Toward Human-AI Alignment in Large-Scale Multi-Player Games

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
• This paper explores the challenge of aligning the behavior of AI agents with the objectives and preferences of human players in large-scale, multi-player games.
• The researchers propose a framework for designing AI agents that can cooperate with and assist human players, while avoiding adversarial or exploitative behavior.
• Key aspects include modeling human preferences, quantifying misalignment between agents, and achieving "principled superhuman" performance in a way that maintains bidirectional human-AI alignment.
Plain English Explanation
As artificial intelligence (AI) systems become more advanced, it's important to ensure they work cooperatively with human players in large-scale, multi-player games, rather than competing against or exploiting them. This paper presents a framework for designing AI agents that can align their objectives and behaviors with the preferences of the human players.
The key ideas are:
-
Modeling human preferences: Understanding what human players actually want and value, rather than just trying to optimize for game score or other narrow metrics.
-
Quantifying misalignment: Measuring how much the AI agent's behavior deviates from what would be best for the humans, so this can be minimized.
-
Achieving "principled superhuman" performance: Developing AI that can outperform humans, but in a way that maintains bidirectional human-AI alignment - the AI helps humans achieve their goals, while also being guided by human preferences.
The overall goal is to create AI assistants that cooperate with and support human players, rather than competing against them in an adversarial way. This could lead to more enjoyable and productive multi-player gaming experiences.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a framework for designing AI agents that can align their behavior with the objectives and preferences of human players in large-scale, multi-player games.
Key elements of the framework include:
-
Preference Modeling: Developing methods to accurately model the preferences and objectives of human players, going beyond just optimizing for game scores or other narrow metrics. This could involve techniques for understanding what humans actually value.
-
Misalignment Quantification: Defining and measuring the degree of misalignment between the AI agent's behavior and the human players' preferences. This quantification of misalignment allows the system to identify and minimize undesirable deviations.
-
Principled Superhuman Performance: Designing AI agents that can outperform human players, but in a way that maintains bidirectional human-AI alignment - the AI assists and cooperates with humans, rather than competing against them in an adversarial manner. The researchers refer to this as "towards principled superhuman AI" for multi-player symmetric games.
The overall goal is to create AI agents that can attain humans' desirable outcomes in large-scale, multi-player game environments, aligning their behavior with human preferences rather than pursuing their own narrow objectives.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a thoughtful and ambitious framework for addressing the challenge of human-AI alignment in the context of large-scale, multi-player games. Some potential areas for further consideration include:
-
Practical Challenges: While the theoretical concepts are well-developed, the paper does not delve into the practical difficulties of implementing such a framework in real-world gaming environments. Scaling the preference modeling and misalignment quantification approaches to handle the complexity and diversity of human players could prove challenging.
-
Generalizability: The paper focuses on multi-player games as the primary application domain. It's unclear how well the proposed techniques would transfer to other interactive environments where human-AI cooperation and alignment is crucial, such as autonomous vehicles or personal assistant systems.
-
Ethical Considerations: The paper does not extensively discuss the potential ethical implications of developing AI agents that can significantly outperform humans. Careful consideration will be needed to ensure that such "principled superhuman" AI systems do not inadvertently lead to unfair advantages or disempowerment of human players.
Overall, the paper presents an innovative and thoughtful approach to the important challenge of human-AI alignment in large-scale, multi-player games. Further research and real-world testing will be needed to fully validate the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed framework.
Conclusion
This paper tackles the critical challenge of aligning the behavior of AI agents with the objectives and preferences of human players in large-scale, multi-player games. The researchers propose a comprehensive framework that encompasses preference modeling, misalignment quantification, and the development of "principled superhuman" AI agents that can cooperate with and assist human players.
The key ideas have the potential to significantly improve the human-AI interaction experience in complex, multi-player gaming environments, leading to more enjoyable and productive gameplay. While the paper presents a well-developed theoretical foundation, further research will be needed to address practical implementation challenges and explore the broader applicability of the techniques beyond the gaming domain.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Toward Human-AI Alignment in Large-Scale Multi-Player Games
Sugandha Sharma, Guy Davidson, Khimya Khetarpal, Anssi Kanervisto, Udit Arora, Katja Hofmann, Ida Momennejad
Achieving human-AI alignment in complex multi-agent games is crucial for creating trustworthy AI agents that enhance gameplay. We propose a method to evaluate this alignment using an interpretable task-sets framework, focusing on high-level behavioral tasks instead of low-level policies. Our approach has three components. First, we analyze extensive human gameplay data from Xbox's Bleeding Edge (100K+ games), uncovering behavioral patterns in a complex task space. This task space serves as a basis set for a behavior manifold capturing interpretable axes: fight-flight, explore-exploit, and solo-multi-agent. Second, we train an AI agent to play Bleeding Edge using a Generative Pretrained Causal Transformer and measure its behavior. Third, we project human and AI gameplay to the proposed behavior manifold to compare and contrast. This allows us to interpret differences in policy as higher-level behavioral concepts, e.g., we find that while human players exhibit variability in fight-flight and explore-exploit behavior, AI players tend towards uniformity. Furthermore, AI agents predominantly engage in solo play, while humans often engage in cooperative and competitive multi-agent patterns. These stark differences underscore the need for interpretable evaluation, design, and integration of AI in human-aligned applications. Our study advances the alignment discussion in AI and especially generative AI research, offering a measurable framework for interpretable human-agent alignment in multiplayer gaming.
Read more6/21/2024

0
Quantifying Misalignment Between Agents
Aidan Kierans, Avijit Ghosh, Hananel Hazan, Shiri Dori-Hacohen
Existing work on the alignment problem has focused mainly on (1) qualitative descriptions of the alignment problem; (2) attempting to align AI actions with human interests by focusing on value specification and learning; and/or (3) focusing on a single agent or on humanity as a monolith. Recent sociotechnical approaches highlight the need to understand complex misalignment among multiple human and AI agents. We address this gap by adapting a computational social science model of human contention to the alignment problem. Our model quantifies misalignment in large, diverse agent groups with potentially conflicting goals across various problem areas. Misalignment scores in our framework depend on the observed agent population, the domain in question, and conflict between agents' weighted preferences. Through simulations, we demonstrate how our model captures intuitive aspects of misalignment across different scenarios. We then apply our model to two case studies, including an autonomous vehicle setting, showcasing its practical utility. Our approach offers enhanced explanatory power for complex sociotechnical environments and could inform the design of more aligned AI systems in real-world applications.
Read more9/10/2024
🤔

0
Designing for Human-Agent Alignment: Understanding what humans want from their agents
Nitesh Goyal, Minsuk Chang, Michael Terry
Our ability to build autonomous agents that leverage Generative AI continues to increase by the day. As builders and users of such agents it is unclear what parameters we need to align on before the agents start performing tasks on our behalf. To discover these parameters, we ran a qualitative empirical research study about designing agents that can negotiate during a fictional yet relatable task of selling a camera online. We found that for an agent to perform the task successfully, humans/users and agents need to align over 6 dimensions: 1) Knowledge Schema Alignment 2) Autonomy and Agency Alignment 3) Operational Alignment and Training 4) Reputational Heuristics Alignment 5) Ethics Alignment and 6) Human Engagement Alignment. These empirical findings expand previous work related to process and specification alignment and the need for values and safety in Human-AI interactions. Subsequently we discuss three design directions for designers who are imagining a world filled with Human-Agent collaborations.
Read more4/9/2024

0
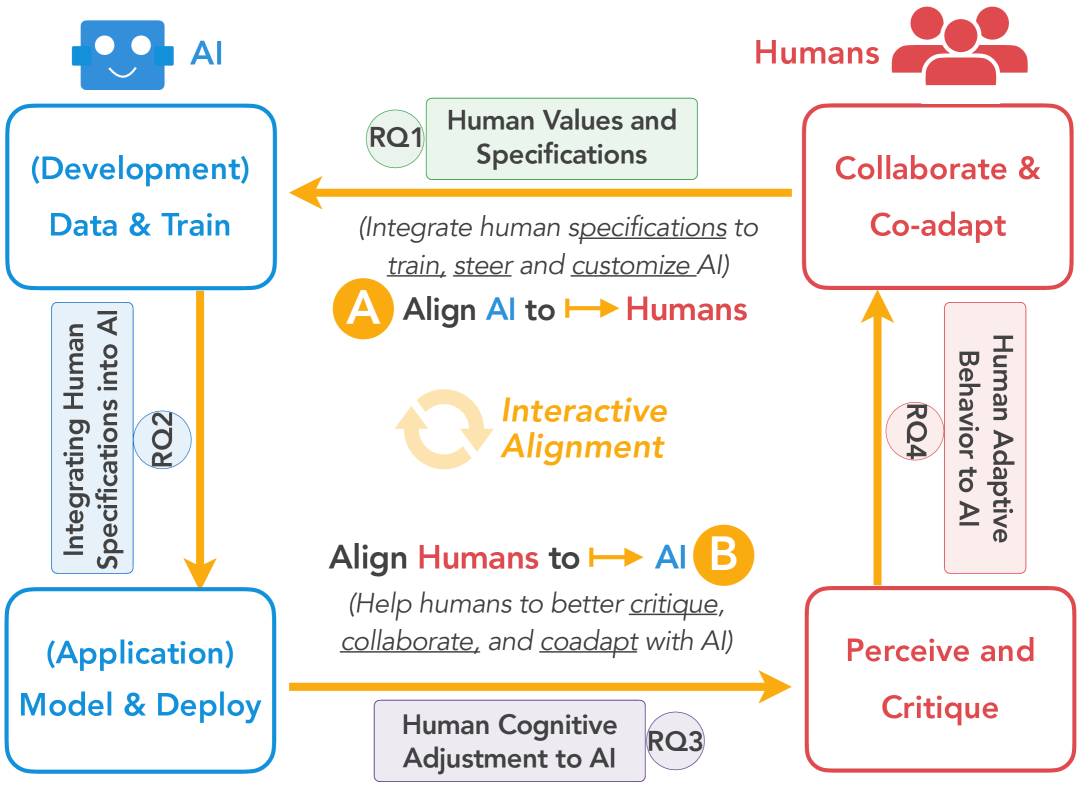
Towards Bidirectional Human-AI Alignment: A Systematic Review for Clarifications, Framework, and Future Directions
Hua Shen, Tiffany Knearem, Reshmi Ghosh, Kenan Alkiek, Kundan Krishna, Yachuan Liu, Ziqiao Ma, Savvas Petridis, Yi-Hao Peng, Li Qiwei, Sushrita Rakshit, Chenglei Si, Yutong Xie, Jeffrey P. Bigham, Frank Bentley, Joyce Chai, Zachary Lipton, Qiaozhu Mei, Rada Mihalcea, Michael Terry, Diyi Yang, Meredith Ringel Morris, Paul Resnick, David Jurgens
Recent advancements in general-purpose AI have highlighted the importance of guiding AI systems towards the intended goals, ethical principles, and values of individuals and groups, a concept broadly recognized as alignment. However, the lack of clarified definitions and scopes of human-AI alignment poses a significant obstacle, hampering collaborative efforts across research domains to achieve this alignment. In particular, ML- and philosophy-oriented alignment research often views AI alignment as a static, unidirectional process (i.e., aiming to ensure that AI systems' objectives match humans) rather than an ongoing, mutual alignment problem. This perspective largely neglects the long-term interaction and dynamic changes of alignment. To understand these gaps, we introduce a systematic review of over 400 papers published between 2019 and January 2024, spanning multiple domains such as Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), Natural Language Processing (NLP), Machine Learning (ML). We characterize, define and scope human-AI alignment. From this, we present a conceptual framework of Bidirectional Human-AI Alignment to organize the literature from a human-centered perspective. This framework encompasses both 1) conventional studies of aligning AI to humans that ensures AI produces the intended outcomes determined by humans, and 2) a proposed concept of aligning humans to AI, which aims to help individuals and society adjust to AI advancements both cognitively and behaviorally. Additionally, we articulate the key findings derived from literature analysis, including literature gaps and trends, human values, and interaction techniques. To pave the way for future studies, we envision three key challenges and give recommendations for future research.
Read more8/13/2024