Raidar: geneRative AI Detection viA Rewriting
2401.12970

0
1
Abstract
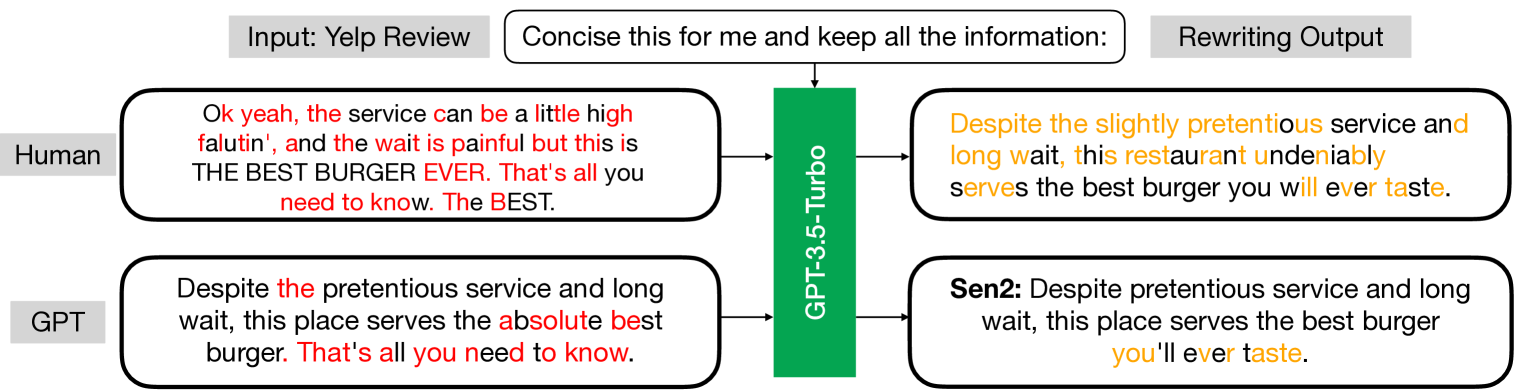
We find that large language models (LLMs) are more likely to modify human-written text than AI-generated text when tasked with rewriting. This tendency arises because LLMs often perceive AI-generated text as high-quality, leading to fewer modifications. We introduce a method to detect AI-generated content by prompting LLMs to rewrite text and calculating the editing distance of the output. We dubbed our geneRative AI Detection viA Rewriting method Raidar. Raidar significantly improves the F1 detection scores of existing AI content detection models -- both academic and commercial -- across various domains, including News, creative writing, student essays, code, Yelp reviews, and arXiv papers, with gains of up to 29 points. Operating solely on word symbols without high-dimensional features, our method is compatible with black box LLMs, and is inherently robust on new content. Our results illustrate the unique imprint of machine-generated text through the lens of the machines themselves.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Provides formatting instructions for submissions to the ICLR 2024 conference
- Covers topics such as paper structure, layout, and citation guidelines
- Aims to ensure a consistent and professional presentation of research papers
Plain English Explanation
This document outlines the formatting requirements for submitting research papers to the ICLR 2024 conference. The instructions cover various aspects of paper structure and layout, such as the organization of sections, the use of figures and tables, and the formatting of citations and references.
The goal is to establish a consistent and professional presentation of the research work being presented at the conference. This helps the reviewers and attendees focus on the content of the papers rather than getting distracted by formatting issues. By adhering to these guidelines, authors can ensure their submissions are easy to read and navigate, making a better impression on the conference organizers and audience.
Technical Explanation
The paper starts with an introduction that outlines the purpose of the formatting instructions and provides an overview of the key requirements. This is followed by a section on related work, which discusses previous efforts to standardize paper formatting for academic conferences.
The bulk of the paper focuses on the specific formatting instructions, covering topics such as page layout, font styles, section headings, figure and table formatting, and citation styles. These guidelines are designed to ensure a consistent and professional appearance for all accepted submissions.
The paper also addresses potential biases that could arise from the formatting requirements, acknowledging that they may have unintended consequences on the diversity and inclusivity of the submissions.
Critical Analysis
The formatting instructions provided in this paper are comprehensive and well-thought-out, addressing a wide range of technical details that are important for ensuring a consistent presentation of research work at the ICLR 2024 conference.
However, one potential limitation is the potential for these guidelines to inadvertently introduce bias into the submission and review process. The authors acknowledge this concern and suggest that further research may be needed to understand the impact of formatting requirements on the diversity and inclusivity of the conference.
Additionally, the instructions may be overly prescriptive in some areas, potentially limiting the creative expression or unique styles of individual authors. It would be beneficial to explore ways to maintain a high level of professionalism while also allowing for more flexibility in the presentation of research.
Conclusion
The formatting instructions provided in this paper are a crucial aspect of ensuring a successful and well-organized ICLR 2024 conference. By establishing clear guidelines for paper structure, layout, and citation styles, the conference organizers can help create a consistent and professional appearance for all accepted submissions.
While there are some potential concerns around the impact of these requirements on diversity and creativity, the overall benefits of having a standardized format likely outweigh these drawbacks. The conference attendees and reviewers will appreciate the ease of navigating and comparing the research papers, allowing them to focus on the content and insights rather than being distracted by formatting issues.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Ai.llude: Encouraging Rewriting AI-Generated Text to Support Creative Expression
David Zhou, Sarah Sterman

0
0
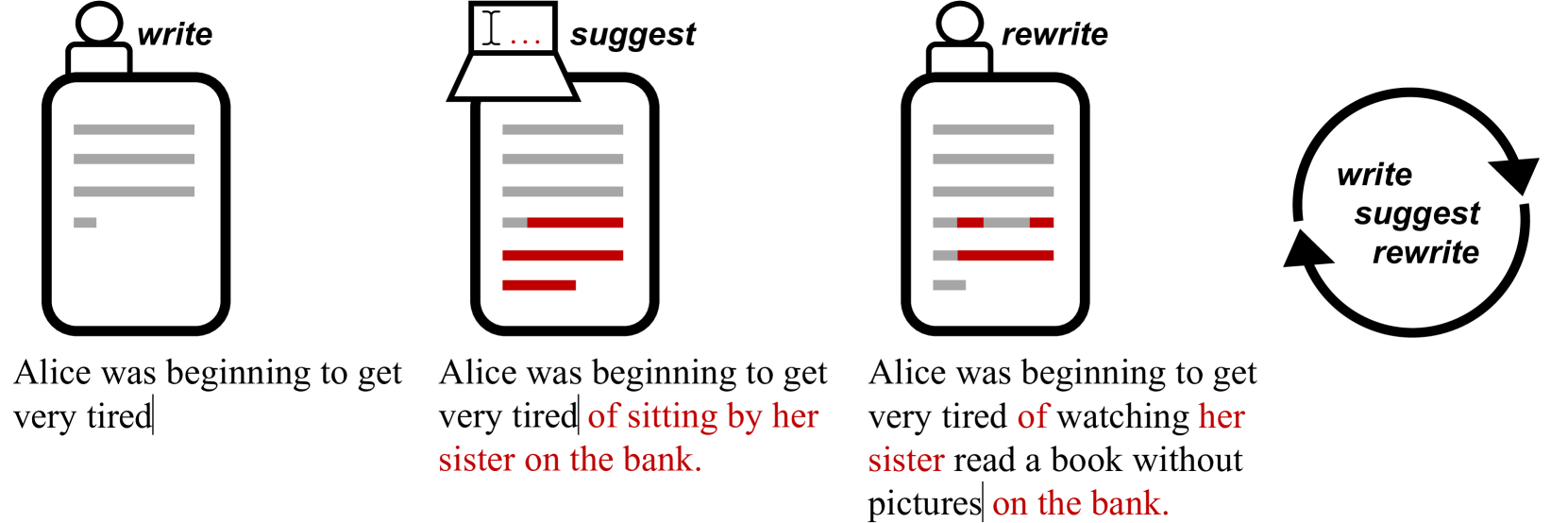
In each step of the creative writing process, writers must grapple with their creative goals and individual perspectives. This process affects the writer's sense of authenticity and their engagement with the written output. Fluent text generation by AIs risks undermining the reflective loop of rewriting. We hypothesize that deliberately generating imperfect intermediate text can encourage rewriting and prompt higher level decision making. Using logs from 27 writing sessions using a text generation AI, we characterize how writers adapt and rewrite AI suggestions, and show that intermediate suggestions significantly motivate and increase rewriting. We discuss the implications of this finding, and future steps for investigating how to leverage intermediate text in AI writing support tools to support ownership over creative expression.
5/29/2024
Who Writes the Review, Human or AI?
Panagiotis C. Theocharopoulos, Spiros V. Georgakopoulos, Sotiris K. Tasoulis, Vassilis P. Plagianakos

0
0
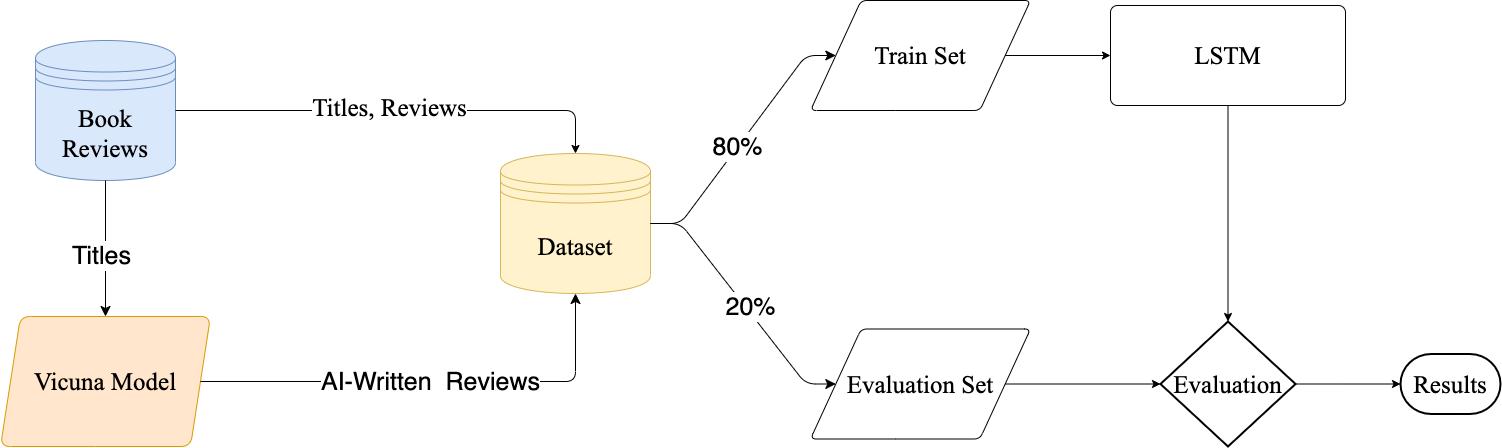
With the increasing use of Artificial Intelligence in Natural Language Processing, concerns have been raised regarding the detection of AI-generated text in various domains. This study aims to investigate this issue by proposing a methodology to accurately distinguish AI-generated and human-written book reviews. Our approach utilizes transfer learning, enabling the model to identify generated text across different topics while improving its ability to detect variations in writing style and vocabulary. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed methodology, we developed a dataset consisting of real book reviews and AI-generated reviews using the recently proposed Vicuna open-source language model. The experimental results demonstrate that it is feasible to detect the original source of text, achieving an accuracy rate of 96.86%. Our efforts are oriented toward the exploration of the capabilities and limitations of Large Language Models in the context of text identification. Expanding our knowledge in these aspects will be valuable for effectively navigating similar models in the future and ensuring the integrity and authenticity of human-generated content.
5/31/2024
Enhancing Text Authenticity: A Novel Hybrid Approach for AI-Generated Text Detection
Ye Zhang, Qian Leng, Mengran Zhu, Rui Ding, Yue Wu, Jintong Song, Yulu Gong

0
0
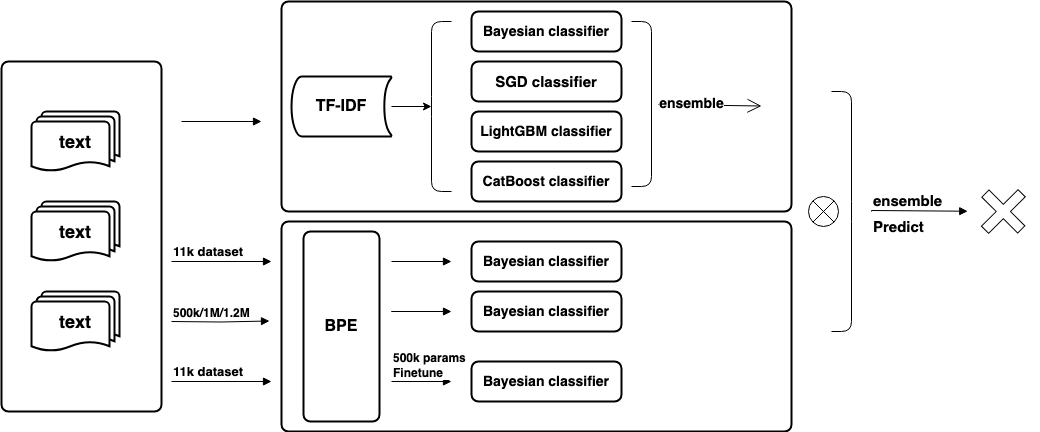
The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) has ushered in an era where AI-generated text is increasingly indistinguishable from human-generated content. Detecting AI-generated text has become imperative to combat misinformation, ensure content authenticity, and safeguard against malicious uses of AI. In this paper, we propose a novel hybrid approach that combines traditional TF-IDF techniques with advanced machine learning models, including Bayesian classifiers, Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD), Categorical Gradient Boosting (CatBoost), and 12 instances of Deberta-v3-large models. Our approach aims to address the challenges associated with detecting AI-generated text by leveraging the strengths of both traditional feature extraction methods and state-of-the-art deep learning models. Through extensive experiments on a comprehensive dataset, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method in accurately distinguishing between human and AI-generated text. Our approach achieves superior performance compared to existing methods. This research contributes to the advancement of AI-generated text detection techniques and lays the foundation for developing robust solutions to mitigate the challenges posed by AI-generated content.
6/12/2024
👀
RaFe: Ranking Feedback Improves Query Rewriting for RAG
Shengyu Mao, Yong Jiang, Boli Chen, Xiao Li, Peng Wang, Xinyu Wang, Pengjun Xie, Fei Huang, Huajun Chen, Ningyu Zhang

0
0
As Large Language Models (LLMs) and Retrieval Augmentation Generation (RAG) techniques have evolved, query rewriting has been widely incorporated into the RAG system for downstream tasks like open-domain QA. Many works have attempted to utilize small models with reinforcement learning rather than costly LLMs to improve query rewriting. However, current methods require annotations (e.g., labeled relevant documents or downstream answers) or predesigned rewards for feedback, which lack generalization, and fail to utilize signals tailored for query rewriting. In this paper, we propose ours, a framework for training query rewriting models free of annotations. By leveraging a publicly available reranker, ours~provides feedback aligned well with the rewriting objectives. Experimental results demonstrate that ours~can obtain better performance than baselines.
5/24/2024