XL-HeadTags: Leveraging Multimodal Retrieval Augmentation for the Multilingual Generation of News Headlines and Tags
2406.03776

0
0
🛸
Abstract
Millions of news articles published online daily can overwhelm readers. Headlines and entity (topic) tags are essential for guiding readers to decide if the content is worth their time. While headline generation has been extensively studied, tag generation remains largely unexplored, yet it offers readers better access to topics of interest. The need for conciseness in capturing readers' attention necessitates improved content selection strategies for identifying salient and relevant segments within lengthy articles, thereby guiding language models effectively. To address this, we propose to leverage auxiliary information such as images and captions embedded in the articles to retrieve relevant sentences and utilize instruction tuning with variations to generate both headlines and tags for news articles in a multilingual context. To make use of the auxiliary information, we have compiled a dataset named XL-HeadTags, which includes 20 languages across 6 diverse language families. Through extensive evaluation, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our plug-and-play multimodal-multilingual retrievers for both tasks. Additionally, we have developed a suite of tools for processing and evaluating multilingual texts, significantly contributing to the research community by enabling more accurate and efficient analysis across languages.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- The paper focuses on the challenge of generating relevant headlines and entity (topic) tags for the millions of news articles published online daily.
- While headline generation has been extensively studied, tag generation remains largely unexplored, yet it offers readers better access to topics of interest.
- The paper proposes to leverage auxiliary information such as images and captions embedded in the articles to retrieve relevant sentences and utilize instruction tuning with variations to generate both headlines and tags for news articles in a multilingual context.
- The researchers have compiled a dataset named XL-HeadTags that includes 20 languages across 6 diverse language families.
- The paper demonstrates the effectiveness of their plug-and-play multimodal-multilingual retrievers for both headline and tag generation tasks.
- The researchers have also developed a suite of tools for processing and evaluating multilingual texts, contributing significantly to the research community.
Plain English Explanation
With the massive amount of news content being published online every day, readers can easily feel overwhelmed. Providing clear and concise headlines and tags that summarize the main topics covered in an article can help readers quickly determine if the content is relevant to their interests. While generating engaging headlines has been studied extensively, generating accurate topic tags has received less attention, even though tags can greatly improve readers' ability to find the information they're looking for.
To address this, the researchers in this paper propose a new approach that leverages additional information included in news articles, such as images and captions, to better identify the most important and relevant parts of the article. They then use this information to generate both attention-grabbing headlines and informative topic tags, all while supporting multiple languages.
To make this possible, the researchers compiled a large dataset called XL-HeadTags that covers 20 different languages across 6 major language families. By testing their new system on this diverse dataset, they were able to demonstrate its effectiveness at generating high-quality headlines and tags that can help readers quickly navigate the flood of online news content.
In addition to the new system, the researchers also developed a suite of tools that make it easier for other researchers to analyze and work with multilingual text data. This is an important contribution, as being able to effectively process and evaluate content in many different languages is crucial for building systems that can serve a global audience.
Technical Explanation
The key innovation in this paper is the researchers' approach to leveraging auxiliary information, such as images and captions, to improve the generation of both headlines and entity (topic) tags for news articles.
To do this, they first compiled the XL-HeadTags dataset, which includes news articles in 20 languages across 6 diverse language families. This dataset provides the raw material for training and evaluating their models.
Next, the researchers developed a "plug-and-play" multimodal-multilingual retrieval system that can identify the most relevant sentences within a news article based on the accompanying images and captions. This allows their language models to focus on the most salient information when generating headlines and tags.
To further enhance the quality of the generated output, the researchers experimented with different instruction tuning techniques. This involves fine-tuning the language models with specific prompts and guidelines to shape the generated headlines and tags.
Through extensive evaluation, the researchers demonstrated that their multimodal-multilingual approach outperforms text-only baseline models for both headline and tag generation tasks. They also found that the instruction tuning techniques helped to improve the conciseness and relevance of the generated outputs.
Beyond the core system, the researchers also developed a suite of tools for processing and evaluating multilingual texts. This includes utilities for tasks like language identification, text preprocessing, and automatic evaluation of multilingual text generation. These tools are a valuable contribution to the research community, as they enable more accurate and efficient analysis across multiple languages.
Critical Analysis
The researchers in this paper have made a compelling case for the importance of improving headline and tag generation for news articles, particularly in a multilingual context. Their use of auxiliary information, such as images and captions, is a promising approach that helps to identify the most salient and relevant content within lengthy articles.
One potential limitation of the research is the reliance on the XL-HeadTags dataset, which may not fully capture the diversity of news content across the web. While the dataset covers 20 languages, it would be interesting to see how the researchers' approach performs on a broader range of news sources and article styles.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the potential biases or ethical considerations that may arise from the use of large language models and other AI-powered systems for generating headlines and tags. As these systems become more widely adopted, it will be crucial to address issues around fairness, transparency, and accountability.
Further research could also explore the integration of the researchers' headline and tag generation system with other news processing and analysis tools, such as those for hierarchical retrieval and augmented generation or subject-conditioning. By combining multiple complementary approaches, it may be possible to create even more robust and accurate systems for identifying salient entities in news articles.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel approach to generating relevant headlines and entity (topic) tags for news articles, leveraging auxiliary information such as images and captions to improve the quality and relevance of the generated output. By compiling the XL-HeadTags dataset and developing a suite of multilingual processing and evaluation tools, the researchers have made significant contributions to the field of news content analysis and accessibility.
The researchers' findings suggest that incorporating multimodal information and utilizing instruction tuning techniques can lead to more concise and informative headlines and tags, which in turn can help readers quickly navigate the vast landscape of online news content. As news consumption continues to evolve, these advancements have the potential to improve the overall user experience and enhance readers' ability to find the information they need.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Reminding Multimodal Large Language Models of Object-aware Knowledge with Retrieved Tags
Daiqing Qi, Handong Zhao, Zijun Wei, Sheng Li

0
0
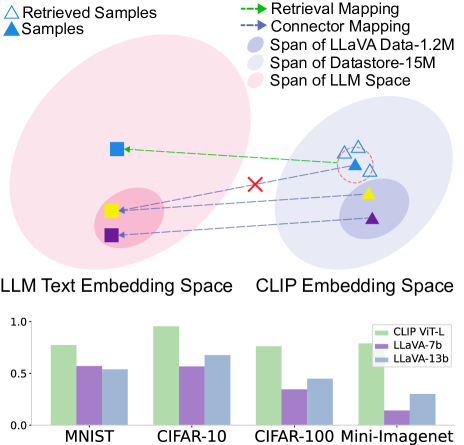
Despite recent advances in the general visual instruction-following ability of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), they still struggle with critical problems when required to provide a precise and detailed response to a visual instruction: (1) failure to identify novel objects or entities, (2) mention of non-existent objects, and (3) neglect of object's attributed details. Intuitive solutions include improving the size and quality of data or using larger foundation models. They show effectiveness in mitigating these issues, but at an expensive cost of collecting a vast amount of new data and introducing a significantly larger model. Standing at the intersection of these approaches, we examine the three object-oriented problems from the perspective of the image-to-text mapping process by the multimodal connector. In this paper, we first identify the limitations of multimodal connectors stemming from insufficient training data. Driven by this, we propose to enhance the mapping with retrieval-augmented tag tokens, which contain rich object-aware information such as object names and attributes. With our Tag-grounded visual instruction tuning with retrieval Augmentation (TUNA), we outperform baselines that share the same language model and training data on 12 benchmarks. Furthermore, we show the zero-shot capability of TUNA when provided with specific datastores.
6/18/2024
Converging Dimensions: Information Extraction and Summarization through Multisource, Multimodal, and Multilingual Fusion
Pranav Janjani, Mayank Palan, Sarvesh Shirude, Ninad Shegokar, Sunny Kumar, Faruk Kazi

0
0
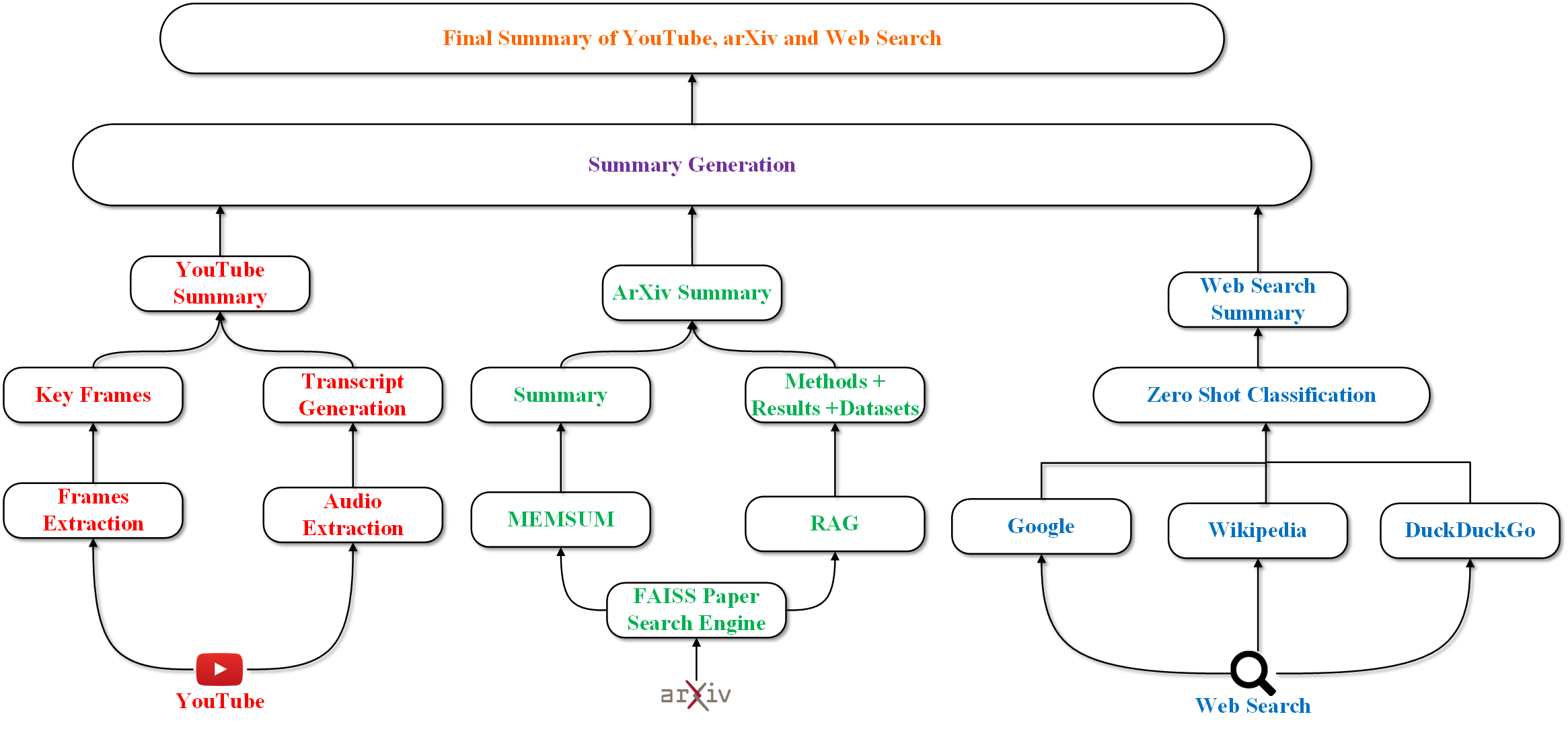
Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have led to new summarization strategies, offering an extensive toolkit for extracting important information. However, these approaches are frequently limited by their reliance on isolated sources of data. The amount of information that can be gathered is limited and covers a smaller range of themes, which introduces the possibility of falsified content and limited support for multilingual and multimodal data. The paper proposes a novel approach to summarization that tackles such challenges by utilizing the strength of multiple sources to deliver a more exhaustive and informative understanding of intricate topics. The research progresses beyond conventional, unimodal sources such as text documents and integrates a more diverse range of data, including YouTube playlists, pre-prints, and Wikipedia pages. The aforementioned varied sources are then converted into a unified textual representation, enabling a more holistic analysis. This multifaceted approach to summary generation empowers us to extract pertinent information from a wider array of sources. The primary tenet of this approach is to maximize information gain while minimizing information overlap and maintaining a high level of informativeness, which encourages the generation of highly coherent summaries.
6/21/2024
💬
Exploring the Potential of the Large Language Models (LLMs) in Identifying Misleading News Headlines
Md Main Uddin Rony, Md Mahfuzul Haque, Mohammad Ali, Ahmed Shatil Alam, Naeemul Hassan

0
0
In the digital age, the prevalence of misleading news headlines poses a significant challenge to information integrity, necessitating robust detection mechanisms. This study explores the efficacy of Large Language Models (LLMs) in identifying misleading versus non-misleading news headlines. Utilizing a dataset of 60 articles, sourced from both reputable and questionable outlets across health, science & tech, and business domains, we employ three LLMs- ChatGPT-3.5, ChatGPT-4, and Gemini-for classification. Our analysis reveals significant variance in model performance, with ChatGPT-4 demonstrating superior accuracy, especially in cases with unanimous annotator agreement on misleading headlines. The study emphasizes the importance of human-centered evaluation in developing LLMs that can navigate the complexities of misinformation detection, aligning technical proficiency with nuanced human judgment. Our findings contribute to the discourse on AI ethics, emphasizing the need for models that are not only technically advanced but also ethically aligned and sensitive to the subtleties of human interpretation.
5/7/2024
EAMA : Entity-Aware Multimodal Alignment Based Approach for News Image Captioning
Junzhe Zhang, Huixuan Zhang, Xunjian Yin, Xiaojun Wan

0
0
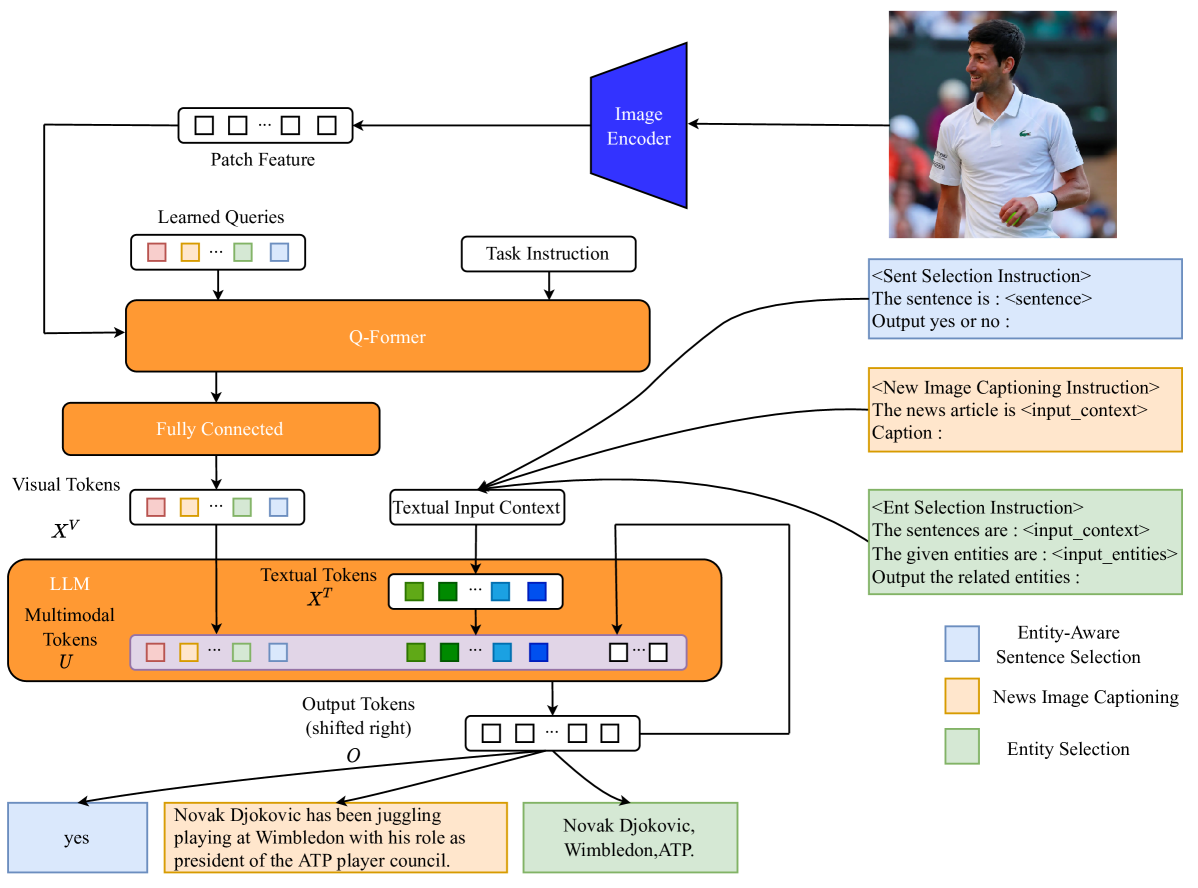
News image captioning requires model to generate an informative caption rich in entities, with the news image and the associated news article. Though Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in addressing various vision-language tasks, our research finds that current MLLMs still bear limitations in handling entity information on news image captioning task. Besides, while MLLMs have the ability to process long inputs, generating high-quality news image captions still requires a trade-off between sufficiency and conciseness of textual input information. To explore the potential of MLLMs and address problems we discovered, we propose : an Entity-Aware Multimodal Alignment based approach for news image captioning. Our approach first aligns the MLLM through Balance Training Strategy with two extra alignment tasks: Entity-Aware Sentence Selection task and Entity Selection task, together with News Image Captioning task, to enhance its capability in handling multimodal entity information. The aligned MLLM will utilizes the additional entity-related information it explicitly extracts to supplement its textual input while generating news image captions. Our approach achieves better results than all previous models in CIDEr score on GoodNews dataset (72.33 -> 88.39) and NYTimes800k dataset (70.83 -> 85.61).
5/7/2024