Prompt-Singer: Controllable Singing-Voice-Synthesis with Natural Language Prompt

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a novel approach called "Prompt-Singer" that enables controllable singing voice synthesis using natural language prompts.
- The system leverages large language models and deep learning techniques to generate singing voices that match the semantics and attributes specified in the input prompts.
- The paper explores the potential of this approach for applications in music production, virtual assistants, and personalized entertainment.
Plain English Explanation
The "Prompt-Singer" system allows users to create singing voices by simply typing in a natural language description. For example, you could type "a soft, soothing female voice singing a love song" and the system would generate an audio clip of a singer matching that description.
This is made possible by connecting large language models, which are AI systems trained on massive amounts of text data, with deep learning models for synthesizing singing voices. The language model can understand the semantics and attributes specified in the text prompt, and then the voice synthesis model generates the corresponding singing voice.
This approach offers several benefits compared to traditional singing voice synthesis methods. First, it provides much more fine-grained control over the vocals, allowing users to customize aspects like the singer's gender, emotion, and singing style. Second, it is more accessible and user-friendly, as users can simply type in a description rather than having to manually configure synthesis parameters.
The researchers envision this technology being useful for a variety of applications, such as aiding music production, enhancing virtual assistants with more expressive singing voices, and enabling personalized entertainment experiences.
Technical Explanation
The Prompt-Singer system consists of two key components: a natural language understanding model and a singing voice synthesis model.
The natural language understanding model is based on a large pre-trained language model, such as GPT-3, which can extract semantic and attribute information from the input text prompt. This includes aspects like the desired singer's gender, emotion, and singing style.
The singing voice synthesis model then takes the extracted attributes and generates the corresponding singing voice audio. This model is built upon recent advancements in voice attribute editing and end-to-end singing voice synthesis techniques.
The researchers trained and evaluated the Prompt-Singer system on a large dataset of singing voice samples, demonstrating its ability to generate high-quality singing voices that closely match the semantics and attributes specified in the text prompts.
Critical Analysis
The Prompt-Singer system represents an exciting advancement in the field of singing voice synthesis, as it offers a more intuitive and controllable approach compared to traditional methods. However, the paper does acknowledge some limitations and areas for further research.
One key challenge is ensuring the generated singing voices maintain consistent quality and coherence across the full length of a song. The current system may struggle with producing seamless, long-form singing performances. Additionally, the researchers note that the system's ability to capture nuanced emotional expression is an area that requires further refinement.
Another potential concern is the ethical implications of this technology, particularly around the potential for misuse in the creation of synthetic media or the exploitation of individuals' vocal characteristics. The paper does not delve deeply into these issues, and further discussion and safeguards may be needed as the technology matures.
Overall, the Prompt-Singer system represents a promising step forward in the quest for more user-friendly and expressive singing voice synthesis. As the field continues to evolve, it will be important to carefully consider both the technical and ethical implications of these advancements.
Conclusion
The Prompt-Singer system introduces a novel approach to singing voice synthesis that leverages natural language prompts to provide users with fine-grained control over the generated vocals. By connecting large language models with deep learning-based singing voice synthesis, the system enables a more intuitive and accessible way to create custom singing performances.
This technology holds great potential for applications in music production, virtual assistants, and personalized entertainment experiences. As the research in this area continues to progress, it will be important to address the remaining technical challenges and carefully consider the ethical implications of this powerful capability.
Overall, the Prompt-Singer system represents an exciting step forward in the field of singing voice synthesis, demonstrating the potential of language-driven techniques to revolutionize how we interact with and create music.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Prompt-Singer: Controllable Singing-Voice-Synthesis with Natural Language Prompt
Yongqi Wang, Ruofan Hu, Rongjie Huang, Zhiqing Hong, Ruiqi Li, Wenrui Liu, Fuming You, Tao Jin, Zhou Zhao
Recent singing-voice-synthesis (SVS) methods have achieved remarkable audio quality and naturalness, yet they lack the capability to control the style attributes of the synthesized singing explicitly. We propose Prompt-Singer, the first SVS method that enables attribute controlling on singer gender, vocal range and volume with natural language. We adopt a model architecture based on a decoder-only transformer with a multi-scale hierarchy, and design a range-melody decoupled pitch representation that enables text-conditioned vocal range control while keeping melodic accuracy. Furthermore, we explore various experiment settings, including different types of text representations, text encoder fine-tuning, and introducing speech data to alleviate data scarcity, aiming to facilitate further research. Experiments show that our model achieves favorable controlling ability and audio quality. Audio samples are available at http://prompt-singer.github.io .
Read more7/10/2024

0
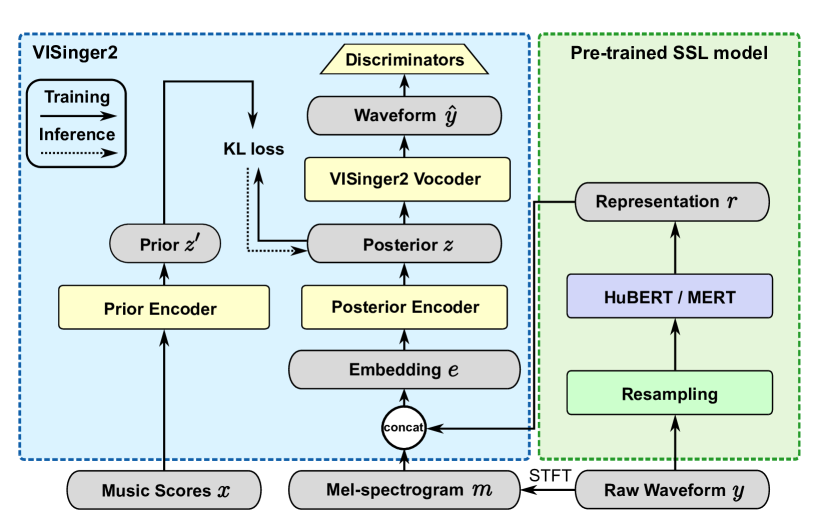
VISinger2+: End-to-End Singing Voice Synthesis Augmented by Self-Supervised Learning Representation
Yifeng Yu, Jiatong Shi, Yuning Wu, Shinji Watanabe
Singing Voice Synthesis (SVS) has witnessed significant advancements with the advent of deep learning techniques. However, a significant challenge in SVS is the scarcity of labeled singing voice data, which limits the effectiveness of supervised learning methods. In response to this challenge, this paper introduces a novel approach to enhance the quality of SVS by leveraging unlabeled data from pre-trained self-supervised learning models. Building upon the existing VISinger2 framework, this study integrates additional spectral feature information into the system to enhance its performance. The integration aims to harness the rich acoustic features from the pre-trained models, thereby enriching the synthesis and yielding a more natural and expressive singing voice. Experimental results in various corpora demonstrate the efficacy of this approach in improving the overall quality of synthesized singing voices in both objective and subjective metrics.
Read more6/14/2024

0
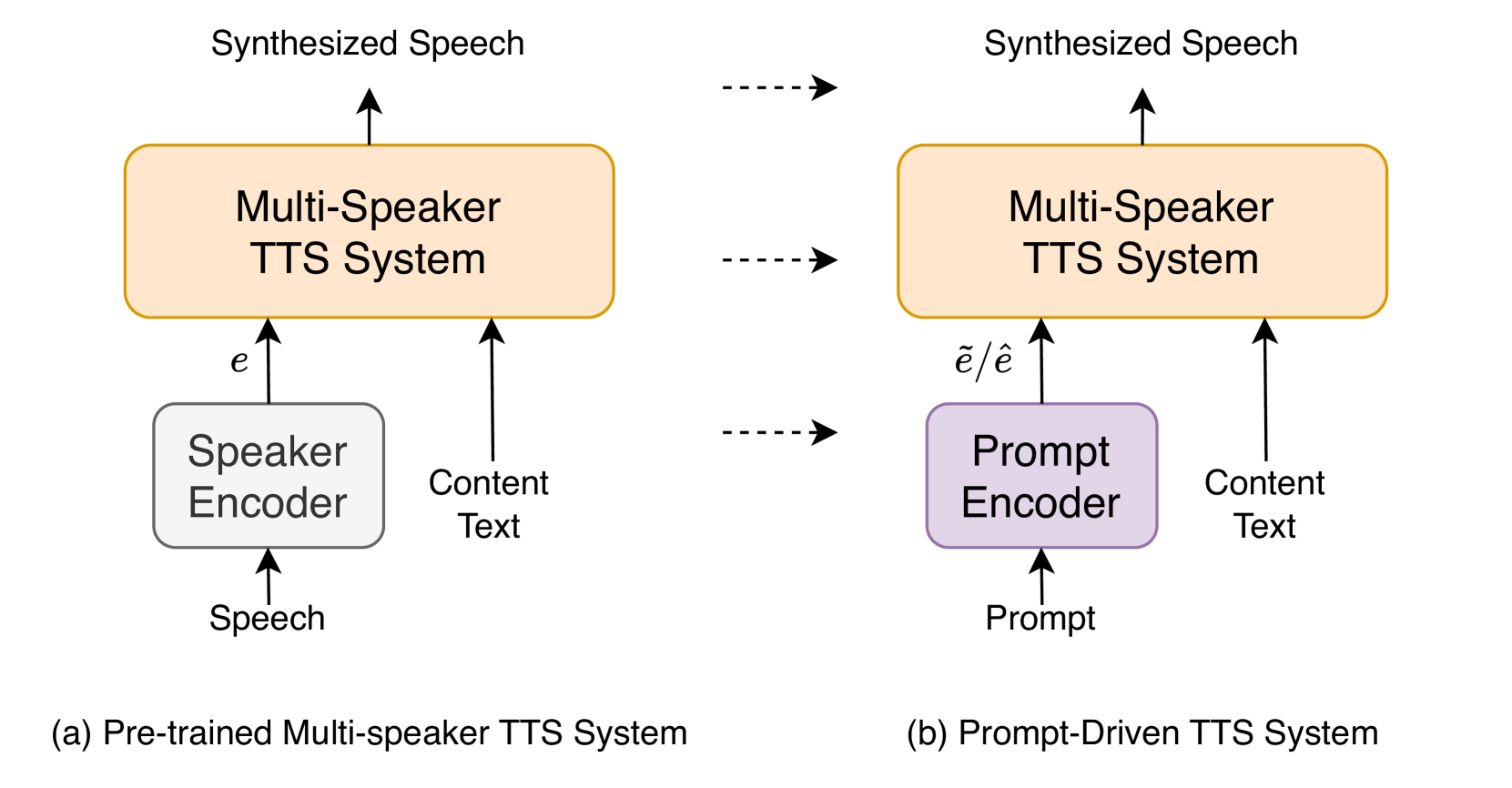
Generating Speakers by Prompting Listener Impressions for Pre-trained Multi-Speaker Text-to-Speech Systems
Zhengyang Chen, Xuechen Liu, Erica Cooper, Junichi Yamagishi, Yanmin Qian
This paper proposes a speech synthesis system that allows users to specify and control the acoustic characteristics of a speaker by means of prompts describing the speaker's traits of synthesized speech. Unlike previous approaches, our method utilizes listener impressions to construct prompts, which are easier to collect and align more naturally with everyday descriptions of speaker traits. We adopt the Low-rank Adaptation (LoRA) technique to swiftly tailor a pre-trained language model to our needs, facilitating the extraction of speaker-related traits from the prompt text. Besides, different from other prompt-driven text-to-speech (TTS) systems, we separate the prompt-to-speaker module from the multi-speaker TTS system, enhancing system flexibility and compatibility with various pre-trained multi-speaker TTS systems. Moreover, for the prompt-to-speaker characteristic module, we also compared the discriminative method and flow-matching based generative method and we found that combining both methods can help the system simultaneously capture speaker-related information from prompts better and generate speech with higher fidelity.
Read more6/14/2024


0
Voice Attribute Editing with Text Prompt
Zhengyan Sheng, Yang Ai, Li-Juan Liu, Jia Pan, Zhen-Hua Ling
Despite recent advancements in speech generation with text prompt providing control over speech style, voice attributes in synthesized speech remain elusive and challenging to control. This paper introduces a novel task: voice attribute editing with text prompt, with the goal of making relative modifications to voice attributes according to the actions described in the text prompt. To solve this task, VoxEditor, an end-to-end generative model, is proposed. In VoxEditor, addressing the insufficiency of text prompt, a Residual Memory (ResMem) block is designed, that efficiently maps voice attributes and these descriptors into the shared feature space. Additionally, the ResMem block is enhanced with a voice attribute degree prediction (VADP) block to align voice attributes with corresponding descriptors, addressing the imprecision of text prompt caused by non-quantitative descriptions of voice attributes. We also establish the open-source VCTK-RVA dataset, which leads the way in manual annotations detailing voice characteristic differences among different speakers. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and generalizability of our proposed method in terms of both objective and subjective metrics. The dataset and audio samples are available on the website.
Read more4/16/2024