VR Cloud Gaming UX: Exploring the Impact of Network Quality on Emotion, Presence, Game Experience and Cybersickness

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Explores the impact of network quality on user experience in cloud-based virtual reality (VR) gaming
- Examines how network quality affects emotions, sense of presence, overall game experience, and cybersickness
- Conducted an experiment with participants playing a VR game under different network conditions
Plain English Explanation
In this study, the researchers looked at how the quality of the internet connection affects the experience of playing virtual reality (VR) games that are streamed from the cloud. They wanted to understand how things like network delays, interruptions, and overall connection quality impact a person's emotions, their feeling of being present in the virtual world, their overall enjoyment of the game, and whether they feel any motion sickness.
The researchers had participants play a VR game under different network conditions - some with a high-quality, stable connection and others with more disruptions and lower quality. They then measured the participants' responses in terms of their emotional state, their sense of being immersed in the virtual environment, how much they enjoyed the game, and whether they experienced any cybersickness (motion sickness from VR).
The goal was to better understand how the technical performance of the cloud gaming system impacts the overall user experience. This is important as more gaming and other applications move to cloud-based streaming models that rely on good network conditions.
Technical Explanation
The study used a within-subjects experimental design, where each participant experienced multiple network quality conditions while playing the same VR game. The network conditions included:
- High Quality - Stable, low-latency connection
- Medium Quality - Moderate network delays and occasional interruptions
- Low Quality - High latency, frequent connection drops
Participants completed questionnaires to assess their emotions, sense of presence in the virtual environment, overall game experience, and levels of cybersickness after each condition.
The results showed that higher network quality led to more positive emotions, greater sense of presence, better game experience, and less cybersickness. Lower quality networks had the opposite effect, decreasing the overall user experience.
Critical Analysis
The study provides valuable insights into how network performance can impact the VR user experience. However, it is limited to a single game scenario and may not generalize to all VR applications. The researchers acknowledge that other factors like game design and individual differences could also play a role.
Additionally, the study did not explore the specific thresholds or tolerances for network quality degradation. Further research could investigate how much latency, jitter, or packet loss is acceptable before the user experience starts to significantly decline.
The paper also does not discuss potential solutions or mitigation strategies for delivering high-quality cloud gaming experiences, such as edge computing, adaptive bitrate streaming, or network optimization techniques. Exploring these aspects could provide more practical guidance for developers and service providers.
Conclusion
This research demonstrates the critical importance of network quality for providing a compelling and comfortable VR user experience in cloud gaming scenarios. The findings highlight the need for cloud infrastructure and delivery mechanisms that can reliably maintain low-latency, high-bandwidth connections to ensure users enjoy the full benefits of immersive virtual experiences. As cloud gaming continues to grow, these insights can help guide the development of more robust and user-friendly VR cloud services.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
VR Cloud Gaming UX: Exploring the Impact of Network Quality on Emotion, Presence, Game Experience and Cybersickness
Maximilian Warsinke, Tanja Koji'c, Maurizio Vergari, Jan-Niklas Voigt-Antons, Sebastian Moller
This study explores the user experience (UX) of virtual reality (VR) cloud gaming under simulated network degradation conditions. Two contrasting games (Beat Saber, Cubism) were streamed via Meta Air Link to a Quest 3 device in a laboratory setup. Packet loss and delay were introduced into the streaming network using NetEm for WiFi traffic manipulation. In a within-subjects experiment, 16 participants played both games under three network conditions (Loss, Delay, Baseline), followed by post-game questionnaires assessing their emotions, perceived quality, game experience, sense of presence, and cybersickness. Friedman's test and Dunn's post-hoc test for pairwise comparisons revealed that packet loss had a greater impact on UX than delay across almost all evaluated aspects. Notably, packet loss in Beat Saber led to a significant increase in cybersickness, whereas in Cubism, players experienced a significant reduction in their sense of presence. Additionally, both games exhibited statistically significant variations between conditions in most game experience dimensions, perceived quality, and emotional responses. This study highlights the critical role of network stability in VR cloud gaming, particularly in minimizing packet loss. The different dynamics between the games suggest the possibility of genre-specific optimization and novel game design considerations for VR cloud games.
Read more8/23/2024


0
Assessing the Impact of Network Quality-of-Service on Metaverse Virtual Reality User Experience
Rahul Dev Tripathi, Minzhao Lyu, Vijay Sivaraman
Metaverse virtual reality (VR) applications enable users to socialise, work, entertain, and study online with immersive experiences beyond the classic PC-based interactions. While the 360-degree immersion enables users to be fully engaged in a virtual scenario, suboptimal Quality-of-Experience (QoE) like poorly displayed 3D graphics, disruptive loading time, or motion lagging caused by degraded network Quality-of-Service (QoS) can be perceived by users much worse (such as dizziness) than a monitor visualisation. This paper empirically measures user QoE of metaverse VR caused by network QoS. Specifically, by focusing on both public social hubs and private user-created events in three popular metaverse VR applications (Rec Room, VRChat and MultiverseVR), we first identify three metrics, including environment freeze level, peripheral content loading time, and control response time, that describe metaverse user experience. By tuning three network QoS parameters (bandwidth, latency, and packet loss), we benchmark each QoE metric's level from excellent to unplayable. Key insights are revealed, such as freeze of metaverse virtual environment is resilient to latency but sensitive to packet loss, and private user-created events demand better network conditions than public social hubs, providing a reference for ISPs to optimise their network QoS for superlative metaverse user experience.
Read more7/16/2024
🛠️

0
Experimental Evaluation of Interactive Edge/Cloud Virtual Reality Gaming over Wi-Fi using Unity Render Streaming
Miguel Casasnovas, Costas Michaelides, Marc Carrascosa-Zamacois, Boris Bellalta
Virtual Reality (VR) streaming enables end-users to seamlessly immerse themselves in interactive virtual environments using even low-end devices. However, the quality of the VR experience heavily relies on Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi) performance, since it serves as the last hop in the network chain. Our study delves into the intricate interplay between Wi-Fi and VR traffic, drawing upon empirical data and leveraging a Wi-Fi simulator. In this work, we further evaluate Wi-Fi's suitability for VR streaming in terms of the Quality of Service (QoS) it provides. In particular, we employ Unity Render Streaming to remotely stream real-time VR gaming content over Wi-Fi 6 using Web Real-Time Communication (WebRTC), considering a server physically located at the network's edge, near the end user. Our findings demonstrate the system's sustained network performance, showcasing minimal round-trip time (RTT) and jitter at 60 and 90 frames per second (fps). In addition, we uncover the characteristics and patterns of the generated traffic streams, unveiling a distinctive video transmission approach inherent to WebRTC-based services: the systematic packetization of video frames (VFs) and their transmission in discrete batches at regular intervals, regardless of the targeted frame rate. This interval-based transmission strategy maintains consistent video packet delays across video frame rates but leads to increased Wi-Fi airtime consumption. Our results demonstrate that shortening the interval between batches is advantageous, as it enhances Wi-Fi efficiency and reduces delays in delivering complete frames.
Read more8/7/2024

0
Mazed and Confused: A Dataset of Cybersickness, Working Memory, Mental Load, Physical Load, and Attention During a Real Walking Task in VR
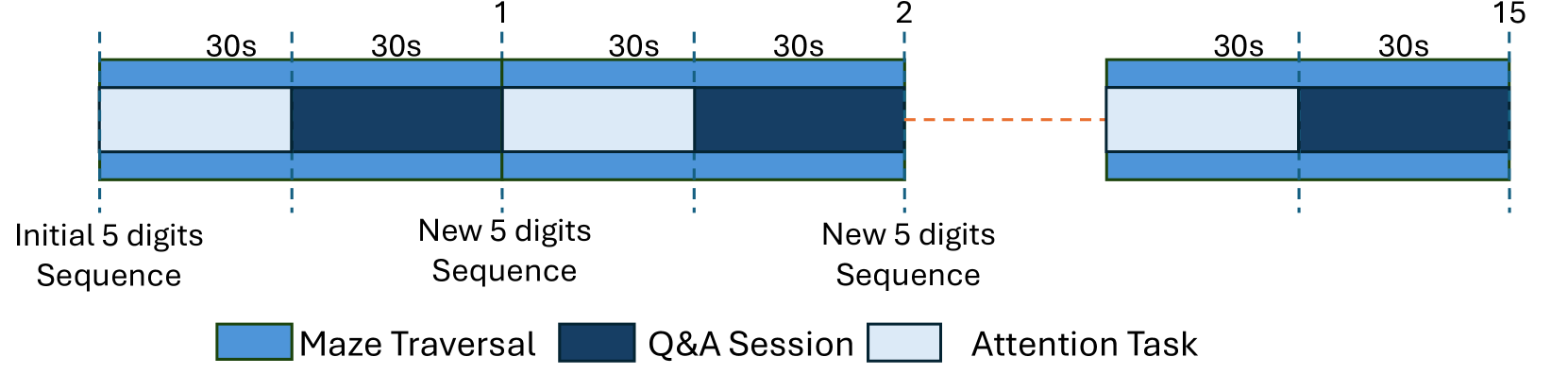
Jyotirmay Nag Setu, Joshua M Le, Ripan Kumar Kundu, Barry Giesbrecht, Tobias Hollerer, Khaza Anuarul Hoque, Kevin Desai, John Quarles
Virtual Reality (VR) is quickly establishing itself in various industries, including training, education, medicine, and entertainment, in which users are frequently required to carry out multiple complex cognitive and physical activities. However, the relationship between cognitive activities, physical activities, and familiar feelings of cybersickness is not well understood and thus can be unpredictable for developers. Researchers have previously provided labeled datasets for predicting cybersickness while users are stationary, but there have been few labeled datasets on cybersickness while users are physically walking. Thus, from 39 participants, we collected head orientation, head position, eye tracking, images, physiological readings from external sensors, and the self-reported cybersickness severity, physical load, and mental load in VR. Throughout the data collection, participants navigated mazes via real walking and performed tasks challenging their attention and working memory. To demonstrate the dataset's utility, we conducted a case study of training classifiers in which we achieved 95% accuracy for cybersickness severity classification. The noteworthy performance of the straightforward classifiers makes this dataset ideal for future researchers to develop cybersickness detection and reduction models. To better understand the features that helped with classification, we performed SHAP(SHapley Additive exPlanations) analysis, highlighting the importance of eye tracking and physiological measures for cybersickness prediction while walking. This open dataset can allow future researchers to study the connection between cybersickness and cognitive loads and develop prediction models. This dataset will empower future VR developers to design efficient and effective Virtual Environments by improving cognitive load management and minimizing cybersickness.
Read more9/12/2024