas such as pose estimation, affordance learning, policy learning, reinforcement learning, and imitation learning.
- The paper discusses how multimodal large language models (LLMs) can be leveraged to enable more natural and intuitive robotic control.
Plain English Explanation
This paper reviews different ways that robots can learn to manipulate objects through embodied learning. Pose estimation helps robots understand the position and orientation of objects. Affordance learning teaches robots how objects can be used. Policy learning and reinforcement learning allow robots to learn manipulation skills through trial-and-error. Imitation learning enables robots to learn by observing human demonstrations.
The paper also discusses how multimodal large language models (LLMs) could make it easier for humans to control and communicate with robots in a more natural way.
Technical Explanation
The paper provides a comprehensive survey of embodied learning approaches for object-centric robotic manipulation. It covers key research areas such as pose estimation, affordance learning, policy learning, reinforcement learning, and imitation learning.
The paper also discusses how multimodal large language models (LLMs) can be leveraged to enable more natural and intuitive robotic control.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough overview of the state-of-the-art in embodied learning for robotic manipulation, but does not delve deeply into the limitations or potential issues with the various approaches discussed.
For example, the paper does not address the challenges of affordance learning in unstructured environments or the sample inefficiency of reinforcement learning methods.
Additionally, while the potential of multimodal LLMs for robotic control is highlighted, the paper does not discuss the limitations of current language models or the challenges of grounding their outputs in physical actions.
Conclusion
This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the state-of-the-art in embodied learning for object-centric robotic manipulation. It covers key research areas and discusses the potential of multimodal large language models to enable more natural and intuitive robotic control. While the paper does not delve deeply into the limitations of the various approaches, it serves as a valuable resource for understanding the current landscape of embodied learning for robotics.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
A Survey of Embodied Learning for Object-Centric Robotic Manipulation
Ying Zheng, Lei Yao, Yuejiao Su, Yi Zhang, Yi Wang, Sicheng Zhao, Yiyi Zhang, Lap-Pui Chau
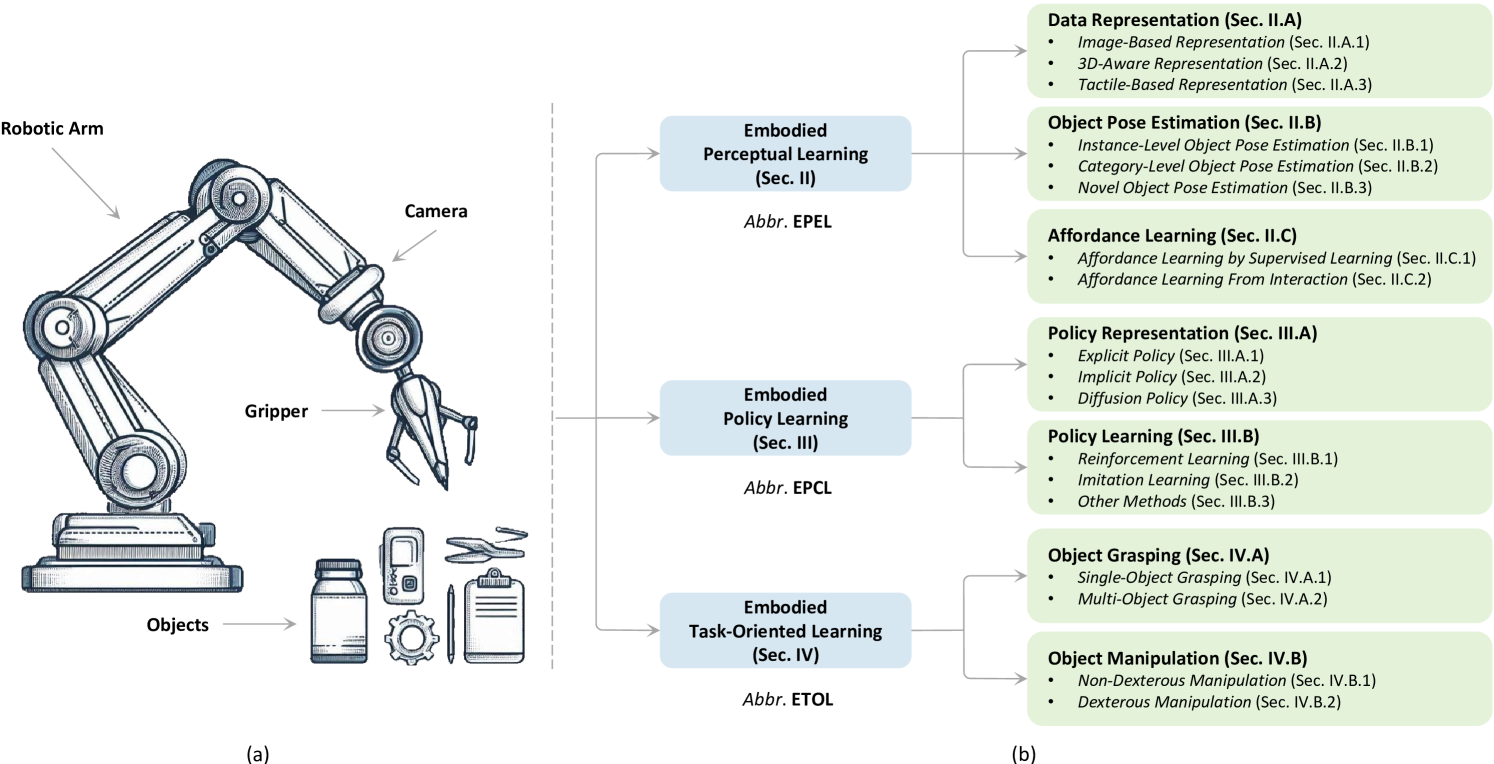
Embodied learning for object-centric robotic manipulation is a rapidly developing and challenging area in embodied AI. It is crucial for advancing next-generation intelligent robots and has garnered significant interest recently. Unlike data-driven machine learning methods, embodied learning focuses on robot learning through physical interaction with the environment and perceptual feedback, making it especially suitable for robotic manipulation. In this paper, we provide a comprehensive survey of the latest advancements in this field and categorize the existing work into three main branches: 1) Embodied perceptual learning, which aims to predict object pose and affordance through various data representations; 2) Embodied policy learning, which focuses on generating optimal robotic decisions using methods such as reinforcement learning and imitation learning; 3) Embodied task-oriented learning, designed to optimize the robot's performance based on the characteristics of different tasks in object grasping and manipulation. In addition, we offer an overview and discussion of public datasets, evaluation metrics, representative applications, current challenges, and potential future research directions. A project associated with this survey has been established at https://github.com/RayYoh/OCRM_survey.
Read more8/22/2024


0
Aligning Cyber Space with Physical World: A Comprehensive Survey on Embodied AI
Yang Liu, Weixing Chen, Yongjie Bai, Guanbin Li, Wen Gao, Liang Lin
Embodied Artificial Intelligence (Embodied AI) is crucial for achieving Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and serves as a foundation for various applications that bridge cyberspace and the physical world. Recently, the emergence of Multi-modal Large Models (MLMs) and World Models (WMs) have attracted significant attention due to their remarkable perception, interaction, and reasoning capabilities, making them a promising architecture for the brain of embodied agents. However, there is no comprehensive survey for Embodied AI in the era of MLMs. In this survey, we give a comprehensive exploration of the latest advancements in Embodied AI. Our analysis firstly navigates through the forefront of representative works of embodied robots and simulators, to fully understand the research focuses and their limitations. Then, we analyze four main research targets: 1) embodied perception, 2) embodied interaction, 3) embodied agent, and 4) sim-to-real adaptation, covering the state-of-the-art methods, essential paradigms, and comprehensive datasets. Additionally, we explore the complexities of MLMs in virtual and real embodied agents, highlighting their significance in facilitating interactions in dynamic digital and physical environments. Finally, we summarize the challenges and limitations of embodied AI and discuss their potential future directions. We hope this survey will serve as a foundational reference for the research community and inspire continued innovation. The associated project can be found at https://github.com/HCPLab-SYSU/Embodied_AI_Paper_List.
Read more7/23/2024
🖼️

0
Closed Loop Interactive Embodied Reasoning for Robot Manipulation
Michal Nazarczuk, Jan Kristof Behrens, Karla Stepanova, Matej Hoffmann, Krystian Mikolajczyk
Embodied reasoning systems integrate robotic hardware and cognitive processes to perform complex tasks typically in response to a natural language query about a specific physical environment. This usually involves changing the belief about the scene or physically interacting and changing the scene (e.g. 'Sort the objects from lightest to heaviest'). In order to facilitate the development of such systems we introduce a new simulating environment that makes use of MuJoCo physics engine and high-quality renderer Blender to provide realistic visual observations that are also accurate to the physical state of the scene. Together with the simulator we propose a new benchmark composed of 10 classes of multi-step reasoning scenarios that require simultaneous visual and physical measurements. Finally, we develop a new modular Closed Loop Interactive Reasoning (CLIER) approach that takes into account the measurements of non-visual object properties, changes in the scene caused by external disturbances as well as uncertain outcomes of robotic actions. We extensively evaluate our reasoning approach in simulation and in the real world manipulation tasks with a success rate above 76% and 64%, respectively.
Read more4/24/2024


0
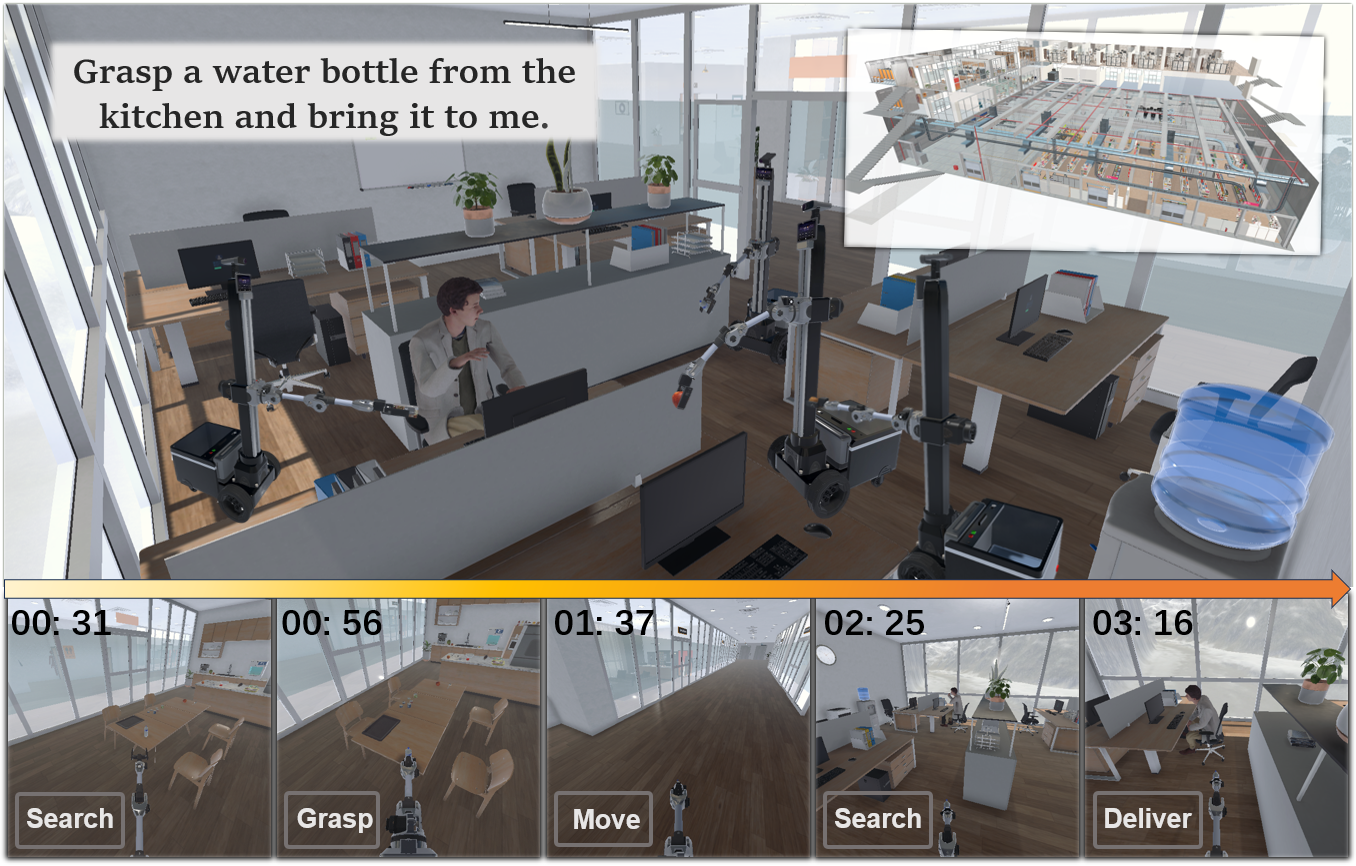
Human-centered In-building Embodied Delivery Benchmark
Zhuoqun Xu, Yang Liu, Xiaoqi Li, Jiyao Zhang, Hao Dong
Recently, the concept of embodied intelligence has been widely accepted and popularized, leading people to naturally consider the potential for commercialization in this field. In this work, we propose a specific commercial scenario simulation, human-centered in-building embodied delivery. Furthermore, for this scenario, we have developed a brand-new virtual environment system from scratch, constructing a multi-level connected building space modeled after a polar research station. This environment also includes autonomous human characters and robots with grasping and mobility capabilities, as well as a large number of interactive items. Based on this environment, we have built a delivery dataset containing 13k language instructions to guide robots in providing services. We simulate human behavior through human characters and sample their various needs in daily life. Finally, we proposed a method centered around a large multimodal model to serve as the baseline system for this dataset. Compared to past embodied data work, our work focuses on a virtual environment centered around human-robot interaction for commercial scenarios. We believe this will bring new perspectives and exploration angles to the embodied community.
Read more6/27/2024