Exploring UAV Networking from the Terrain Information Completeness Perspective: A Tutorial
2404.04505

0
0
Abstract
Terrain information is a crucial factor affecting the performance of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) networks. As a tutorial, this article provides a unique perspective on the completeness of terrain information, summarizing and enhancing the research on terrain-based UAV deployment. In the presence of complete terrain information, two highly discussed topics are UAV-aided map construction and dynamic trajectory design based on maps. We propose a case study illustrating the mutually reinforcing relationship between them. When terrain information is incomplete, and only terrain-related feature parameters are available, we discuss how existing models map terrain features to blockage probabilities. By introducing the application of this model with stochastic geometry, a case study is proposed to analyze the accuracy of the model. When no terrain information is available, UAVs gather terrain information during the real-time networking process and determine the next position by collected information. This real-time search method is currently limited to relay communication. In the case study, we extend it to a multi-user scenario and summarize three trade-offs of the method. Finally, we conduct a qualitative analysis to assess the impact of three factors that have been overlooked in terrain-based UAV deployment.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Explores the impact of terrain information completeness on UAV networking performance
- Investigates how terrain blockage affects communication links between UAVs and ground stations
- Provides a tutorial-style overview of the research in this area
Plain English Explanation
The paper examines how the completeness of terrain information affects the performance of communication networks involving unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). When UAVs are used for tasks like surveillance or delivery, they need to maintain reliable connections with ground stations. However, the terrain between the UAVs and ground stations can block or disrupt these communication links.
The researchers investigate how accurate terrain data, such as from detailed aerial lidar maps, can help predict and mitigate these blockage issues. By understanding the terrain obstacles, UAV operators can plan better flight paths and network configurations to ensure robust connectivity. This is especially important in challenging environments like urban areas or rugged landscapes.
The paper serves as a tutorial, walking through the key concepts and research approaches in this field. It covers topics like channel measurement between UAVs and ground stations, trajectory optimization for UAV flights, and security considerations for UAV networks. The goal is to help readers understand the importance of terrain information and how it can be leveraged to improve the reliability and performance of UAV communication networks.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a comprehensive review of research on the impact of terrain information completeness on UAV networking performance. The authors highlight how accurate terrain data, such as from high-resolution aerial lidar maps, can enable better prediction and mitigation of communication link blockages between UAVs and ground stations.
The paper covers various technical aspects of this challenge, including:
- Channel Measurement: Experimental studies on UAV-to-ground channel characteristics and how terrain features affect signal propagation.
- Blockage Verification: Algorithms and models for identifying terrain-induced blockages in UAV communication links.
- Network Performance Optimization: Techniques for optimizing UAV trajectories and network configurations to maintain connectivity in the presence of terrain obstacles.
- Security Considerations: Approaches for securing UAV networks against potential threats posed by terrain-induced vulnerabilities.
The paper presents a thorough review of the state-of-the-art research in this field, highlighting the key challenges, methodologies, and findings. It serves as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners interested in understanding and improving the performance of UAV communication networks in complex terrain environments.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the current research on the impact of terrain information completeness on UAV networking performance. However, the authors acknowledge several caveats and areas for further exploration:
- The effectiveness of the proposed techniques may be limited by the availability and accuracy of terrain data, which can be challenging to obtain, especially in remote or inaccessible areas.
- The paper focuses primarily on line-of-sight communication between UAVs and ground stations, but other communication modes, such as mesh or relay-based networks, may be necessary in more complex environments.
- The security considerations discussed in the paper are high-level, and further research is needed to develop robust and scalable security solutions for UAV networks operating in diverse terrain conditions.
- The paper does not address the potential trade-offs between terrain awareness, computational complexity, and real-time decision-making required for UAV network management.
Overall, the paper presents a solid foundation for understanding the importance of terrain information in UAV networking, but additional research is needed to address the practical challenges and limitations identified in the work.
Conclusion
This tutorial-style paper provides a comprehensive overview of the research on the impact of terrain information completeness on UAV networking performance. The authors highlight the critical role that accurate terrain data, such as from high-resolution aerial lidar maps, can play in predicting and mitigating communication link blockages between UAVs and ground stations.
The paper covers a range of technical aspects, including channel measurement, blockage verification, network performance optimization, and security considerations. By understanding these concepts, researchers and practitioners can develop more reliable and resilient UAV communication networks, particularly in challenging terrain environments.
While the paper presents a solid foundation, the authors also identify several caveats and areas for further research, such as the availability and accuracy of terrain data, the need for alternative communication modes, and the trade-offs between terrain awareness and real-time decision-making. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for unlocking the full potential of UAV networking in diverse real-world applications.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🎯
Ground-to-UAV 140 GHz channel measurement and modeling
Da Li, Peian Li, Jiabiao Zhao, Jianjian Liang, Jiacheng Liu, Guohao Liu, Yuanshuai Lei, Wenbo Liu, Jianqin Deng, Fuyong Liu, Jianjun Ma

0
0
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) assisted terahertz (THz) wireless communications have been expected to play a vital role in the next generation of wireless networks. UAVs can serve as either repeaters or data collectors within the communication link, thereby potentially augmenting the efficacy of communication systems. Despite their promise, the channel analysis and modeling specific to THz wireless channels leveraging UAVs remain under explored. This work delves into a ground-to-UAV channel at 140 GHz, with a specific focus on the influence of UAV hovering behavior on channel performance. Employing experimental measurements through an unmodulated channel setup and a geometry-based stochastic model (GBSM) that integrates three-dimensional positional coordinates and beamwidth, this work evaluates the impact of UAV dynamic movements and antenna orientation on channel performance. Our findings highlight the minimal impact of UAV orientation adjustments on channel performance and underscore the diminishing necessity for precise alignment between UAVs and ground stations as beamwidth increases.
4/4/2024
UAV Navigation in Tunnels with 2D tilted LiDARs
Danilo Tardioli, Lorenzo Cano, Alejandro R. Mosteo

0
0
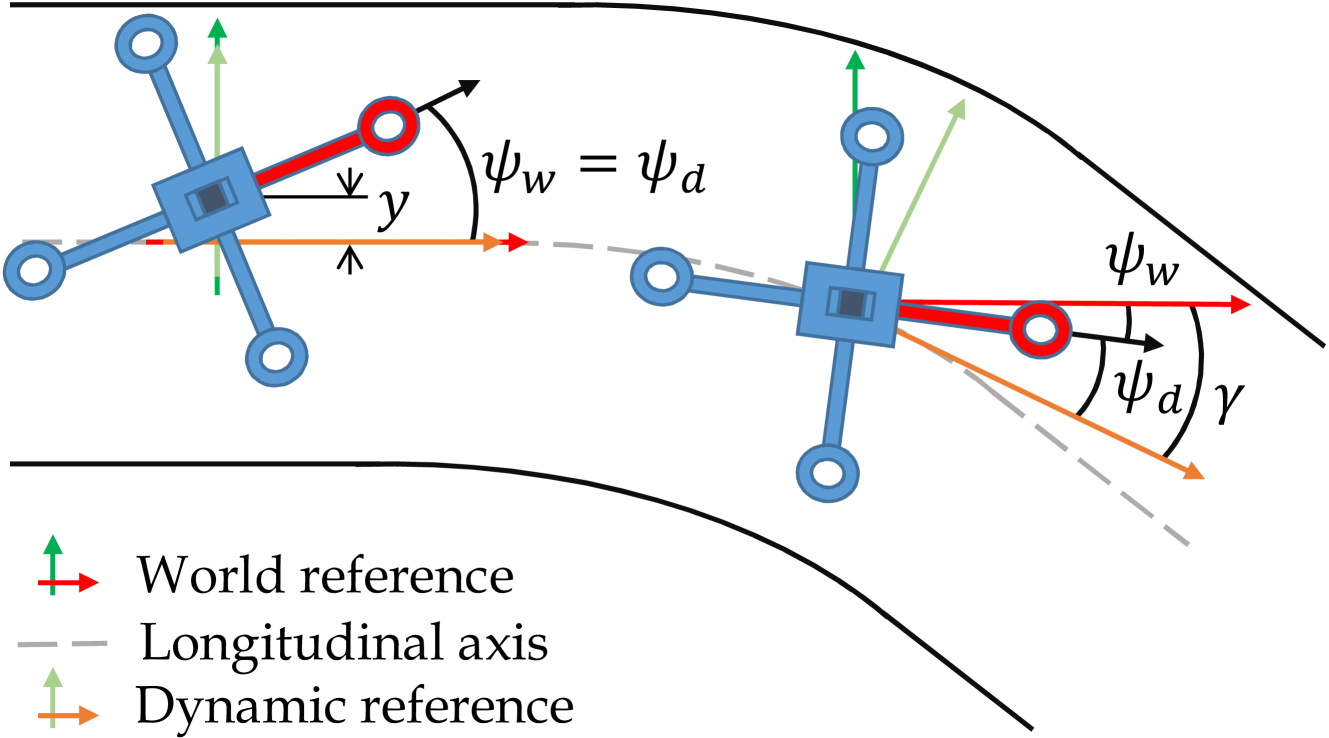
Navigation of UAVs in challenging environments like tunnels or mines, where it is not possible to use GNSS methods to self-localize, illumination may be uneven or nonexistent, and wall features are likely to be scarce, is a complex task, especially if the navigation has to be done at high speed. In this paper we propose a novel proof-of-concept navigation technique for UAVs based on the use of LiDAR information through the joint use of geometric and machine-learning algorithms. The perceived information is processed by a deep neural network to establish the yaw of the UAV with respect to the tunnel's longitudinal axis, in order to adjust the direction of navigation. Additionally, a geometric method is used to compute the safest location inside the tunnel (i.e. the one that maximizes the distance to the closest obstacle). This information proves to be sufficient for simple yet effective navigation in straight and curved tunnels.
4/16/2024
Leveraging edge detection and neural networks for better UAV localization
Theo Di Piazza, Enric Meinhardt-Llopis, Gabriele Facciolo, Benedicte Bascle, Corentin Abgrall, Jean-Clement Devaux

0
0
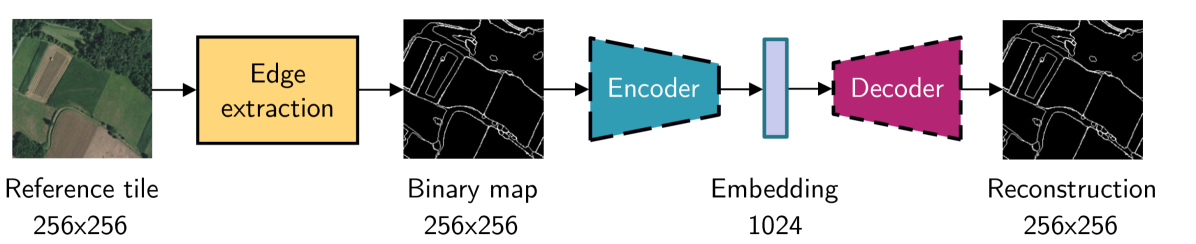
We propose a novel method for geolocalizing Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) in environments lacking Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS). Current state-of-the-art techniques employ an offline-trained encoder to generate a vector representation (embedding) of the UAV's current view, which is then compared with pre-computed embeddings of geo-referenced images to determine the UAV's position. Here, we demonstrate that the performance of these methods can be significantly enhanced by preprocessing the images to extract their edges, which exhibit robustness to seasonal and illumination variations. Furthermore, we establish that utilizing edges enhances resilience to orientation and altitude inaccuracies. Additionally, we introduce a confidence criterion for localization. Our findings are substantiated through synthetic experiments.
6/4/2024
🌐
Green UAV-enabled Internet-of-Things Network with AI-assisted NOMA for Disaster Management
Muhammad Ali Jamshed, Ferheen Ayaz, Aryan Kaushik, Carlo Fischione, Masood Ur-Rehman

0
0
Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-assisted communication is becoming a streamlined technology in providing improved coverage to the internet-of-things (IoT) based devices. Rapid deployment, portability, and flexibility are some of the fundamental characteristics of UAVs, which make them ideal for effectively managing emergency-based IoT applications. This paper studies a UAV-assisted wireless IoT network relying on non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) to facilitate uplink connectivity for devices spread over a disaster region. The UAV setup is capable of relaying the information to the cellular base station (BS) using decode and forward relay protocol. By jointly utilizing the concepts of unsupervised machine learning (ML) and solving the resulting non-convex problem, we can maximize the total energy efficiency (EE) of IoT devices spread over a disaster region. Our proposed approach uses a combination of k-medoids and Silhouette analysis to perform resource allocation, whereas, power optimization is performed using iterative methods. In comparison to the exhaustive search method, our proposed scheme solves the EE maximization problem with much lower complexity and at the same time improves the overall energy consumption of the IoT devices. Moreover, in comparison to a modified version of greedy algorithm, our proposed approach improves the total EE of the system by 19% for a fixed 50k target number of bits.
6/18/2024