RealitySummary: On-Demand Mixed Reality Document Enhancement using Large Language Models

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a system called "RealitySummary" that uses large language models to enhance digital documents with on-demand mixed reality content.
- The system aims to provide readers with a more engaging and informative reading experience by overlaying relevant multimedia content, such as images, videos, and 3D models, onto the text.
- The researchers explore how large language models can be leveraged to understand the context and content of a document and dynamically generate appropriate mixed reality enhancements.
Plain English Explanation
The researchers have developed a system called "RealitySummary" that can enhance digital documents with interactive mixed reality content. When you're reading a document on a computer or mobile device, RealitySummary can automatically add things like images, videos, and 3D models that are relevant to the text you're reading.
The key idea is to use powerful language AI models, known as large language models, to understand the meaning and context of the document. Based on this understanding, the system can then generate or retrieve appropriate multimedia content to overlay on top of the text, creating a more immersive and informative reading experience.
For example, if you're reading a science article about a new chemical compound, RealitySummary might display a 3D model of the molecular structure or a video explaining the compound's properties. Or if you're reading a historical document, the system could show relevant photographs or maps to help bring the text to life.
The researchers believe this technology could make reading and learning more engaging, especially for complex or technical subjects. By integrating multimedia content directly into the reading experience, RealitySummary aims to help readers better understand and retain the information.
Technical Explanation
The researchers present the "RealitySummary" system, which leverages large language models to enhance digital documents with on-demand mixed reality content. The key components of the system include:
-
Document Understanding: The system uses a large language model to analyze the content and context of the input document. This allows it to identify key concepts, entities, and relationships within the text.
-
Multimedia Retrieval: Based on the understanding of the document, the system can then retrieve or generate relevant multimedia content, such as images, videos, and 3D models, to overlay on the text.
-
Mixed Reality Integration: The multimedia content is seamlessly integrated into the reading experience, creating a mixed reality interface where the virtual elements are spatially aligned with the physical document.
The researchers evaluate their system on a range of document types, including scientific papers, news articles, and historical texts. They demonstrate the system's ability to accurately identify appropriate multimedia enhancements and provide a more immersive and informative reading experience for users.
The paper also discusses the technical challenges involved, such as aligning the virtual content with the physical document, ensuring the multimedia enhancements are contextually relevant, and optimizing the system for performance and usability.
Critical Analysis
The researchers have presented an interesting and innovative approach to enhancing digital document reading experiences using large language models and mixed reality technology. The key strengths of the RealitySummary system include its ability to link to "Characterizing Multimodal Long-Form Summarization" understand the context and content of a document, and its integration of relevant multimedia content to create a more engaging and informative reading experience.
However, the paper also acknowledges several limitations and areas for further research. For example, the system's performance may be influenced by the quality and accuracy of the underlying large language model, as well as the availability and relevance of the multimedia content in its database. Link to "Utilizing GPT to Enhance Text Summarization Strategy"
Additionally, the researchers note that the system's integration with physical documents may present challenges in terms of user interaction and alignment of the virtual content. Link to "Assisting Humans Complex Comparisons Automated Information Comparison"
It would also be interesting to explore the potential of Link to "Improving Topic Relevance Model by Mix Structured" the RealitySummary system to adapt to individual user preferences and learning styles, further enhancing the personalization and effectiveness of the reading experience.
Conclusion
The RealitySummary system presented in this paper represents a promising step towards integrating large language models and mixed reality technology to create more engaging and informative document reading experiences. By dynamically overlaying relevant multimedia content onto digital texts, the system has the potential to make learning and information consumption more interactive and accessible, especially for complex or technical subjects.
As Link to "Adapted Large Language Models Can Outperform Medical" the researchers continue to refine and expand the capabilities of the RealitySummary system, it could have significant implications for education, research, and a wide range of other domains where effective communication and knowledge transfer are crucial.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
RealitySummary: On-Demand Mixed Reality Document Enhancement using Large Language Models
Aditya Gunturu, Shivesh Jadon, Nandi Zhang, Jarin Thundathil, Wesley Willett, Ryo Suzuki
We introduce RealitySummary, a mixed reality reading assistant that can enhance any printed or digital document using on-demand text extraction, summarization, and augmentation. While augmented reading tools promise to enhance physical reading experiences with overlaid digital content, prior systems have typically required pre-processed documents, which limits their generalizability and real-world use cases. In this paper, we explore on-demand document augmentation by leveraging large language models. To understand generalizable techniques for diverse documents, we first conducted an exploratory design study which identified five categories of document enhancements (summarization, augmentation, navigation, comparison, and extraction). Based on this, we developed a proof-of-concept system that can automatically extract and summarize text using Google Cloud OCR and GPT-4, then embed information around documents using a Microsoft Hololens 2 and Apple Vision Pro. We demonstrate real-time examples of six specific document augmentations: 1) summaries, 2) comparison tables, 3) timelines, 4) keyword lists, 5) summary highlighting, and 6) information cards. Results from a usability study (N=12) and in-the-wild study (N=11) highlight the potential benefits of on-demand MR document enhancement and opportunities for future research.
Read more5/30/2024


0
MetaSumPerceiver: Multimodal Multi-Document Evidence Summarization for Fact-Checking
Ting-Chih Chen, Chia-Wei Tang, Chris Thomas
Fact-checking real-world claims often requires reviewing multiple multimodal documents to assess a claim's truthfulness, which is a highly laborious and time-consuming task. In this paper, we present a summarization model designed to generate claim-specific summaries useful for fact-checking from multimodal, multi-document datasets. The model takes inputs in the form of documents, images, and a claim, with the objective of assisting in fact-checking tasks. We introduce a dynamic perceiver-based model that can handle inputs from multiple modalities of arbitrary lengths. To train our model, we leverage a novel reinforcement learning-based entailment objective to generate summaries that provide evidence distinguishing between different truthfulness labels. To assess the efficacy of our approach, we conduct experiments on both an existing benchmark and a new dataset of multi-document claims that we contribute. Our approach outperforms the SOTA approach by 4.6% in the claim verification task on the MOCHEG dataset and demonstrates strong performance on our new Multi-News-Fact-Checking dataset.
Read more7/19/2024
⛏️

0
Thesis: Document Summarization with applications to Keyword extraction and Image Retrieval
Jayaprakash Sundararaj
Automatic summarization is the process of reducing a text document in order to generate a summary that retains the most important points of the original document. In this work, we study two problems - i) summarizing a text document as set of keywords/caption, for image recommedation, ii) generating opinion summary which good mix of relevancy and sentiment with the text document. Intially, we present our work on an recommending images for enhancing a substantial amount of existing plain text news articles. We use probabilistic models and word similarity heuristics to generate captions and extract Key-phrases which are re-ranked using a rank aggregation framework with relevance feedback mechanism. We show that such rank aggregation and relevant feedback which are typically used in Tagging Documents, Text Information Retrieval also helps in improving image retrieval. These queries are fed to the Yahoo Search Engine to obtain relevant images 1. Our proposed method is observed to perform better than all existing baselines. Additonally, We propose a set of submodular functions for opinion summarization. Opinion summarization has built in it the tasks of summarization and sentiment detection. However, it is not easy to detect sentiment and simultaneously extract summary. The two tasks conflict in the sense that the demand of compression may drop sentiment bearing sentences, and the demand of sentiment detection may bring in redundant sentences. However, using submodularity we show how to strike a balance between the two requirements. Our functions generate summaries such that there is good correlation between document sentiment and summary sentiment along with good ROUGE score. We also compare the performances of the proposed submodular functions.
Read more6/4/2024
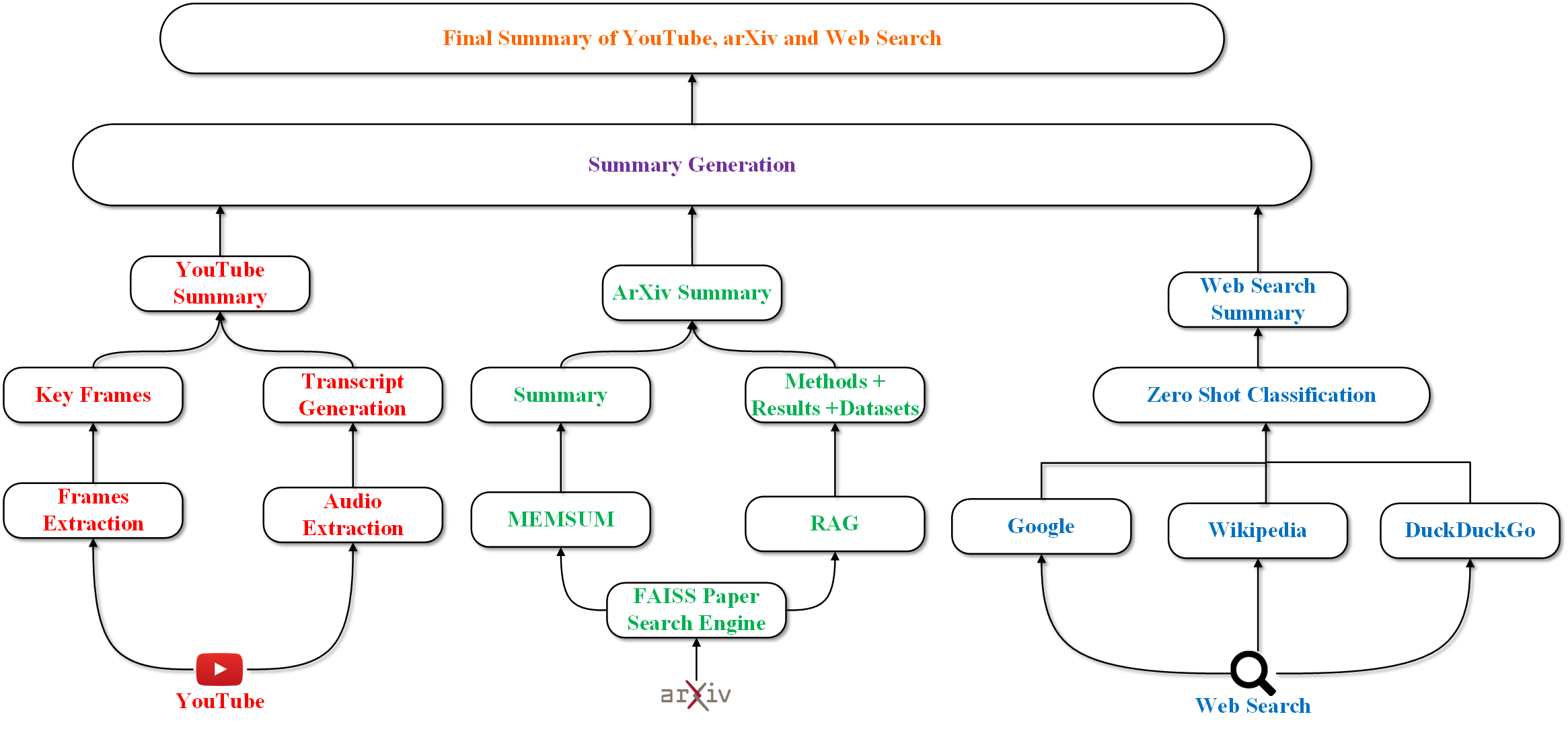

0
Converging Dimensions: Information Extraction and Summarization through Multisource, Multimodal, and Multilingual Fusion
Pranav Janjani, Mayank Palan, Sarvesh Shirude, Ninad Shegokar, Sunny Kumar, Faruk Kazi
Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have led to new summarization strategies, offering an extensive toolkit for extracting important information. However, these approaches are frequently limited by their reliance on isolated sources of data. The amount of information that can be gathered is limited and covers a smaller range of themes, which introduces the possibility of falsified content and limited support for multilingual and multimodal data. The paper proposes a novel approach to summarization that tackles such challenges by utilizing the strength of multiple sources to deliver a more exhaustive and informative understanding of intricate topics. The research progresses beyond conventional, unimodal sources such as text documents and integrates a more diverse range of data, including YouTube playlists, pre-prints, and Wikipedia pages. The aforementioned varied sources are then converted into a unified textual representation, enabling a more holistic analysis. This multifaceted approach to summary generation empowers us to extract pertinent information from a wider array of sources. The primary tenet of this approach is to maximize information gain while minimizing information overlap and maintaining a high level of informativeness, which encourages the generation of highly coherent summaries.
Read more6/21/2024