Symbiotic Game and Foundation Models for Cyber Deception Operations in Strategic Cyber Warfare

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Describes a framework for using game theory and foundation models to enable cyber deception in strategic cyber warfare
- Proposes a symbiotic relationship between game-theoretic models and foundation models to enhance cyber deception capabilities
- Discusses the role of game-theoretic models in cyber deception and the potential of foundation models to improve decision-making
Plain English Explanation
The research paper presents a framework that combines game theory and foundation models to enable more effective cyber deception operations in strategic cyber warfare.
The authors argue that game-theoretic models can help analyze and optimize cyber deception strategies, while foundation models can provide a powerful tool for improving the decision-making capabilities of cyber defenders. By creating a symbiotic relationship between these two approaches, the researchers aim to enhance the overall effectiveness of cyber deception tactics.
The paper explores how game-theoretic models can be used to model the interactions between cyber attackers and defenders, and how foundation models can be leveraged to better understand the adversary's decision-making processes and vulnerabilities. This integrated approach is intended to help cyber defenders anticipate and respond to adversarial actions more effectively.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a framework that integrates game-theoretic models and foundation models to enable more effective cyber deception operations in strategic cyber warfare.
The authors first discuss the role of game-theoretic models in cyber deception, highlighting how they can be used to analyze the interactions between attackers and defenders, and to optimize deception strategies. They then explore the potential of foundation models to enhance the decision-making capabilities of cyber defenders by providing a deeper understanding of adversarial behavior and vulnerabilities.
The paper outlines a symbiotic relationship between these two approaches, where game-theoretic models inform the design and deployment of cyber deception tactics, while foundation models continuously refine and improve the decision-making processes of the cyber defenders. This integration is intended to create a more agile and resilient cyber defense system that can adapt to evolving adversarial threats.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach to enhancing cyber deception capabilities, but it also acknowledges several caveats and areas for further research. For example, the authors note the challenge of maintaining the accuracy and reliability of foundation models in the face of adversarial manipulation and the need for robust model governance and oversight.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the potential ethical and societal implications of the proposed framework, such as the risk of cyber deception being used for malicious purposes or the potential for unintended consequences. Further research and discussion on these issues would be valuable to ensure the responsible development and deployment of these technologies.
Conclusion
The research paper introduces a novel framework that leverages the complementary strengths of game-theoretic models and foundation models to enhance cyber deception capabilities in strategic cyber warfare. By creating a symbiotic relationship between these two approaches, the authors aim to improve the decision-making and adaptability of cyber defenders, enabling them to anticipate and respond to evolving adversarial threats more effectively.
While the proposed framework shows promise, further research is needed to address the potential challenges and ethical considerations associated with the deployment of such technologies. Nonetheless, this work represents an important step towards developing more sophisticated and resilient cyber defense strategies in the face of increasingly complex and dynamic cyber threats.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Symbiotic Game and Foundation Models for Cyber Deception Operations in Strategic Cyber Warfare
Tao Li, Quanyan Zhu
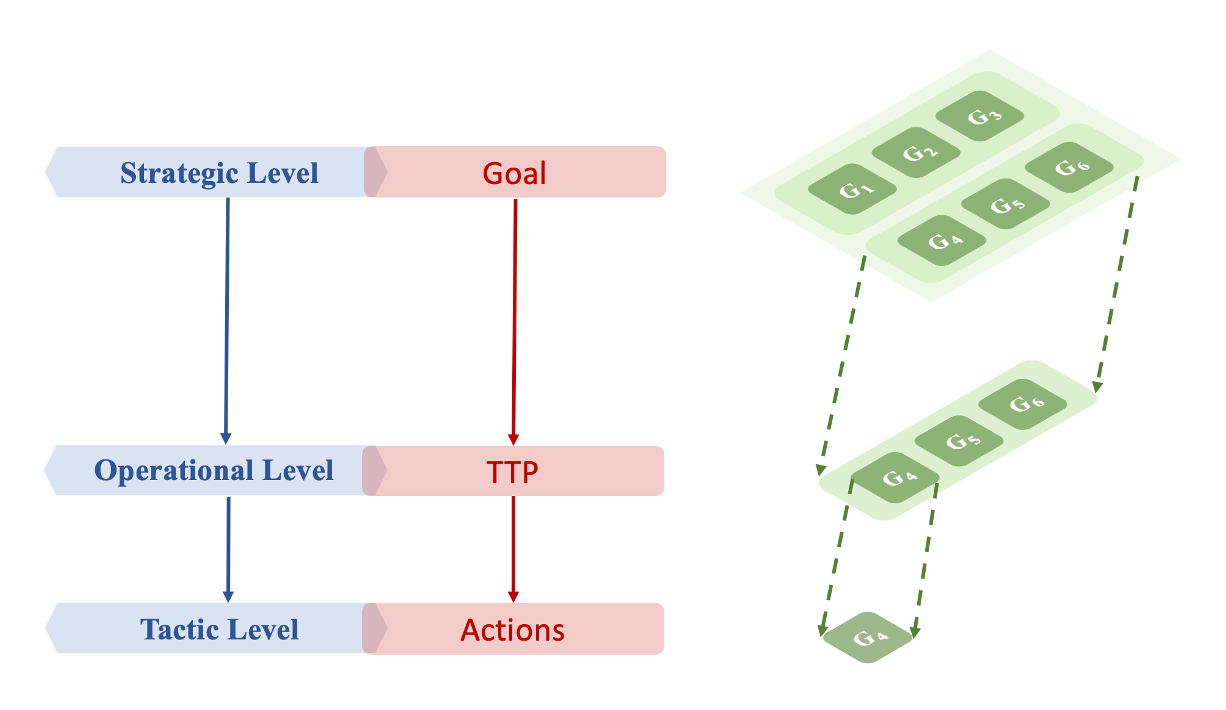
We are currently facing unprecedented cyber warfare with the rapid evolution of tactics, increasing asymmetry of intelligence, and the growing accessibility of hacking tools. In this landscape, cyber deception emerges as a critical component of our defense strategy against increasingly sophisticated attacks. This chapter aims to highlight the pivotal role of game-theoretic models and foundation models (FMs) in analyzing, designing, and implementing cyber deception tactics. Game models (GMs) serve as a foundational framework for modeling diverse adversarial interactions, allowing us to encapsulate both adversarial knowledge and domain-specific insights. Meanwhile, FMs serve as the building blocks for creating tailored machine learning models suited to given applications. By leveraging the synergy between GMs and FMs, we can advance proactive and automated cyber defense mechanisms by not only securing our networks against attacks but also enhancing their resilience against well-planned operations. This chapter discusses the games at the tactical, operational, and strategic levels of warfare, delves into the symbiotic relationship between these methodologies, and explores relevant applications where such a framework can make a substantial impact in cybersecurity. The chapter discusses the promising direction of the multi-agent neurosymbolic conjectural learning (MANSCOL), which allows the defender to predict adversarial behaviors, design adaptive defensive deception tactics, and synthesize knowledge for the operational level synthesis and adaptation. FMs serve as pivotal tools across various functions for MANSCOL, including reinforcement learning, knowledge assimilation, formation of conjectures, and contextual representation. This chapter concludes with a discussion of the challenges associated with FMs and their application in the domain of cybersecurity.
Read more8/20/2024


0
Cyber Deception: State of the art, Trends and Open challenges
Pedro Beltr'an L'opez, Manuel Gil P'erez, Pantaleone Nespoli
The growing interest in cybersecurity has significantly increased articles designing and implementing various Cyber Deception (CYDEC) mechanisms. This trend reflects the urgent need for new strategies to address cyber threats effectively. Since its emergence, CYDEC has established itself as an innovative defense against attackers, thanks to its proactive and reactive capabilities, finding applications in numerous real-life scenarios. Despite the considerable work devoted to CYDEC, the literature still presents significant gaps. In particular, there has not been (i) a comprehensive analysis of the main components characterizing CYDEC, (ii) a generic classification covering all types of solutions, nor (iii) a survey of the current state of the literature in various contexts. This article aims to fill these gaps through a detailed review of the main features that comprise CYDEC, developing a comprehensive classification taxonomy. In addition, the different frameworks used to generate CYDEC are reviewed, presenting a more comprehensive one. Existing solutions in the literature using CYDEC, both without Artificial Intelligence (AI) and with AI, are studied and compared. Finally, the most salient trends of the current state of the art are discussed, offering a list of pending challenges for future research.
Read more9/12/2024


0
Deception Analysis with Artificial Intelligence: An Interdisciplinary Perspective
Stefan Sarkadi
Humans and machines interact more frequently than ever and our societies are becoming increasingly hybrid. A consequence of this hybridisation is the degradation of societal trust due to the prevalence of AI-enabled deception. Yet, despite our understanding of the role of trust in AI in the recent years, we still do not have a computational theory to be able to fully understand and explain the role deception plays in this context. This is a problem because while our ability to explain deception in hybrid societies is delayed, the design of AI agents may keep advancing towards fully autonomous deceptive machines, which would pose new challenges to dealing with deception. In this paper we build a timely and meaningful interdisciplinary perspective on deceptive AI and reinforce a 20 year old socio-cognitive perspective on trust and deception, by proposing the development of DAMAS -- a holistic Multi-Agent Systems (MAS) framework for the socio-cognitive modelling and analysis of deception. In a nutshell this paper covers the topic of modelling and explaining deception using AI approaches from the perspectives of Computer Science, Philosophy, Psychology, Ethics, and Intelligence Analysis.
Read more6/12/2024
🤖

0
Building an Ethical and Trustworthy Biomedical AI Ecosystem for the Translational and Clinical Integration of Foundational Models
Simha Sankar Baradwaj, Destiny Gilliland, Jack Rincon, Henning Hermjakob, Yu Yan, Irsyad Adam, Gwyneth Lemaster, Dean Wang, Karol Watson, Alex Bui, Wei Wang, Peipei Ping
Foundational Models (FMs) are gaining increasing attention in the biomedical AI ecosystem due to their ability to represent and contextualize multimodal biomedical data. These capabilities make FMs a valuable tool for a variety of tasks, including biomedical reasoning, hypothesis generation, and interpreting complex imaging data. In this review paper, we address the unique challenges associated with establishing an ethical and trustworthy biomedical AI ecosystem, with a particular focus on the development of FMs and their downstream applications. We explore strategies that can be implemented throughout the biomedical AI pipeline to effectively tackle these challenges, ensuring that these FMs are translated responsibly into clinical and translational settings. Additionally, we emphasize the importance of key stewardship and co-design principles that not only ensure robust regulation but also guarantee that the interests of all stakeholders, especially those involved in or affected by these clinical and translational applications are adequately represented. We aim to empower the biomedical AI community to harness these models responsibly and effectively. As we navigate this exciting frontier, our collective commitment to ethical stewardship, co-design, and responsible translation will be instrumental in ensuring that the evolution of FMs truly enhances patient care and medical decision making, ultimately leading to a more equitable and trustworthy biomedical AI ecosystem.
Read more8/15/2024