Prompting ChatGPT for Translation: A Comparative Analysis of Translation Brief and Persona Prompts

0
🎯
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The paper explores the potential of using translation concepts, such as the translation brief and the personas of translator and author, in prompt design for translation tasks in the language model ChatGPT.
- While certain elements of these translation concepts are found to be constructive for human-to-human communication in translation, their effectiveness is limited for improving translation quality in ChatGPT.
- The paper highlights the need for further research on how translation theory and practice can be adapted for the emerging workflow involving human-machine interaction in language models.
Plain English Explanation
The paper investigates whether incorporating ideas from the field of translation studies can help improve the translation quality of the language model ChatGPT. Specifically, the researchers looked at using the concept of a "translation brief" and the personas of the "translator" and "author" in the prompt design for translation tasks.
The translation brief is a key tool used by human translators - it outlines the purpose, target audience, and other important details about a translation project. The researchers wanted to see if incorporating this concept into prompts for ChatGPT could lead to better translations.
They also explored using the distinct roles of the translator and the original author as part of the prompt, as these personas are important in human-to-human translation workflows.
While the researchers found that some of these translation-focused elements were helpful for facilitating communication between humans for translation tasks, their effectiveness was limited when it came to actually improving the translation quality produced by ChatGPT.
This suggests that the conceptual tools developed for human-to-human translation may need to be adapted or expanded upon to work well in the context of human-machine collaboration for translation using language models like ChatGPT. More research is needed to figure out how translation studies can best inform the training and use of these emerging AI technologies.
Technical Explanation
The paper explores the potential of incorporating translation concepts, such as the translation brief and the personas of translator and author, into prompt design for translation tasks in the language model ChatGPT.
The translation brief is a key tool used in human translation workflows, as it outlines important details about the translation project, including the purpose, target audience, and other constraints. The researchers hypothesized that incorporating this concept into prompts for ChatGPT could lead to improved translation quality.
They also investigated using the distinct roles of the translator and the original author as part of the prompt design, as these personas are central to human-to-human translation processes.
The study involved conducting translation tasks with ChatGPT using prompts that did or did not incorporate these translation-focused elements. The researchers then evaluated the translations produced in terms of quality and compared the results.
While the findings suggest that certain elements of the translation brief and personas can be constructive for facilitating human-to-human communication for translation, their effectiveness was limited when it came to improving the actual translation quality generated by ChatGPT.
This indicates that the conceptual tools developed in translation studies for human-to-human workflows may need to be adapted or expanded upon to work effectively in the context of human-machine collaboration for translation using language models. The paper emphasizes the need for further research on how translation theory and practice can inform the training and use of these emerging AI technologies.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thoughtful exploration of how translation concepts could be leveraged to enhance prompt design for translation tasks in ChatGPT. By incorporating elements like the translation brief and distinct translator/author personas, the researchers aimed to better align the language model's outputs with the nuances of human translation workflows.
However, the finding that these translation-focused prompt elements had limited effectiveness in actually improving ChatGPT's translation quality highlights the challenges of directly applying human-centric translation frameworks to human-machine collaboration. This suggests the need for more fundamental research on how to adapt and extend translation theory to account for the unique dynamics of human-AI interaction.
One area that could be explored further is the role of personalized prompts in translation tasks. The paper's focus on generic prompt structures may have overlooked potential benefits of tailoring the prompts to the individual user's preferences and translation needs.
Additionally, the evaluation of translation quality was limited to the researchers' own assessments. Incorporating human evaluation as well as more objective, automated metrics could provide a more comprehensive understanding of the translation performance.
Overall, this paper represents an important step in bridging the gap between translation studies and the emerging field of human-AI collaboration for language tasks. The insights and directions for future research outlined in the paper will be valuable for continued exploration in this space.
Conclusion
This paper explores the potential of incorporating translation concepts, such as the translation brief and the personas of translator and author, into prompt design for translation tasks in the language model ChatGPT. While the findings suggest that certain elements of these translation-focused prompts can be helpful for facilitating human-to-human communication, their effectiveness in improving the actual translation quality produced by ChatGPT was limited.
This highlights the need for further research on how translation theory and practice can be adapted to the emerging workflows involving human-machine interaction in language models. Developing conceptual tools that can effectively bridge the gap between human and AI translation capabilities will be crucial for unlocking the full potential of these technologies in real-world translation applications.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🎯

0
Prompting ChatGPT for Translation: A Comparative Analysis of Translation Brief and Persona Prompts
Sui He
Prompt engineering has shown potential for improving translation quality in LLMs. However, the possibility of using translation concepts in prompt design remains largely underexplored. Against this backdrop, the current paper discusses the effectiveness of incorporating the conceptual tool of translation brief and the personas of translator and author into prompt design for translation tasks in ChatGPT. Findings suggest that, although certain elements are constructive in facilitating human-to-human communication for translation tasks, their effectiveness is limited for improving translation quality in ChatGPT. This accentuates the need for explorative research on how translation theorists and practitioners can develop the current set of conceptual tools rooted in the human-to-human communication paradigm for translation purposes in this emerging workflow involving human-machine interaction, and how translation concepts developed in translation studies can inform the training of GPT models for translation tasks.
Read more4/30/2024


0
Gradable ChatGPT Translation Evaluation
Hui Jiao, Bei Peng, Lu Zong, Xiaojun Zhang, Xinwei Li
ChatGPT, as a language model based on large-scale pre-training, has exerted a profound influence on the domain of machine translation. In ChatGPT, a Prompt refers to a segment of text or instruction employed to steer the model towards generating a specific category of response. The design of the translation prompt emerges as a key aspect that can wield influence over factors such as the style, precision and accuracy of the translation to a certain extent. However, there is a lack of a common standard and methodology on how to design and select a translation prompt. Accordingly, this paper proposes a generic taxonomy, which defines gradable translation prompts in terms of expression type, translation style, POS information and explicit statement, thus facilitating the construction of prompts endowed with distinct attributes tailored for various translation tasks. Specific experiments and cases are selected to validate and illustrate the effectiveness of the method.
Read more6/5/2024
🤯

0
Prompt engineering paradigms for medical applications: scoping review and recommendations for better practices
Jamil Zaghir, Marco Naguib, Mina Bjelogrlic, Aur'elie N'ev'eol, Xavier Tannier, Christian Lovis
Prompt engineering is crucial for harnessing the potential of large language models (LLMs), especially in the medical domain where specialized terminology and phrasing is used. However, the efficacy of prompt engineering in the medical domain remains to be explored. In this work, 114 recent studies (2022-2024) applying prompt engineering in medicine, covering prompt learning (PL), prompt tuning (PT), and prompt design (PD) are reviewed. PD is the most prevalent (78 articles). In 12 papers, PD, PL, and PT terms were used interchangeably. ChatGPT is the most commonly used LLM, with seven papers using it for processing sensitive clinical data. Chain-of-Thought emerges as the most common prompt engineering technique. While PL and PT articles typically provide a baseline for evaluating prompt-based approaches, 64% of PD studies lack non-prompt-related baselines. We provide tables and figures summarizing existing work, and reporting recommendations to guide future research contributions.
Read more5/3/2024
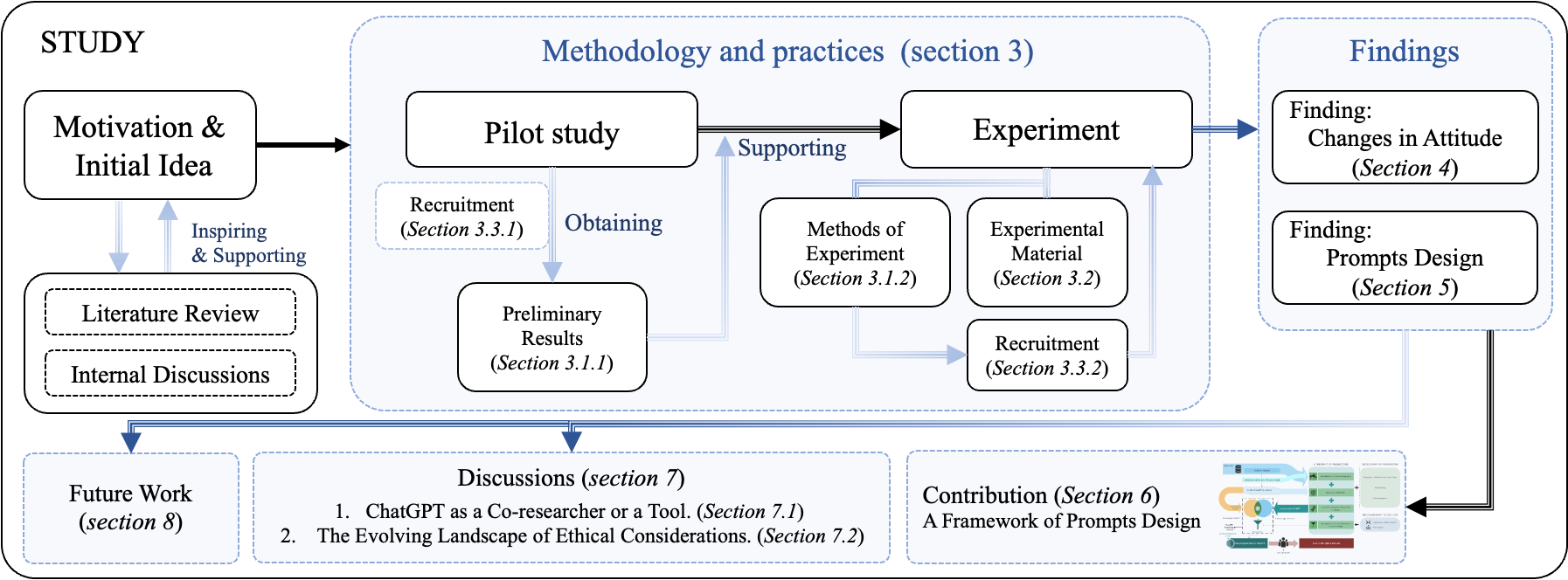

0
Redefining Qualitative Analysis in the AI Era: Utilizing ChatGPT for Efficient Thematic Analysis
He Zhang, Chuhao Wu, Jingyi Xie, Yao Lyu, Jie Cai, John M. Carroll
AI tools, particularly large-scale language model (LLM) based applications such as ChatGPT, have the potential to simplify qualitative research. Through semi-structured interviews with seventeen participants, we identified challenges and concerns in integrating ChatGPT into the qualitative analysis process. Collaborating with thirteen qualitative researchers, we developed a framework for designing prompts to enhance the effectiveness of ChatGPT in thematic analysis. Our findings indicate that improving transparency, providing guidance on prompts, and strengthening users' understanding of LLMs' capabilities significantly enhance the users' ability to interact with ChatGPT. We also discovered and revealed the reasons behind researchers' shift in attitude towards ChatGPT from negative to positive. This research not only highlights the importance of well-designed prompts in LLM applications but also offers reflections for qualitative researchers on the perception of AI's role. Finally, we emphasize the potential ethical risks and the impact of constructing AI ethical expectations by researchers, particularly those who are novices, on future research and AI development.
Read more5/29/2024