How ChatGPT Changed the Media's Narratives on AI: A Semi-Automated Narrative Analysis Through Frame Semantics

0
🌿
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Examines the impact of the recent surge in attention to AI, particularly around the launch of the ChatGPT chatbot.
- Analyzes a dataset of over 49,000 sentences from 5,846 news articles to understand changes in AI discourse.
- Finds that media attention increased tenfold in the six months after ChatGPT's launch, with a shift towards experts and political leaders and more focus on AI dangers and risks.
- Suggests a qualitative change in the types of threats associated with AI and the anthropomorphic qualities ascribed to it.
Plain English Explanation
The paper looks at how the public conversation around AI has changed, especially after the launch of the ChatGPT chatbot. The researchers analyzed over 49,000 sentences from nearly 6,000 news articles to see what has happened. They found that media coverage of AI increased a lot - by 10 times - in the 6 months after ChatGPT came out. During this time, the discussion started to focus more on experts and political leaders and on the dangers and risks of AI. The data also suggests that people's views on the types of threats AI poses and the human-like qualities they ascribe to it have changed qualitatively.
Technical Explanation
The researchers performed a mixed-method frame semantics-based analysis on a large dataset of news articles that mention AI. The dataset covers the 12-month period around the launch of OpenAI's ChatGPT chatbot, collected from the most popular English-language news publishers.
Their analysis shows that media attention to AI rose tenfold in the 6 months after ChatGPT's launch, even though coverage was already at historically high levels. During this period, the discourse became more centered around experts and political leaders, and AI became more closely associated with dangers and risks.
A deeper review of the data also suggests a qualitative shift in the types of threats AI is perceived to represent, as well as the anthropomorphic qualities ascribed to it.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive analysis of how the public discourse around AI has evolved, particularly in the context of the high-profile launch of ChatGPT. The researchers' use of a large, diverse dataset and mixed-method analysis helps to ensure the robustness of their findings.
However, the paper does not delve deeply into the potential reasons or drivers behind the observed shifts in the discourse. For example, it would be helpful to understand whether the changes are a result of media framing, public sentiment, political positioning, or a combination of factors. Exploring these underlying causes could provide additional insights.
Additionally, the paper could have benefited from a more critical examination of the implications of the changing discourse. While the researchers note the qualitative shifts in the perceived threats and anthropomorphic qualities of AI, they do not fully unpack the potential consequences of these changes for public understanding, policy, and the development of AI technologies.
Conclusion
This study offers valuable insights into how the public conversation around AI has rapidly evolved, particularly in the wake of the ChatGPT launch. The findings suggest a significant increase in media attention and a shift in the discourse towards a greater focus on experts, political leaders, and the risks and dangers associated with AI.
These changes in the AI discourse have important implications for public perception, policy discussions, and the future development of AI systems. The researchers' work highlights the need for continued monitoring and analysis of how the societal understanding of AI is shifting, to ensure that the development of these transformative technologies is guided by well-informed, nuanced, and constructive dialogue.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🌿

0
How ChatGPT Changed the Media's Narratives on AI: A Semi-Automated Narrative Analysis Through Frame Semantics
Igor Ryazanov, Carl Ohman, Johanna Bjorklund
The recent explosion of attention to AI is arguably one of the biggest in the technology's media coverage. To investigate the effects it has on the discourse, we perform a mixed-method frame semantics-based analysis on a dataset of more than 49,000 sentences collected from 5846 news articles that mention AI. The dataset covers the twelve-month period centred around the launch of OpenAI's chatbot ChatGPT and is collected from the most visited open-access English-language news publishers. Our findings indicate that during the half year succeeding the launch, media attention rose tenfold$unicode{x2014}$from already historically high levels. During this period, discourse has become increasingly centred around experts and political leaders, and AI has become more closely associated with dangers and risks. A deeper review of the data also suggests a qualitative shift in the types of threat AI is thought to represent, as well as the anthropomorphic qualities ascribed to it.
Read more8/13/2024
🤖

0
New!Journalists, Emotions, and the Introduction of Generative AI Chatbots: A Large-Scale Analysis of Tweets Before and After the Launch of ChatGPT
Seth C. Lewis, David M. Markowitz, Jon Benedik Bunquin
As part of a broader look at the impact of generative AI, this study investigated the emotional responses of journalists to the release of ChatGPT at the time of its launch. By analyzing nearly 1 million Tweets from journalists at major U.S. news outlets, we tracked changes in emotional tone and sentiment before and after the introduction of ChatGPT in November 2022. Using various computational and natural language processing techniques to measure emotional shifts in response to ChatGPT's release, we found an increase in positive emotion and a more favorable tone post-launch, suggesting initial optimism toward AI's potential. This research underscores the pivotal role of journalists as interpreters of technological innovation and disruption, highlighting how their emotional reactions may shape public narratives around emerging technologies. The study contributes to understanding the intersection of journalism, emotion, and AI, offering insights into the broader societal impact of generative AI tools.
Read more9/16/2024
💬

0
Using ChatGPT for Thematic Analysis
Aleksei Turobov, Diane Coyle, Verity Harding
The utilisation of AI-driven tools, notably ChatGPT, within academic research is increasingly debated from several perspectives including ease of implementation, and potential enhancements in research efficiency, as against ethical concerns and risks such as biases and unexplained AI operations. This paper explores the use of the GPT model for initial coding in qualitative thematic analysis using a sample of UN policy documents. The primary aim of this study is to contribute to the methodological discussion regarding the integration of AI tools, offering a practical guide to validation for using GPT as a collaborative research assistant. The paper outlines the advantages and limitations of this methodology and suggests strategies to mitigate risks. Emphasising the importance of transparency and reliability in employing GPT within research methodologies, this paper argues for a balanced use of AI in supported thematic analysis, highlighting its potential to elevate research efficacy and outcomes.
Read more5/16/2024
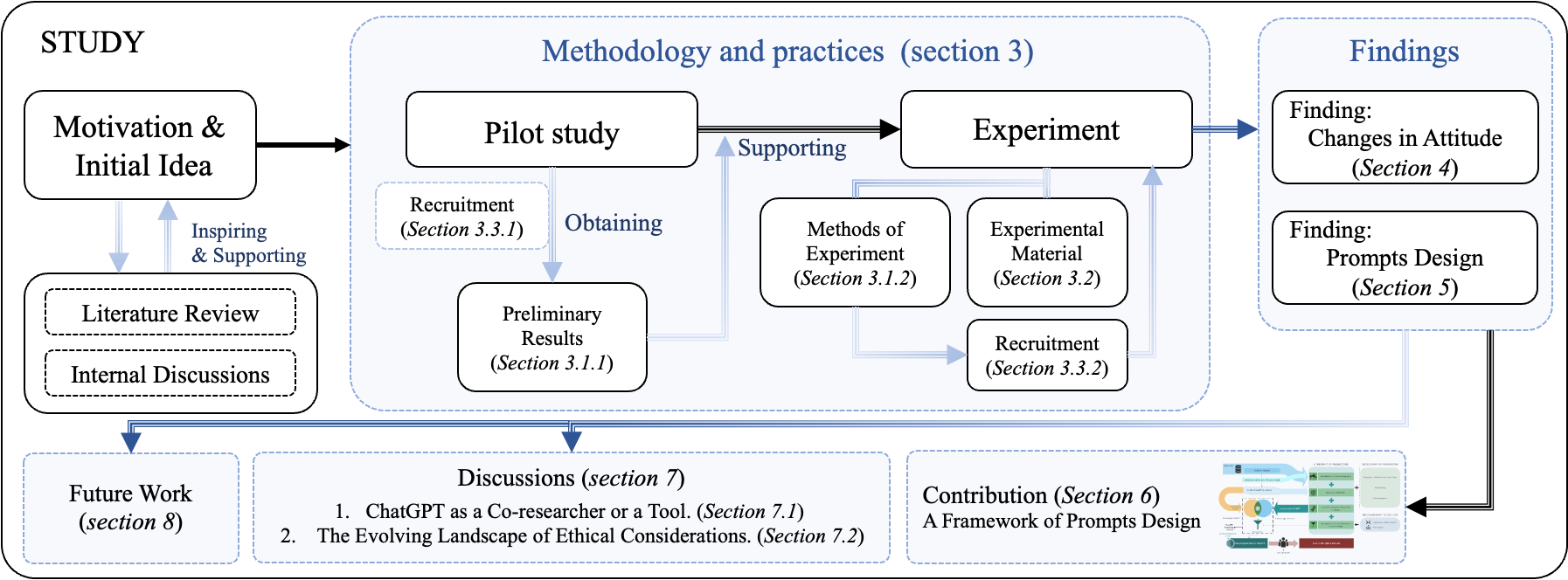

0
Redefining Qualitative Analysis in the AI Era: Utilizing ChatGPT for Efficient Thematic Analysis
He Zhang, Chuhao Wu, Jingyi Xie, Yao Lyu, Jie Cai, John M. Carroll
AI tools, particularly large-scale language model (LLM) based applications such as ChatGPT, have the potential to simplify qualitative research. Through semi-structured interviews with seventeen participants, we identified challenges and concerns in integrating ChatGPT into the qualitative analysis process. Collaborating with thirteen qualitative researchers, we developed a framework for designing prompts to enhance the effectiveness of ChatGPT in thematic analysis. Our findings indicate that improving transparency, providing guidance on prompts, and strengthening users' understanding of LLMs' capabilities significantly enhance the users' ability to interact with ChatGPT. We also discovered and revealed the reasons behind researchers' shift in attitude towards ChatGPT from negative to positive. This research not only highlights the importance of well-designed prompts in LLM applications but also offers reflections for qualitative researchers on the perception of AI's role. Finally, we emphasize the potential ethical risks and the impact of constructing AI ethical expectations by researchers, particularly those who are novices, on future research and AI development.
Read more5/29/2024