Addressing the Load Estimation Problem: Cell Switching in HAPS-Assisted Sustainable 6G Networks

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Explores the use of High-Altitude Platform Stations (HAPS) to assist in sustainable 6G network management
- Focuses on the challenge of accurately estimating traffic load and dynamically adjusting cell coverage through cell switching
- Aims to improve energy efficiency and reduce power consumption in 6G networks
Plain English Explanation
The paper discusses how High-Altitude Platform Stations (HAPS) can be used to help manage 6G cellular networks in a more sustainable and energy-efficient way. One of the key challenges in 6G networks is accurately estimating the traffic load in different areas so that cell coverage can be adjusted dynamically through a process called "cell switching."
By using HAPS to monitor the network and estimate traffic patterns, the researchers believe they can more effectively adjust which cells are active at any given time. This can help reduce overall power consumption and improve the sustainability of the 6G network. The approach is designed to work within a virtual heterogeneous network (vHetNet) architecture, where base stations can be dynamically activated and deactivated as needed.
The researchers propose a framework that combines traffic load estimation, cell switching decisions, and power consumption optimization to create a more energy-efficient 6G network. By leveraging the aerial perspective and monitoring capabilities of HAPS, they aim to enhance the overall performance and sustainability of these future mobile networks.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a framework for addressing the traffic load estimation problem in HAPS-assisted 6G networks, with the goal of enabling dynamic cell switching to improve energy efficiency. The key components of the proposed system include:
-
Traffic Load Estimation: The researchers develop a model to estimate the traffic load in different cells based on data collected from the HAPS. This allows for more accurate monitoring of the network's usage patterns.
-
Cell Switching: Using the traffic load estimates, the framework can make decisions on which cells to activate or deactivate at any given time. This dynamic cell switching helps match the network capacity to the actual demand, reducing unnecessary power consumption.
-
Power Consumption Optimization: The paper also includes an optimization model to minimize the overall power consumption of the network, taking into account the cell switching decisions and other factors like user distribution and QoS requirements.
The proposed framework is evaluated through simulations, demonstrating its ability to accurately estimate traffic loads and effectively manage cell switching to achieve significant power savings compared to traditional static cell deployment approaches.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach to addressing the challenges of traffic load estimation and cell switching in HAPS-assisted 6G networks. By leveraging the aerial perspective and monitoring capabilities of HAPS, the researchers aim to improve the responsiveness and energy efficiency of these future mobile networks.
One potential limitation is the reliance on accurate traffic load estimation, which can be influenced by various factors, such as user mobility and unpredictable usage patterns. The researchers acknowledge this challenge and suggest further research into more advanced prediction models to enhance the reliability of the load estimation.
Additionally, the paper focuses primarily on the technical aspects of the framework and does not delve deeply into the practical deployment considerations, such as the integration of HAPS infrastructure with existing cellular networks or the regulatory and operational challenges that may arise. Further research could explore these real-world implementation challenges and their impact on the proposed solutions.
Conclusion
The research presented in this paper offers a compelling approach to improving the sustainability and energy efficiency of 6G networks through the use of HAPS-assisted traffic load estimation and dynamic cell switching. By accurately monitoring network usage patterns and adaptively adjusting cell coverage, the proposed framework aims to reduce power consumption and enhance the overall performance of future mobile communications systems.
As 6G networks continue to evolve, addressing the challenges of energy efficiency and sustainability will be crucial. The insights and strategies outlined in this paper contribute to the ongoing efforts to develop more sustainable and environmentally-friendly mobile technologies, paving the way for a greener and more resilient 6G ecosystem.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Addressing the Load Estimation Problem: Cell Switching in HAPS-Assisted Sustainable 6G Networks
Maryam Salamatmoghadasi, Metin Ozturk, Halim Yanikomeroglu
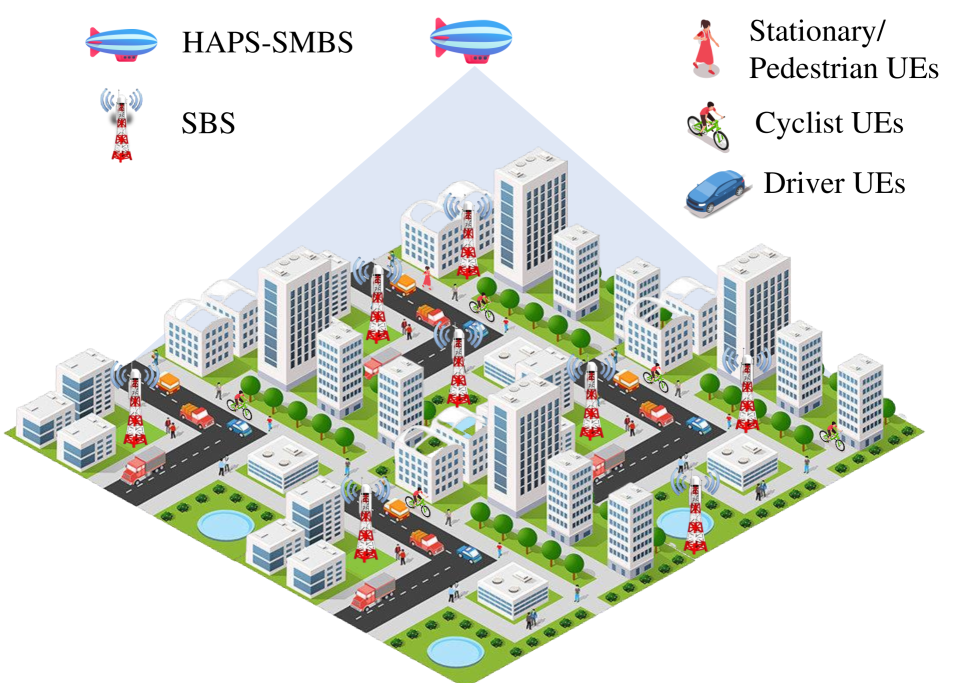
This study aims to introduce and address the problem of traffic load estimation in the cell switching concept within the evolving landscape of vertical heterogeneous networks (vHetNets). The problem is that the practice of cell switching faces a significant challenge due to the lack of accurate data on the traffic load of sleeping small base stations (SBSs). This problem makes the majority of the studies in the literature, particularly those employing load-dependent approaches, impractical due to their basic assumption of perfect knowledge of the traffic loads of sleeping SBSs for the next time slot. Rather than developing another advanced cell switching algorithm, this study investigates the impacts of estimation errors and explores possible solutions through established methodologies in a novel vHetNet environment that includes the integration of a high altitude platform (HAPS) as a super macro base station (SMBS) into the terrestrial network. In other words, this study adopts a more foundational perspective, focusing on eliminating a significant obstacle for the application of advanced cell switching algorithms. To this end, we explore the potential of three distinct spatial interpolation-based estimation schemes: random neighboring selection, distance-based selection, and clustering-based selection. Utilizing a real dataset for empirical validations, we evaluate the efficacy of our proposed traffic load estimation schemes. Our results demonstrate that the multi-level clustering (MLC) algorithm performs exceptionally well, with an insignificant difference (i.e., 0.8%) observed between its estimated and actual network power consumption, highlighting its potential to significantly improve energy efficiency in vHetNets.
Read more5/6/2024

0
Cell Switching in HAPS-Aided Networking: How the Obscurity of Traffic Loads Affects the Decision
Berk c{C}ilou{g}lu, Gorkem Berkay Koc{c}, Metin Ozturk, Halim Yanikomeroglu
This study aims to introduce the cell load estimation problem of cell switching approaches in cellular networks specially-presented in a high-altitude platform station (HAPS)-assisted network. The problem arises from the fact that the traffic loads of sleeping base stations for the next time slot cannot be perfectly known, but they can rather be estimated, and any estimation error could result in divergence from the optimal decision, which subsequently affects the performance of energy efficiency. The traffic loads of the sleeping base stations for the next time slot are required because the switching decisions are made proactively in the current time slot. Two different Q-learning algorithms are developed; one is full-scale, focusing solely on the performance, while the other one is lightweight and addresses the computational cost. Results confirm that the estimation error is capable of changing cell switching decisions that yields performance divergence compared to no-error scenarios. Moreover, the developed Q-learning algorithms perform well since an insignificant difference (i.e., 0.3%) is observed between them and the optimum algorithm.
Read more5/2/2024

0
User Association and Channel Allocation in 5G Mobile Asymmetric Multi-band Heterogeneous Networks
Miao Dai, Gang Sun, Hongfang Yu, Sheng Wang, Dusit Niyato
With the proliferation of mobile terminals and the continuous upgrading of services, 4G LTE networks are showing signs of weakness. To enhance the capacity of wireless networks, millimeter waves are introduced to drive the evolution of networks towards multi-band 5G heterogeneous networks. The distinct propagation characteristics of mmWaves and microwaves, as well as the vastly different hardware configurations of heterogeneous base stations, make traditional access strategies no longer effective. Therefore, to narrowing the gap between theory and practice, we investigate the access strategy in multi-band 5G heterogeneous networks, taking into account the characteristics of mobile users, asynchronous switching between uplink and downlink of pico base stations, asymmetric service requirements, and user communication continuity. We formulate the problem as integer nonlinear programming and prove its intractability. Thereby, we decouple it into three subproblems: user association, switch point selection, and subchannel allocation, and design an algorithm based on optimal matching and spectral clustering to solve it efficiently. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm outperforms the comparison methods in terms of overall data rate, effective data rate, and number of satisfied users.
Read more5/30/2024


0
Hybrid Semantic/Bit Communication Based Networking Problem Optimization
Le Xia, Yao Sun, Dusit Niyato, Lan Zhang, Lei Zhang, Muhammad Ali Imran
This paper jointly investigates user association (UA), mode selection (MS), and bandwidth allocation (BA) problems in a novel and practical next-generation cellular network where two modes of semantic communication (SemCom) and conventional bit communication (BitCom) coexist, namely hybrid semantic/bit communication network (HSB-Net). Concretely, we first identify a unified performance metric of message throughput for both SemCom and BitCom links. Next, we comprehensively develop a knowledge matching-aware two-stage tandem packet queuing model and theoretically derive the average packet loss ratio and queuing latency. Combined with several practical constraints, we then formulate a joint optimization problem for UA, MS, and BA to maximize the overall message throughput of HSB-Net. Afterward, we propose an optimal resource management strategy by employing a Lagrange primal-dual method and devising a preference list-based heuristic algorithm. Finally, numerical results validate the performance superiority of our proposed strategy compared with different benchmarks.
Read more8/20/2024