Evaluating the Application of ChatGPT in Outpatient Triage Guidance: A Comparative Study

0
👁️
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This study investigates the potential of using the Large Language Model (LLM) ChatGPT to support outpatient triage in healthcare settings.
- The researchers evaluate the consistency of responses provided by different versions of ChatGPT (3.5 and 4.0) when answering questions related to outpatient guidance.
- The study aims to provide insights into the capabilities and limitations of LLMs in healthcare operations, particularly in streamlining workflows and enhancing efficiency for outpatient triage.
Plain English Explanation
The paper explores how artificial intelligence (AI) models like ChatGPT can be used to assist with patient triage in outpatient healthcare settings. Triage is the process of prioritizing patients based on the severity of their condition, which is critical for managing patient flow and ensuring efficient use of healthcare resources.
The researchers compared the responses of two versions of ChatGPT (3.5 and 4.0) to see how consistent they were when providing guidance on outpatient care. They found that the newer version, ChatGPT-4.0, had significantly higher internal consistency in its recommendations compared to the older version, ChatGPT-3.5. However, the consistency between the two versions was relatively low, meaning that the recommendations often differed between the two.
Interestingly, the researchers also found that ChatGPT-3.5 was more likely to provide complete responses than ChatGPT-4.0, suggesting that the newer version may have differences in how it processes information and generates responses.
The findings of this study offer insights into how AI-powered systems can be integrated into healthcare workflows to streamline operations and improve patient care. However, the researchers also highlight the need for careful optimization of these systems to ensure they align with the specific needs of effective outpatient triage.
Technical Explanation
The study aimed to evaluate the consistency of responses provided by two versions of the Large Language Model (LLM) ChatGPT in the context of outpatient guidance. The researchers compared the within-version response consistency of ChatGPT-4.0 and ChatGPT-3.5, as well as the between-version consistency of their recommendations.
For the within-version analysis, the results showed that ChatGPT-4.0 had significantly higher internal response consistency (71.2%) compared to ChatGPT-3.5 (59.6%), indicating that the newer version provided more consistent top recommendations. However, the between-version consistency was relatively low, with a mean consistency score of 1.43 out of 3 and a median of 1, suggesting that the recommendations often differed between the two versions.
Interestingly, the researchers also found that ChatGPT-3.5 responses were more likely to be complete compared to ChatGPT-4.0 (p=0.02). This suggests potential differences in information processing and response generation between the two versions of the LLM.
Critical Analysis
The study provides valuable insights into the potential and limitations of using Large Language Models, such as ChatGPT, in healthcare operations, particularly for outpatient triage. The findings highlight the importance of carefully optimizing these systems to align with the specific needs and workflows of healthcare settings.
While the study demonstrates the consistency of responses within individual ChatGPT versions, the relatively low between-version consistency raises questions about the reliability and predictability of these systems across different versions. This could be a concern for healthcare providers who may need to rely on consistent recommendations to make informed decisions.
Additionally, the differences in response completeness between the two versions suggest that further research is needed to understand the impact of model updates and refinements on the quality and usability of the generated outputs. Factors such as user trust, transparency, and the integration of these systems into existing healthcare workflows should also be carefully considered.
Conclusion
This study provides valuable insights into the potential of using Large Language Models, such as ChatGPT, to support outpatient triage in healthcare settings. The findings highlight the need for careful optimization of these systems to ensure they align with the specific needs and workflows of healthcare operations.
While the study demonstrates the potential of LLMs in enhancing efficiency and streamlining workflows, it also raises important questions about the reliability and consistency of these systems across different versions. Further research is needed to address these challenges and explore ways to seamlessly integrate AI-powered tools into the healthcare ecosystem.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
👁️

0
Evaluating the Application of ChatGPT in Outpatient Triage Guidance: A Comparative Study
Dou Liu, Ying Han, Xiandi Wang, Xiaomei Tan, Di Liu, Guangwu Qian, Kang Li, Dan Pu, Rong Yin
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare presents a transformative potential for enhancing operational efficiency and health outcomes. Large Language Models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT, have shown their capabilities in supporting medical decision-making. Embedding LLMs in medical systems is becoming a promising trend in healthcare development. The potential of ChatGPT to address the triage problem in emergency departments has been examined, while few studies have explored its application in outpatient departments. With a focus on streamlining workflows and enhancing efficiency for outpatient triage, this study specifically aims to evaluate the consistency of responses provided by ChatGPT in outpatient guidance, including both within-version response analysis and between-version comparisons. For within-version, the results indicate that the internal response consistency for ChatGPT-4.0 is significantly higher than ChatGPT-3.5 (p=0.03) and both have a moderate consistency (71.2% for 4.0 and 59.6% for 3.5) in their top recommendation. However, the between-version consistency is relatively low (mean consistency score=1.43/3, median=1), indicating few recommendations match between the two versions. Also, only 50% top recommendations match perfectly in the comparisons. Interestingly, ChatGPT-3.5 responses are more likely to be complete than those from ChatGPT-4.0 (p=0.02), suggesting possible differences in information processing and response generation between the two versions. The findings offer insights into AI-assisted outpatient operations, while also facilitating the exploration of potentials and limitations of LLMs in healthcare utilization. Future research may focus on carefully optimizing LLMs and AI integration in healthcare systems based on ergonomic and human factors principles, precisely aligning with the specific needs of effective outpatient triage.
Read more5/3/2024
🤖

0
How Reliable AI Chatbots are for Disease Prediction from Patient Complaints?
Ayesha Siddika Nipu, K M Sajjadul Islam, Praveen Madiraju
Artificial Intelligence (AI) chatbots leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) are gaining traction in healthcare for their potential to automate patient interactions and aid clinical decision-making. This study examines the reliability of AI chatbots, specifically GPT 4.0, Claude 3 Opus, and Gemini Ultra 1.0, in predicting diseases from patient complaints in the emergency department. The methodology includes few-shot learning techniques to evaluate the chatbots' effectiveness in disease prediction. We also fine-tune the transformer-based model BERT and compare its performance with the AI chatbots. Results suggest that GPT 4.0 achieves high accuracy with increased few-shot data, while Gemini Ultra 1.0 performs well with fewer examples, and Claude 3 Opus maintains consistent performance. BERT's performance, however, is lower than all the chatbots, indicating limitations due to limited labeled data. Despite the chatbots' varying accuracy, none of them are sufficiently reliable for critical medical decision-making, underscoring the need for rigorous validation and human oversight. This study reflects that while AI chatbots have potential in healthcare, they should complement, not replace, human expertise to ensure patient safety. Further refinement and research are needed to improve AI-based healthcare applications' reliability for disease prediction.
Read more5/24/2024
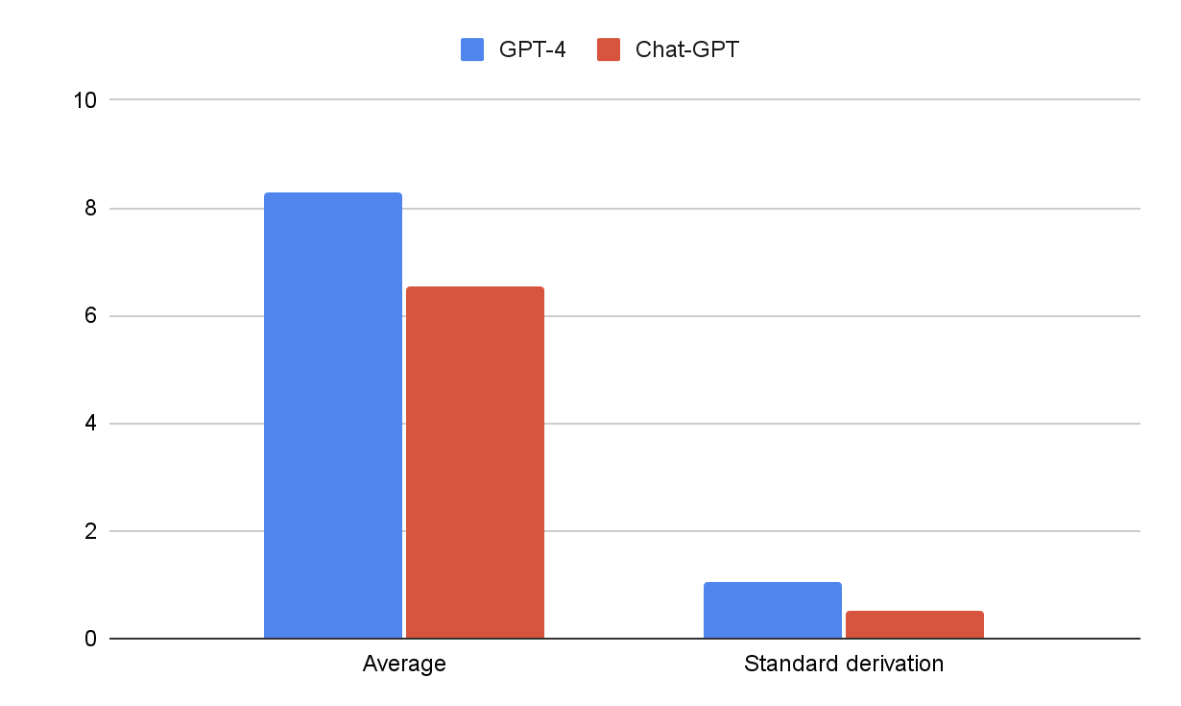

0
Comparing the Efficacy of GPT-4 and Chat-GPT in Mental Health Care: A Blind Assessment of Large Language Models for Psychological Support
Birger Moell
Background: Rapid advancements in natural language processing have led to the development of large language models with the potential to revolutionize mental health care. These models have shown promise in assisting clinicians and providing support to individuals experiencing various psychological challenges. Objective: This study aims to compare the performance of two large language models, GPT-4 and Chat-GPT, in responding to a set of 18 psychological prompts, to assess their potential applicability in mental health care settings. Methods: A blind methodology was employed, with a clinical psychologist evaluating the models' responses without knowledge of their origins. The prompts encompassed a diverse range of mental health topics, including depression, anxiety, and trauma, to ensure a comprehensive assessment. Results: The results demonstrated a significant difference in performance between the two models (p > 0.05). GPT-4 achieved an average rating of 8.29 out of 10, while Chat-GPT received an average rating of 6.52. The clinical psychologist's evaluation suggested that GPT-4 was more effective at generating clinically relevant and empathetic responses, thereby providing better support and guidance to potential users. Conclusions: This study contributes to the growing body of literature on the applicability of large language models in mental health care settings. The findings underscore the importance of continued research and development in the field to optimize these models for clinical use. Further investigation is necessary to understand the specific factors underlying the performance differences between the two models and to explore their generalizability across various populations and mental health conditions.
Read more5/16/2024


0
Integrating AI in College Education: Positive yet Mixed Experiences with ChatGPT
Xinrui Song, Jiajin Zhang, Pingkun Yan, Juergen Hahn, Uwe Kruger, Hisham Mohamed, Ge Wang
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots into higher education marks a shift towards a new generation of pedagogical tools, mirroring the arrival of milestones like the internet. With the launch of ChatGPT-4 Turbo in November 2023, we developed a ChatGPT-based teaching application (https://chat.openai.com/g/g-1imx1py4K-chatge-medical-imaging) and integrated it into our undergraduate medical imaging course in the Spring 2024 semester. This study investigates the use of ChatGPT throughout a semester-long trial, providing insights into students' engagement, perception, and the overall educational effectiveness of the technology. We systematically collected and analyzed data concerning students' interaction with ChatGPT, focusing on their attitudes, concerns, and usage patterns. The findings indicate that ChatGPT offers significant advantages such as improved information access and increased interactivity, but its adoption is accompanied by concerns about the accuracy of the information provided and the necessity for well-defined guidelines to optimize its use.
Read more7/9/2024